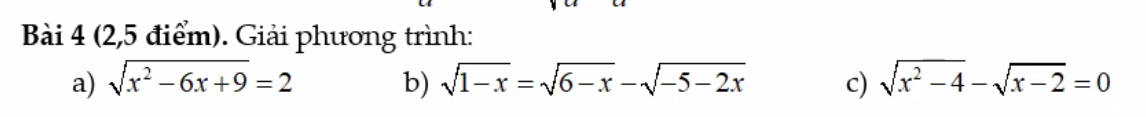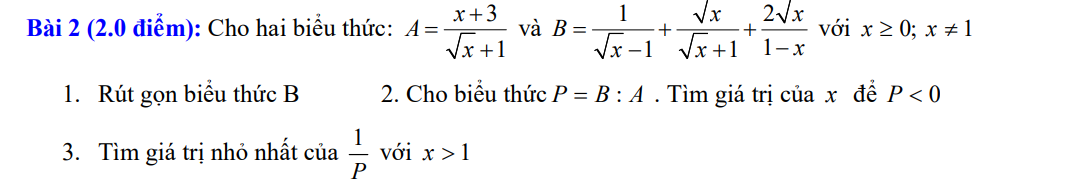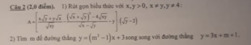Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a, \(\sqrt{x^2-6x+9}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-3\right)^2}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x-3\right|=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=2\\x-3=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
a: Ta có: \(\sqrt{x^2-6x+9}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)

Bài 1:
1:
a: \(\sqrt{12}+3\sqrt{48}-5\sqrt{75}\)
\(=2\sqrt{3}+12\sqrt{3}-25\sqrt{3}\)
\(=-11\sqrt{3}\)



a: Ta có: \(\sqrt{x^2-4x+4}=\sqrt{4x^2-12x+9}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x-2\right|=\left|2x-3\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-3=x-2\\2x-3=2-x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=\dfrac{5}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: Ta có: \(\sqrt{4x^2-4x+1}=\sqrt{x^2-6x+9}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x-1\right|=\left|x-3\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=x-3\\2x-1=3-x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Câu 2.2
để 2 đt song song khi \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m^2-1=3\\m+1\ne3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m^2=4\\m\ne2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m=2\)
Câu 2:
1: \(A=\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}-\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}-y\right)\cdot\left(\sqrt{y}-2\right)\)
\(=\left(2\sqrt{y}-y\right)\left(\sqrt{y}-2\right)=-\sqrt{y}\left(y-4\sqrt{y}+4\right)=-y\sqrt{y}+4y-4\sqrt{y}\)

a) Ta thấy \(x^3+y^3=\left(x+y\right)^3-3xy\left(x+y\right)\) và \(x^2+y^2=\left(x+y\right)^2-2xy\) nên nếu đặt \(x+y=S,xy=P\) thì ta có hệ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}S^3-3SP=2\\S^2-2P=2\end{matrix}\right.\) . Từ pt (2) suy ra \(P=\dfrac{S^2-2}{2}\). Thay vào (1), ta có \(S^3-3S.\dfrac{S^2-2}{2}=2\) \(\Leftrightarrow-S^3+6S-4=0\) hay \(S^3-6S+4=0\)
Đến đây ta dễ dàng nhẩm ra được \(S=2\). Do đó ta lập sơ đồ Horner:
| \(x\) | 1 | 0 | -6 | 4 |
| \(2\) | 1 | 2 | -2 | 0 |
Nghĩa là từ \(S^3-6S+4=0\) ta sẽ có \(\left(S-2\right)\left(S^2+2S-2\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}S=2\\S=-1\pm\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\).
Nếu \(S=2\) thì \(P=\dfrac{S^2-2}{2}=1\). Ta thấy \(S^2-4P=0\) nên x, y sẽ là nghiệm của pt \(X^2-2X+1=0\Leftrightarrow\left(X-1\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow X=1\) hay \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(1;1\right)\).
Nếu \(S=-1+\sqrt{3}\) thì \(P=\dfrac{S^2-2}{2}=1-\sqrt{3}\). Ta thấy \(S^2-4P>0\) nên x, y là nghiệm của pt \(X^2-\left(\sqrt{3}-1\right)X+1-\sqrt{3}=0\). \(\Delta=2\sqrt{3}\) nên \(X=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-1\pm\sqrt{2\sqrt{3}}}{2}\) hay \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-1+\sqrt{2\sqrt{3}}}{2};\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-1-2\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)\) và hoán vị của nó.
Nếu \(S=-1-\sqrt{3}\) thì \(P=\dfrac{S^2-2}{2}=1+\sqrt{3}\). Mà \(S^2-4P=-2\sqrt{3}< 0\) nên không tìm được nghiệm (x; y)
Như vậy hệ phương trình đã cho có các cặp nghiệm \(\left(1;1\right);\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-1+\sqrt{2\sqrt{3}}}{2};\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-1-\sqrt{2\sqrt{3}}}{2}\right)\)\(\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-1-\sqrt{2\sqrt{3}}}{2};\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-1+2\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)\)
b) Ta thấy \(x^3+y^3+xy=\left(x+y\right)^3-3xy\left(x+y\right)+xy\) nên nếu đặt \(S=x+y,P=xy\) thì ta có hệ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}S^3-3SP+P=3\\S+P=3\end{matrix}\right.\), suy ra \(P=3-S\)
\(\Rightarrow S^3-3S\left(3-S\right)+3-S=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow S^3-10S+3S^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow S\left(S^2+3S-10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}S=0\\S=2\\S=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Nếu \(S=0\) thì \(P=3\). Khi đó vì \(S^2-4P< 0\) nên không tìm được nghiệm (x; y)
Nếu \(S=2\) thì suy ra \(P=1\). Ta có \(S^2-4P=0\) nên x, y là nghiệm của pt \(X^2-2X+1=0\Leftrightarrow X=1\) hay \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(1;1\right)\)
Nếu \(S=-5\) thì suy ra \(P=8\). Ta có \(S^2-4P< 0\) nên không thể tìm được nghiệm (x; y).
Như vậy hpt đã cho có nghiệm duy nhất \(\left(1;1\right)\)