
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) 12 . ( x - 1 ) = 0
x - 1 = 0 : 12
x - 1 = 0
x = 0 + 1
x = 1
b) ( 6x - 39 ) : 3 = 201
6x - 39 = 201 . 3
6x - 39 = 603
6x = 603 + 39
6x = 642
x = 642 : 6
x = 107
c) 23 + 3x = 56 : 53
23 + 3x = 53
23 + 3x = 125
3x = 125 - 23
3x = 102
x = 102 : 3
x = 34
Các phần d , e , f Đỗ Ngọc Hoàng Hải làm tương tự như phần trên .
a/x =1 nha
b/(6x-39):3=201
6x-39 =201x3
6x-39 =603
6x = 603+39
6x = 642
6= 642:6=107
c/ 23+3.x=125
3x= 125-23=102
x= 102:3=34
d/ 541+(281-x)=735
281-x= 735-541=194
x=281-194=87
e/ 9x+2=20
9x=20-2
9x=18
x=18:9=9
f/71+(26-3x):5=75
(26-3x):5=75-71=4
26-3x=4x5=20
3x=26-20=6
x=6:3=2
tk nha ^^

17: \(x-\sqrt{x}-2=\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\)
18: \(x-3\sqrt{x}+2=\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\)
19: \(x\sqrt{x}-x+\sqrt{x}-1=\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
20: \(x\sqrt{x}+y\sqrt{y}+x-y\)
\(=\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)\left(x-\sqrt{xy}+y\right)+\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{y}\right)\)
\(=\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)\left(x-\sqrt{xy}+y+\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{y}\right)\)
\(17,=\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\\ 18,=\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\\ 19,=\left(x+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\\ 20,=???\)
bn xem lại đề câu 20 nha
tik mik nha

1) Ta có: P=4
nên \(x-2\sqrt{x}+22=4\sqrt{x}+12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-6\sqrt{x}+10=0\)(Vô lý)
3) Thay \(x=3-2\sqrt{2}\) vào P, ta được:
\(P=\dfrac{3-2\sqrt{2}-2\left(\sqrt{2}-1\right)+22}{\sqrt{2}-1+3}\)
\(=\dfrac{3-2\sqrt{2}-2\sqrt{2}+2+22}{2+\sqrt{2}}\)
\(=\dfrac{27-4\sqrt{2}}{2+\sqrt{2}}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(27-4\sqrt{2}\right)\left(\sqrt{2}-1\right)}{\sqrt{2}}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(27\sqrt{2}-8\right)\left(\sqrt{2}-1\right)}{2}\)
\(=\dfrac{54-27\sqrt{2}-8\sqrt{2}+8}{2}\)
\(=\dfrac{64-35\sqrt{2}}{2}\)

1.
ĐKXĐ: \(x< 5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\dfrac{42}{5-x}}-3+\sqrt{\dfrac{60}{7-x}}-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\dfrac{42}{5-x}-9}{\sqrt{\dfrac{42}{5-x}}+3}+\dfrac{\dfrac{60}{7-x}-9}{\sqrt{\dfrac{60}{7-x}}+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{9x-3}{\left(5-x\right)\left(\sqrt{\dfrac{42}{5-x}}+3\right)}+\dfrac{9x-3}{\left(7-x\right)\left(\sqrt{\dfrac{60}{7-x}}+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(9x-3\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{\left(5-x\right)\left(\sqrt{\dfrac{42}{5-x}}+3\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(7-x\right)\left(\sqrt{\dfrac{60}{7-x}}+3\right)}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
b.
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge2\)
\(\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-1\right)}+\sqrt{x+3}=\sqrt{x-2}+\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-1\right)}-\sqrt{x-2}+\sqrt{x+3}-\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-2}\left(\sqrt{x-1}-1\right)-\sqrt{x+3}\left(\sqrt{x-1}-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x-1}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x-2}-\sqrt{x+3}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x-1}-1=0\\\sqrt{x-2}-\sqrt{x+3}=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=1\\x-2=x+3\left(vn\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x=2\)

a)
( x − 3 ) 2 + ( x + 4 ) 2 = 23 − 3 x ⇔ x 2 − 6 x + 9 + x 2 + 8 x + 16 = 23 − 3 x ⇔ x 2 − 6 x + 9 + x 2 + 8 x + 16 + 3 x − 23 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 + 5 x + 2 = 0
Có a = 2; b = 5; c = 2 ⇒ Δ = 5 2 – 4 . 2 . 2 = 9 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
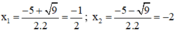
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 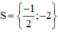
b)
x 3 + 2 x 2 − ( x − 3 ) 2 = ( x − 1 ) x 2 − 2 ⇔ x 3 + 2 x 2 − x 2 − 6 x + 9 = x 3 − x 2 − 2 x + 2 ⇔ x 3 + 2 x 2 − x 2 + 6 x − 9 − x 3 + x 2 + 2 x − 2 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 + 8 x − 11 = 0
Có a = 2; b = 8; c = -11 ⇒ Δ ’ = 4 2 – 2 . ( - 11 ) = 38 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
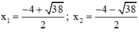
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 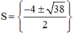
c)
( x − 1 ) 3 + 0 , 5 x 2 = x x 2 + 1 , 5 ⇔ x 3 − 3 x 2 + 3 x − 1 + 0 , 5 x 2 = x 3 + 1 , 5 x ⇔ x 3 + 1 , 5 x − x 3 + 3 x 2 − 3 x + 1 − 0 , 5 x 2 = 0 ⇔ 2 , 5 x 2 − 1 , 5 x + 1 = 0
Có a = 2,5; b = -1,5; c = 1
⇒ Δ = ( - 1 , 5 ) 2 – 4 . 2 , 5 . 1 = - 7 , 75 < 0
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm.
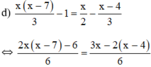
⇔ 2 x ( x − 7 ) − 6 = 3 x − 2 ( x − 4 ) ⇔ 2 x 2 − 14 x − 6 = 3 x − 2 x + 8 ⇔ 2 x 2 − 14 x − 6 − 3 x + 2 x − 8 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 − 15 x − 14 = 0
Có a = 2; b = -15; c = -14
⇒ Δ = ( - 15 ) 2 – 4 . 2 . ( - 14 ) = 337 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
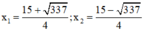
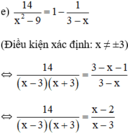
⇔ 14 = ( x - 2 ) ( x + 3 ) ⇔ 14 = x 2 - 2 x + 3 x - 6 ⇔ x 2 + x - 20 = 0
Có a = 1; b = 1; c = -20
⇒ Δ = 1 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 20 ) = 81 > 0
Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
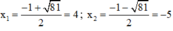
Cả hai nghiệm đều thỏa mãn điều kiện xác định.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-5; 4}.
f) Điều kiện: x≠-1;x≠4

Ta có: a= 1, b = -7, c = - 8
∆ = ( - 7 ) 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 8 ) = 81
=> Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
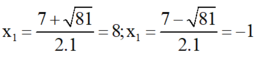
Kết hợp với diều kiện, nghiệm của phương trình đã cho là x = 8

1: =>x^2+3x-4=0
=>(x+4)(x-1)=0
=>x=1 hoặc x=-4
2: =>2x-3y=1 và 3x=4y+2
=>2x-3y=1 và 3x-4y=2
=>x=2 và y=1
541 + ( 218 - x ) = 735
=> 541 + 218 - x = 735
=> x = 541 + 218 - 735
=> x = 24
96 - 3 . ( x + 1 ) = 42
=> 3 . ( x + 1 ) = 96 - 42
=> 3 . ( x + 1 ) = 54
=> x + 1 = 54 : 3
=> x + 1 = 18
=> x = 18 - 1
=> x = 17
541+(218-x)=735
218-x = 735-541
218-x = 194
x=218-194=24
96-3.(x+1)=42
3.(x+1)=96-42
3.(x+1)=54
x+1=54:3=18
x=18-1=17