Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a, \(2\left(x+3\right)\left(x-4\right)=\left(2x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)-27\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2-4x+3x-12\right)=2x^2+4x-x-2-27\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-2x-24=2x^2+3x-29\Leftrightarrow-5x+5=0\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
b, \(\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)-x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=26\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-8-x\left(x^2-9\right)=26\Leftrightarrow-8+9x=26\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x=18\Leftrightarrow x=2\)

a) ( x - 3)4 + ( x - 5)4 = 82
Đặt : x - 4 = a , ta có :
( a + 1)4 + ( a - 1)4 = 82
⇔ a4 + 4a3 + 6a2 + 4a + 1 + a4 - 4a3 + 6a2 - 4a + 1 = 82
⇔ 2a4 + 12a2 - 80 = 0
⇔ 2( a4 + 6a2 - 40) = 0
⇔ a4 - 4a2 + 10a2 - 40 = 0
⇔ a2( a2 - 4) + 10( a2 - 4) = 0
⇔ ( a2 - 4)( a2 + 10) = 0
Do : a2 + 10 > 0
⇒ a2 - 4 = 0
⇔ a = + - 2
+) Với : a = 2 , ta có :
x - 4 = 2
⇔ x = 6
+) Với : a = -2 , ta có :
x - 4 = -2
⇔ x = 2
KL.....
b) ( n - 6)( n - 5)( n - 4)( n - 3) = 5.6.7.8
⇔ ( n - 6)( n - 3)( n - 5)( n - 4) = 1680
⇔ ( n2 - 9n + 18)( n2 - 9n + 20) = 1680
Đặt : n2 - 9n + 19 = t , ta có :
( t - 1)( t + 1) = 1680
⇔ t2 - 1 = 1680
⇔ t2 - 412 = 0
⇔ ( t - 41)( t + 41) = 0
⇔ t = 41 hoặc t = - 41
+) Với : t = 41 , ta có :
n2 - 9n + 19 = 41
⇔ n2 - 9n - 22 = 0
⇔ n2 + 2n - 11n - 22 = 0
⇔ n( n + 2) - 11( n + 2) = 0
⇔ ( n + 2)( n - 11) = 0
⇔ n = - 2 hoặc n = 11
+) Với : t = -41 ( giải tương tự )
@Giáo Viên Hoc24.vn
@Giáo Viên Hoc24h
@Giáo Viên
@giáo viên chuyên
@Akai Haruma

e: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=1\\\dfrac{3}{x}+\dfrac{4}{y}=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{x}-\dfrac{3}{y}=3\\\dfrac{3}{x}+\dfrac{4}{y}=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{-7}{y}=-2\\\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{7}{2}\\\dfrac{1}{x}=1+\dfrac{2}{7}=\dfrac{9}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=\dfrac{7}{9}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) 3x(x - 1) + 2(x - 1) = 0
<=> (3x + 2)(x - 1) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x+2=0\\x-1=0\end{cases}}\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{2}{3}\\x=1\end{cases}}\)
Vậy S = {-2/3; 1}
b) x2 - 1 - (x + 5)(2 - x) = 0
<=> x2 - 1 - 2x + x2 - 10 + 5x = 0
<=> 2x2 + 3x - 11 = 0
<=> 2(x2 + 3/2x + 9/16 - 97/16) = 0
<=> (x + 3/4)2 - 97/16 = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+\frac{3}{4}=\frac{\sqrt{97}}{4}\\x+\frac{3}{4}=-\frac{\sqrt{97}}{4}\end{cases}}\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{\sqrt{97}-3}{4}\\x=-\frac{\sqrt{97}-3}{4}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy S = {\(\frac{\sqrt{97}-3}{4}\); \(-\frac{\sqrt{97}-3}{4}\)
d) x(2x - 3) - 4x + 6 = 0
<=> x(2x - 3) - 2(2x - 3) = 0
<=> (x - 2)(2x - 3) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-2=0\\2x-3=0\end{cases}}\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=\frac{3}{2}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy S = {2; 3/2}
e) x3 - 1 = x(x - 1)
<=> (x - 1)(x2 + x + 1) - x(x - 1) = 0
<=> (x - 1)(x2 + x + 1 - x) = 0
<=> (x - 1)(x2 + 1) = 0
<=> x - 1 = 0
<=> x = 1
Vậy S = {1}
f) (2x - 5)2 - x2 - 4x - 4 = 0
<=> (2x - 5)2 - (x + 2)2 = 0
<=> (2x - 5 - x - 2)(2x - 5 + x + 2) = 0
<=> (x - 7)(3x - 3) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-7=0\\3x-3=0\end{cases}}\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=7\\x=1\end{cases}}\)
Vậy S = {7; 1}
h) (x - 2)(x2 + 3x - 2) - x3 + 8 = 0
<=> (x - 2)(x2 + 3x - 2) - (x- 2)(x2 + 2x + 4) = 0
<=> (x - 2)(x2 + 3x - 2 - x2 - 2x - 4) = 0
<=> (x - 2)(x - 6) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-2=0\\x-6=0\end{cases}}\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=6\end{cases}}\)
Vậy S = {2; 6}
\(a,3x\left(x-1\right)+2\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(3x.x-3x+2x-2=0\)
\(2x-2=0\)
\(2x=2\)
\(x=1\)

a) (x – 3)2 + (x + 4)2 = 23 – 3x ⇔ x2 – 6x + 9 + x2 + 8x + 16 = 23 – 3x
⇔ 2x2 + 5x + 2 = 0
∆ = 25 – 16 = 9
x1 = -2, x2 =
b) x3 + 2x2 – (x – 3)2 = (x – 1)(x2 – 2)
⇔ x3 + 2x2 – x2 + 6x – 9 = x3 – x2 – 2x + 2 ⇔ 2x2 + 8x – 11 = 0
∆’ = 16 + 22 = 38
x1 = , x2 =
c) (x – 1)3 + 0,5x2 = x(x2 + 1,5)
⇔ x3 – 3x2 + 3x – 1 + 0,5x2 = x3 + 1,5x
⇔ 2,5x2 – 1,5x + 1 = 0
⇔ 5x2 – 3x + 2 = 0; ∆ = 9 – 40 = -31 < 0
Phương trình vô nghiệm
d) – 1 =
-
⇔ 2x(x – 7) – 6 = 3x – 2(x – 4)
⇔ 2x2 – 14x – 6 = 3x – 2x + 8
⇔ 2x2 – 15x – 14 = 0; ∆ = 225 + 112 = 337
x1 = , x2 =
e) = 1 -
. Điều kiện: x ≠ ±3
Phương trình được viết lại: = 1 +
⇔ 14 = x2 – 9 + x + 3
⇔ x2 + x – 20 = 0, ∆ = 1 + 4 . 20 = 81
√∆ = 9
Nên x1 = = -5; x2 =
= 4 (thỏa mãn)
Vậy phương trình có hai nghiệm x1 = -5, x2 = 4.
f) =
. Điều kiện: x ≠ -1, x ≠ 4
Phương trình tương đương với:
2x(x – 4) = x2 – x + 8 ⇔ 2x2 – 8x – x2 + x – 8 = 0
⇔ x2 – 7x – 8 = 0
Có a – b + c = 1 – (-7) – 8 = 0 nên x1 = -1, x2 = 8
Vì x1 = -1 không thỏa mãn điều kiện của ẩn nên: phương trình có một nghiệm là x = 8.

a.
$x^2-11=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2=11$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\pm \sqrt{11}$
b. $x^2-12x+52=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x^2-12x+36)+16=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-6)^2=-16< 0$ (vô lý)
Vậy pt vô nghiệm.
c.
$x^2-3x-28=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2+4x-7x-28=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x(x+4)-7(x+4)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+4)(x-7)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x+4=0$ hoặc $x-7=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=-4$ hoặc $x=7$
d.
$x^2-11x+38=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x^2-11x+5,5^2)+7,75=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-5,5)^2=-7,75< 0$ (vô lý)
Vậy pt vô nghiệm
e.
$6x^2+71x+175=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 6x^2+21x+50x+175=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 3x(2x+7)+25(2x+7)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+25)(2x+7)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 3x+25=0$ hoặc $2x+7=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{25}{3}$ hoặc $x=-\frac{7}{2}$

c: Ta có: \(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{9x-9}-\sqrt{4x-4}=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{x-1}=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=4\)
hay x=5
e: Ta có: \(\sqrt{4x^2-28x+49}-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x-7\right|=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-7=5\\2x-7=-5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
a. ĐKXĐ: $x\in\mathbb{R}$
PT $\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{(x-2)^2}=2-x$
$\Leftrightarrow |x-2|=2-x$
$\Leftrightarrow 2-x\geq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow x\leq 2$
b. ĐKXĐ: $x\geq 2$
PT $\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{4}.\sqrt{x-2}-\frac{1}{5}\sqrt{25}.\sqrt{x-2}=3\sqrt{x-2}-1$
$\Leftrightarrow 2\sqrt{x-2}-\sqrt{x-2}=3\sqrt{x-2}-1$
$\Leftrightarrow 1=2\sqrt{x-2}$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{1}{2}=\sqrt{x-2}$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{1}{4}=x-2$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{9}{4}$ (tm)
a)
( x − 3 ) 2 + ( x + 4 ) 2 = 23 − 3 x ⇔ x 2 − 6 x + 9 + x 2 + 8 x + 16 = 23 − 3 x ⇔ x 2 − 6 x + 9 + x 2 + 8 x + 16 + 3 x − 23 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 + 5 x + 2 = 0
Có a = 2; b = 5; c = 2 ⇒ Δ = 5 2 – 4 . 2 . 2 = 9 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm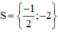
b)
x 3 + 2 x 2 − ( x − 3 ) 2 = ( x − 1 ) x 2 − 2 ⇔ x 3 + 2 x 2 − x 2 − 6 x + 9 = x 3 − x 2 − 2 x + 2 ⇔ x 3 + 2 x 2 − x 2 + 6 x − 9 − x 3 + x 2 + 2 x − 2 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 + 8 x − 11 = 0
Có a = 2; b = 8; c = -11 ⇒ Δ ’ = 4 2 – 2 . ( - 11 ) = 38 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm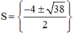
c)
( x − 1 ) 3 + 0 , 5 x 2 = x x 2 + 1 , 5 ⇔ x 3 − 3 x 2 + 3 x − 1 + 0 , 5 x 2 = x 3 + 1 , 5 x ⇔ x 3 + 1 , 5 x − x 3 + 3 x 2 − 3 x + 1 − 0 , 5 x 2 = 0 ⇔ 2 , 5 x 2 − 1 , 5 x + 1 = 0
Có a = 2,5; b = -1,5; c = 1
⇒ Δ = ( - 1 , 5 ) 2 – 4 . 2 , 5 . 1 = - 7 , 75 < 0
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm.
⇔ 2 x ( x − 7 ) − 6 = 3 x − 2 ( x − 4 ) ⇔ 2 x 2 − 14 x − 6 = 3 x − 2 x + 8 ⇔ 2 x 2 − 14 x − 6 − 3 x + 2 x − 8 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 − 15 x − 14 = 0
Có a = 2; b = -15; c = -14
⇒ Δ = ( - 15 ) 2 – 4 . 2 . ( - 14 ) = 337 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
⇔ 14 = ( x - 2 ) ( x + 3 ) ⇔ 14 = x 2 - 2 x + 3 x - 6 ⇔ x 2 + x - 20 = 0
Có a = 1; b = 1; c = -20
⇒ Δ = 1 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 20 ) = 81 > 0
Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
Cả hai nghiệm đều thỏa mãn điều kiện xác định.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-5; 4}.
f) Điều kiện: x≠-1;x≠4
Ta có: a= 1, b = -7, c = - 8
∆ = ( - 7 ) 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 8 ) = 81
=> Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
Kết hợp với diều kiện, nghiệm của phương trình đã cho là x = 8