
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Nhận thấy tử và mẫu phân thức đều có tổng các hệ số bằng 0, Theo Bezout ta có : \(3x^3-7x^2+5x-1⋮x-1,2x^3-x^2-4x+3⋮x-1\)
Thực hiện phép chia ta sẽ có biểu thức
=\(\frac{\left(x-1\right)\left(3x^2-4x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(2x^2+x-3\right)}=\frac{3x^2-4x+1}{2x^2+x-3}\).Ta lại thấy tử và mẫu có tổng các hệ số bằng 0, theo Bơ du chúng sẽ chia ht x-1.Thực hiện phép chia rồi rút gọn đc
\(\frac{3x-1}{2x+3}\)

Ta có: \(P\left(x\right)⋮Q\left(x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^3-7x^2+5x+1⋮2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^3-x^2-6x^2+3x+2x-1+2⋮2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2⋮2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-1\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\in\left\{2;0;3;-1\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;0;\dfrac{3}{2};-\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)

a, 3x2 - 8x2 - 2x+3=0
2x(3-8) - 2x+3=0
2x5 - 2x+3=0
2x5 - 2x=0-3=
2x5 - 2x=-3
2x(5-x)=-3
5-x=-3/2
5-x=1,5
x=5-1,5
x=3,5

a)\(f\left(x\right)=2x^2-x-3+5=\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-3\right)+5\)
Để \(f\left(x\right)⋮g\left(x\right)\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-3\right)+5⋮\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5⋮\left(x+1\right)\)
mà \(x+1\in Z\Rightarrow x+1\in U\left(5\right)=\left\{-1;1;5;-5\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-2;0;4;-6\right\}\)
Vậy...
b) \(f\left(x\right)=3x^2-4x+6=\left(3x^2-4x+1\right)+5=\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-1\right)+5\)
Để \(f\left(x\right)⋮g\left(x\right)\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-1\right)+5⋮\left(3x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5⋮\left(3x-1\right)\) mà \(3x-1\in Z\Rightarrow3x-1\in U\left(5\right)=\left\{-1;1;5;-5\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{0;\dfrac{2}{3};2;-\dfrac{4}{3}\right\}\) mà x nguyên\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{0;2\right\}\)
Vậy...
c)\(f\left(x\right)=\left(-2x^3-7x^2-5x+2\right)+3\)\(=\left(-2x^3-4x^2-3x^2-6x+x+2\right)+3\)\(=\left[-2x^2\left(x+2\right)-3x\left(x+2\right)+\left(x+2\right)\right]+3\)
\(=\left(x+2\right)\left(-2x^2-3x+1\right)+3\)
Làm tương tự như trên \(\Rightarrow x+2\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left\{-3;-1;1;3\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-5;-3;-1;1\right\}\)
Vậy...
d)\(f\left(x\right)=x^3-3x^2-4x+3=x\left(x^2-3x-4\right)+3=x\left(x+1\right)\left(x-4\right)+3\)
Làm tương tự như trên \(\Rightarrow x+1\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left\{-3;-1;1;3\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{-4;-2;0;2\right\}\)
Vậy...

a. \(2x^3-3x^2=x^2\left(2x-3\right)\)
b. \(3x^4-24x=3x\left(x^3-8\right)=3x\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+4\right)\)
c. \(x^3y+5x^2y=x^2y\left(x+5\right)\)
d. \(7x^2+14xy=7x\left(x+2y\right)\)
a)2x^3-3x^2=x^2(2x-3)
b)3x^4-24x
=3x(x^3-8x)
=3x(x-2)(x^2+2x+4)
c)x^3y+5x^2y
=x^2y(x+5)
d)7x^2+14xy
=7x(x+2y)
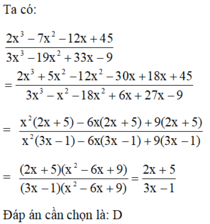
2x3-7x2+5x=0
<=>x*(2x2-7x+5)=0
<=>x*(2x2-2x-5x+5)=0
<=>x*[(2x2-2x)-(5x-5)]=0
<=>x*[2x*(x-1)-5*(x-1)]=0
<=>x*(x-1)*(2x-5)=0