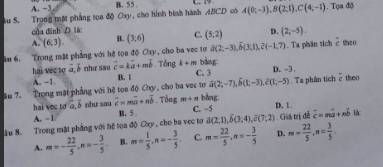
giải ra giúp mk vs cảm ơn ạ
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1.needn't
2.impressed
3.the
4.send
5.the
6.who
ko biết đúng ko nữa
Part 1
1 needn't
2 impressed
3 with
4 send
5 the
6 who
Part 2
1f 2d 3c 4b 5a 6g
Part 3
1 was cooking
2 surfing
3 went
4 was going to visit
5 try
6 widened
7 cultural
8 conveniently
Part 4
1 serious -> seriously
2 well-preserved -> be well-preserved
Part 5
1 my english were good
2 going to the english-
3 area has been spoiled
4 which I read
Part 6
1 without
2 be damaged
3 healthy
4 destruction
Part 7
2F 3F 4F

a) (a + b + c)2 = [(a + b) + c]2 = (a + b)2 + 2(a + b)c + c2
= a2+ 2ab + b2 + 2ac + 2bc + c2
= a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ac.
b) (a + b – c)2 = [(a + b) – c]2 = (a + b)2 - 2(a + b)c + c2
= a2 + 2ab + b2 - 2ac - 2bc + c2
= a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab - 2bc - 2ac.
c) (a – b –c)2 = [(a – b) – c]2 = (a – b)2 – 2(a – b)c + c2
= a2 – 2ab + b2 – 2ac + 2bc + c2
= a2 + b2 + c2 – 2ab + 2bc – 2ac.
bài này phải không nếu đúng thì tích hộ mình

Để dòng điện chạy qua mạch, cần có nguồn điện (pin), vật dẫn (giấy bạc) và một mạch kín.
Giấy bạc gồm nhôm, thép và thiếc, do đó đây là vật dẫn lý tưởng cho dòng điện.
Khi gắn hai đầu giấy bạc vào các cực của pin, ta có một mạch điện đơn giản.
Giấy bạc có phần nối rộng 2 mm. Vật dẫn càng mỏng, điện trở càng lớn, năng lượng giải phóng càng nhiều.
Do đó, khi dòng điện chạy qua sợi giấy bạc, nó làm nóng dải hẹp đó. Phần nối bị nóng lên, giống dây tóc hình xoắn trong bóng đèn. Nhiệt độ cao khiến nó bùng cháy.


a) Ta có: O hóa trị II, ta gọi hóa trị Mn cần tìm trong hợp chất MnO2 là x: \(Mn^xO_2^{II}\)
Theo quy tắc hóa trị, ta có:
1.x=2.II
=>x= (2.II)/1= IV
=> Hóa trị x của Mn cần tìm trong hợp chất MnO2 là IV.
a) Ta có: (PO4) hóa trị II, ta gọi hóa trị Mn cần tìm trong hợp chất là y: \(Ba^y_3\left(PO_4\right)^{III}_2\)
Theo quy tắc hóa trị, ta có:
3.y=III.2
=>y=(III.2)/3=II
=> Hóa trị y của Ba cần tìm trong hợp chất Ba3(PO4)2 là II.

Bài 1:
\(a,A=6\sqrt{2}-6\sqrt{2}+2\sqrt{5}=2\sqrt{5}\\ b,B=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}\left(\sqrt{3}-1\right)}{\sqrt{3}-1}+\dfrac{\sqrt{2}\left(\sqrt{2}-1\right)}{\sqrt{2}-1}=\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{2}\\ c,=2\sqrt{3}-6\sqrt{3}+15\sqrt{3}-4\sqrt{3}=7\sqrt{3}\\ d,=1+6\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{3}-1=5\sqrt{3}\\ e,=4\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{2}-6\sqrt{2}+3\sqrt{2}=2\sqrt{2}\)
Bài 2:
\(a,ĐK:x\ge\dfrac{3}{2}\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x-3}=5\Leftrightarrow2x-3=25\Leftrightarrow x=14\\ b,PT\Leftrightarrow x^2=\sqrt{\dfrac{98}{2}}=\sqrt{49}=7\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{7}\\x=-\sqrt{7}\end{matrix}\right.\\ c,ĐK:x\ge3\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-3}\left(\sqrt{x+3}+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-3}=0\left(\sqrt{x+3}+1>0\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x=3\\ d,ĐK:x\ge1\\ PT\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{x-1}-\sqrt{x-1}+3\sqrt{x-1}=4\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-1}=1\Leftrightarrow x=2\left(tm\right)\\ e,PT\Leftrightarrow2x-1=16\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{17}{2}\\ f,PT\Leftrightarrow\left|2x-1\right|=\sqrt{3}-1\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=\sqrt{3}-1\\2x-1=1-\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\\x=\dfrac{2-\sqrt{3}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bài 3:
\(a,Q=\dfrac{1+5}{3-1}=3\\ b,P=\dfrac{x+\sqrt{x}-6+x-2\sqrt{x}-3-x+4\sqrt{x}+9}{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)}\\ P=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-3}\\ c,M=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-3}\cdot\dfrac{3-\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+5}=\dfrac{-\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+5}\)
Vì \(-\sqrt{x}\le0;\sqrt{x}+5>0\) nên \(M< 0\)
Do đó \(\left|M\right|>\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow M< -\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+5}+\dfrac{1}{2}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{x}-5}{2\left(\sqrt{x}+5\right)}< 0\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}-5< 0\left(\sqrt{x}+5>0\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow0\le x< 25\)
Bài 4:
\(a,A=\dfrac{16+2\cdot4+5}{4-3}=29\\ b,B=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-9-x+9+2x-3\sqrt{x}-2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}\\ B=\dfrac{x-\sqrt{x}-2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-3}\\ c,P=\dfrac{x+2\sqrt{x}+5}{\sqrt{x}-3}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-3}{\sqrt{x}+1}=\dfrac{x+2\sqrt{x}+5}{\sqrt{x}+1}\\ P=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)^2+4}{\sqrt{x}+1}=\sqrt{x}+1+\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{x}+1}\\ P\ge2\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\cdot\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{x}+1}}=2\sqrt{4}=4\\ P_{min}=4\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)^2=4\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}+1=2\Leftrightarrow x=1\left(tm\right)\)

Câu 5:
ABCD là hình bình hành
=>vecto AB=vecto DC
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4-x=2-0=2\\-1-y=1+3=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow D\left(2;-5\right)\)
Câu 6:
vecto c=k*vecto a+m*vecto b
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-1=2k+3m\\7=-3k+m\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}k=-2\\m=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>k+m=-1
Câu 7: B
Câu 8: C