Tính delta phương trình này hộ em ạ
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



Điều kiện xác định :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-2\ne0\\x-1\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x\ne2\\x\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ne1\)
\(\dfrac{2x+1}{2x-2}=\dfrac{2}{x-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x+1}{2x-2}-\dfrac{2}{x-1}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x+1}{2\left(x-1\right)}-\dfrac{2}{x-1}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x+1-2.2}{2\left(x-1\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+1-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}\left(tmdk\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)

\(\left(x-1\right)^3+x^3+\left(x+1\right)^3=\left(x+2\right)^3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-3x^2+3x-1+x^3+x^3+3x^2+3x+1-x^3-6x^2-12x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^3-6x^2-6x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2.\left(x^3-3x^2-3x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-4x^2+x^2-4x+x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2.\left(x-4\right)+x.\left(x-4\right)+\left(x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right).\left(x^2+x+1\right)=0\)
Mà \(x^2+x+1=\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}>0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-4=0\Leftrightarrow x=4\)

Có : G - T = 140 nu
2T + 3G = 2520
=> A = T = 420 nu
G = X = 560 nu
N = 2 ( A + G ) = 1960 nu
l = N x 3,4 : 2 = 3332Ao
Ta có: \(G-T=140\)
\(2T+3G=2520\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}A=T=420nu\\G=X=560nu\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(N=2A+2G=2\cdot420+2\cdot560=1960nu\)
\(l=\dfrac{2N}{3,4}=\dfrac{2\cdot1960}{3,4}=1152,94A^o\)

Mình nghĩ với pt tổng quát: \(ax^2+bx+c=0\) có \(\Delta=b^2-4ac\)
Nếu như vậy thì: \(1.x^2+6x+m\) có \(\Delta=6^2-4m\)chứ?
Riêng mình thì bài này mình dùng delta phẩy cho lẹ:
Lời giải
Để pt \(x^2+6x+m=0\) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt thì:
\(\Delta'=\left(\frac{b}{2}\right)^2-ac=3^2-m>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m< 9\)

\(3x^2-2x+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+x^2-2x+1+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+\left(x-1\right)^2=-4\)
Phương trình vô nghiệm.
Sai đề phải là 3x2-2x-5=0
Ta có:3x2-2x-5=0
<=> 3x2+3x-5x-5=0
<=> 3x(x+1)-5(x+1)=0
<=> (x+1)(3x-5)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=\dfrac{5}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(ĐK:x\ge5\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}=a\\\sqrt{x-5}=b\end{matrix}\right.\left(a,b\ge0\right)\Leftrightarrow4b^2-3a^2=x-20\)
\(PT\Leftrightarrow4b^2-3a^2+a+b+ab=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4ab+4b^2-3a^2-3ab+a+b=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4b\left(a+b\right)-3a\left(a+b\right)+\left(a+b\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(a+b\right)\left(4b-3a+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a+b=0\left(\text{loại do }a+b>0\right)\\4b-3a+1=0\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ \left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow4\sqrt{x-5}=3\sqrt{x}-1\\ \Leftrightarrow16x-80=9x-6\sqrt{x}+1\\ \Leftrightarrow7x+6\sqrt{x}-81=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}=3\\\sqrt{x}=-\dfrac{27}{7}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=9\left(nhận\right)\)

 mọi ng giải hộ em bài này với ạ( có lập bảng và giải bằng hệ phương trình ạ) e cần gấp
mọi ng giải hộ em bài này với ạ( có lập bảng và giải bằng hệ phương trình ạ) e cần gấp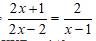


 giúp em bài này với ạ ( đặt tính hộ em luôn ạ)
giúp em bài này với ạ ( đặt tính hộ em luôn ạ)



- \(m=0\)dễ thấy không thỏa mãn.
- \(m\ne0\):
\(\Delta'=\left(m-1\right)^2-3\left(m-2\right).m=-2m^2+4m+1\)
Để phương trình đã cho có hai nghiệm \(x_1,x_2\)thì \(\Delta'\ge0\Rightarrow-2m^2+4m+1\ge0\).
Khi phương trình có hai nghiệm \(x_1,x_2\), theo Viete ta có:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x_1+x_2=\frac{2\left(m-1\right)}{m}\\x_1x_2=\frac{3\left(m-2\right)}{m}\end{cases}}\)
Ta có: \(x_1+2x_2=1\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x_1+2x_2-1\right)\left(x_2+2x_1-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x_1x_2+2\left(x_1^2+x_2^2\right)-3\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-3\left(x_1+x_2\right)+x_1x_2+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow2\left[\frac{2\left(m-1\right)}{m}\right]^2-\frac{6\left(m-1\right)}{m}+\frac{3\left(m-2\right)}{m}+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8\left(m-1\right)^2-6m\left(m-1\right)+3m\left(m-2\right)+m^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6m^2-16m+8=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}m=2\\m=\frac{2}{3}\end{cases}}\)
Thử lại đều thỏa mãn.
hok bé ơi