trong mặt phẳng Oxy cho hai điểm A(-1;5) và B(3;-1) trung điểm I của đoạn thẳng AB có độ là
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


(1); vecto u=2*vecto a-vecto b
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\cdot1-0=2\\y=2\cdot\left(-4\right)-2=-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
(2): vecto u=-2*vecto a+vecto b
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\cdot\left(-7\right)+4=18\\y=-2\cdot3+1=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
(3): vecto a=2*vecto u-5*vecto v
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2\cdot\left(-5\right)-5\cdot0=-10\\b=2\cdot4-5\cdot\left(-3\right)=15+8=23\end{matrix}\right.\)
(4): vecto OM=(x;y)
2 vecto OA-5 vecto OB=(-18;37)
=>x=-18; y=37
=>x+y=19

Ta có C ∈ O x nên C(x, 0) và A C → = x − 1 ; − 3 B C → = x − 4 ; − 2 .
Do C A = C B ⇔ C A 2 = C B 2 .
⇔ x − 1 2 + − 3 2 = x − 4 2 + − 2 2 ⇔ x 2 − 2 x + 1 + 9 = x 2 − 8 x + 16 + 4 ⇔ 6 x = 10 ⇔ x = 5 3 ⇒ C 5 3 ; 0
Chọn B.
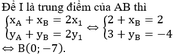


\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_I=\dfrac{x_A+x_B}{2}=\dfrac{-1+3}{2}=1\\y_I=\dfrac{y_A+y_B}{2}=\dfrac{5+\left(-1\right)}{2}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow I\left(1;2\right)\)
Giúp mik với