
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(2sin^2\dfrac{x}{2}=cos5x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-cos5x=1-2.sin^2\dfrac{x}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-cos5x=cosx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(5x\right)=cos\left(\pi-x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5x=\pi-x+k2\pi\\5x=-\pi+x+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+\dfrac{k\pi}{3}\\x=-\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) (k nguyên)
Vậy..

x3 - 6xy + y3 = 8
<=> (x + y)3 - 3xy(x + y) - 6xy + 8 = 16
<=> (x + y + 2)(x2 + y2 - xy - 2x - 2y + 4) = 16
<=> \(\left(x+y+2\right)\left[\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}y-1\right)^2+3\left(\dfrac{1}{2}y-1\right)^2\right]=16\)
Nhận thấy \(\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}y-1\right)^2+3\left(\dfrac{1}{2}y-1\right)^2\ge0\)
=> x + y + 2 > 0
Khi đó 16 = 1.16 = 2.8 = 4.4
Lập bảng
| x + y + 2 | 1 | 16 | 4 | 2 | 8 | |
| \(\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}y-1\right)^2+3\left(\dfrac{1}{2}y-1\right)^2\) | 16 | 1 | 4 | 8 | 2 | |
| x | ||||||
| y | | |
Đến đó bạn thế x qua y rồi làm tiếp nha

pt: \(\left(1-2x\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2+2\right)=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}1-2x=0\\x+3=0\\x^2+2=0\end{cases}}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{2}\\x=-3\\x^2=-2\left(loại\right)\end{cases}}\)
vậy: \(x=\frac{1}{2}\),\(x=-3\)


Dễ nhận thấy pt này có một nghiệm là 1 nên ta sẽ tạo nhân tử là x-1
Ta có: \(2x^4+4x^3-7x^2-5x+6=0\)
<=> \(\left(2x^4-2x^3\right)+\left(6x^3-6x^2\right)-\left(x^2-x\right)-\left(6x-6\right)=0\)
<=> \(2x^3\left(x-1\right)+6x^2\left(x-1\right)-x\left(x-1\right)-6\left(x-1\right)=0\)
<=> \(\left(x-1\right)\left(2x^3+6x^2-x-6\right)=0\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\2x^3+6x-x-6=0\end{cases}}\)
Bạn có thể giải pt 2x3+6x-x-6=0 bằng pp Cardano nha, cm dài lắm
Ta tách được \(2x^4+4x^3-7x^2-5x+6=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2x^3+6x-x-6\right)=0\)
Vậy pt có 1 nghiệm x= 1.
Ta giải pt bậc ba theo công thức Cardano:
\(2x^3+6x^2-x-6=0\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow x^3+3x^2-\frac{1}{2}x-3=0\)
Đặt \(x=y-1\Rightarrow y^3-\frac{7}{2}y-\frac{1}{2}=0\left(2\right)\)
\(\Delta=27\left(\frac{-1}{2}\right)^2-4\left(\frac{7}{2}\right)^3=-\frac{659}{4}< 0\)
Vậy pt (2) có 3 nghiệm phân biệt thuộc khoảng \(\left(-\frac{\sqrt{42}}{3};\frac{\sqrt{42}}{3}\right)\)
Đặt \(y=\frac{\sqrt{42}}{3}cost\left(t\in\left(0;\pi\right)\right)\). Thay vào pt(2) ta có: \(cos\left(3t\right)=\frac{3\sqrt{42}}{98}\)
Ta tìm được 3 nghiệm t thuộc khoảng \(\left(0;\pi\right)\), sau đó tìm cost rồi suy ra y và x.
Cô tìm một nghiệm để giúp em kiểm chứng nhé. Em có thể thay giá trị nghiệm để kiểm tra.
\(cos\left(3t\right)=\frac{3\sqrt{42}}{98}\Rightarrow t=\frac{arccos\left(\frac{3\sqrt{42}}{98}\right)}{3}\Rightarrow y=\frac{\sqrt{42}}{3}.cos\frac{arccos\left(\frac{3\sqrt{42}}{98}\right)}{3}\)
Vậy \(x=\frac{\sqrt{42}}{3}.cos\frac{arccos\left(\frac{3\sqrt{42}}{98}\right)}{3}-1\). Đó là một nghiệm, em có thể tìm 2 nghiệm còn lại bằng cách tương tự.

Bài 8:
a: Khi a=1 thì phương trình sẽ là \(\left(1-4\right)x-12x+7=0\)
=>-3x-12x+7=0
=>-15x+7=0
=>-15x=-7
hay x=7/15
b: Thay x=1 vào pt, ta được:
\(a^2-4-12+7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a-3\right)\left(a+3\right)=0\)
hay \(a\in\left\{3;-3\right\}\)
c: Pt suy ra là \(\left(a^2-16\right)x+7=0\)
Để phương trình đã cho luôn có một nghiệm duy nhất thì (a-4)(a+4)<>0
hay \(a\notin\left\{4;-4\right\}\)

\(ĐK:x\ne\dfrac{1}{2};x\ne1;x\ne\dfrac{3}{2};x\ne2;x\ne\dfrac{5}{2}\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(x-1\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(3x-2\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(3x-2\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(5x-2\right)}=\dfrac{4}{21}\\ \Leftrightarrow2\left[\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}}{\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\left(x-1\right)}+\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)}+\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}}{\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-\dfrac{5}{2}\right)}\right]=\dfrac{4}{21}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{1}{x-\dfrac{1}{2}}+\dfrac{1}{x-\dfrac{3}{2}}-\dfrac{1}{x-1}+\dfrac{1}{x-2}-\dfrac{1}{x-\dfrac{3}{2}}+\dfrac{1}{x-\dfrac{5}{2}}-\dfrac{1}{x-2}=\dfrac{2}{21}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{1}{x-\dfrac{5}{2}}=\dfrac{2}{21}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-\dfrac{5}{2}-x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-\dfrac{5}{2}\right)}=\dfrac{2}{21}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-\dfrac{3}{2}}{x^2-\dfrac{7}{2}x+\dfrac{5}{2}}=\dfrac{2}{21}\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-\dfrac{7}{2}x+\dfrac{5}{2}=-\dfrac{63}{4}\\ \Leftrightarrow4x^2-14x+10=-63\\ \Leftrightarrow4x^2-14x+73=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\in\varnothing\)

\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x-2\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(2x-2\right)\left(2x-3\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x-4\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(2x-4\right)\left(2x-5\right)}=\dfrac{4}{21}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{2x-2}-\dfrac{1}{2x-1}+\dfrac{1}{2x-3}-\dfrac{1}{2x-2}+\dfrac{1}{2x-4}-\dfrac{1}{2x-3}+\dfrac{1}{2x-5}-\dfrac{1}{2x-4}=\dfrac{4}{21}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{2x-5}-\dfrac{1}{2x-1}=\dfrac{4}{21}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{4}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x-5\right)}=\dfrac{4}{21}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x-5\right)=21\)
\(\Rightarrow4x^2-12x-16=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=4\end{matrix}\right.\)

đkxđ: \(\dfrac{x+3}{x-1}\ge0\)
Ptr ⇔\(\left(x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)+\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)\sqrt{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-1\right)}}{x-1}=8\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)+2\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)}-8=0\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)}=a\) (a≥0)
Ptr ⇔ \(a^2+2a-8=0\)
⇔a=2 (tm) hoặc a=-4 (loại)
⇒\(\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)}=2\)
⇔\(x^2+2x-3=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-7=0\)
⇔ \(x=-1+2\sqrt{2}\) (tm)
hoặc \(x=-1-2\sqrt{2}\) (tm)
Vậy...

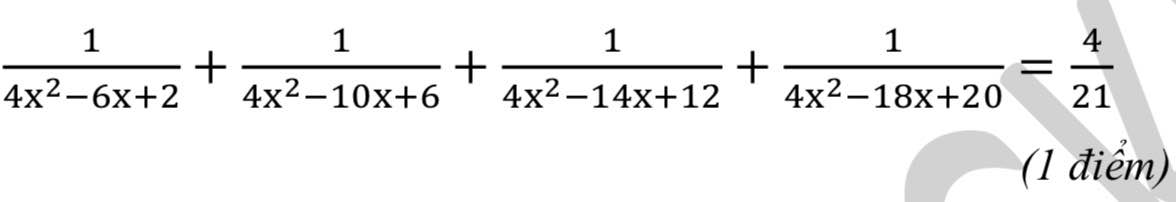
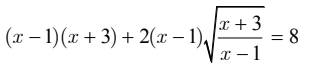 ( bài này giải theo phương pháp đặt ẩn phụ đúng không mọi người ? giải giúp mình với
( bài này giải theo phương pháp đặt ẩn phụ đúng không mọi người ? giải giúp mình với