Giúp vs ạ e cảm ơn 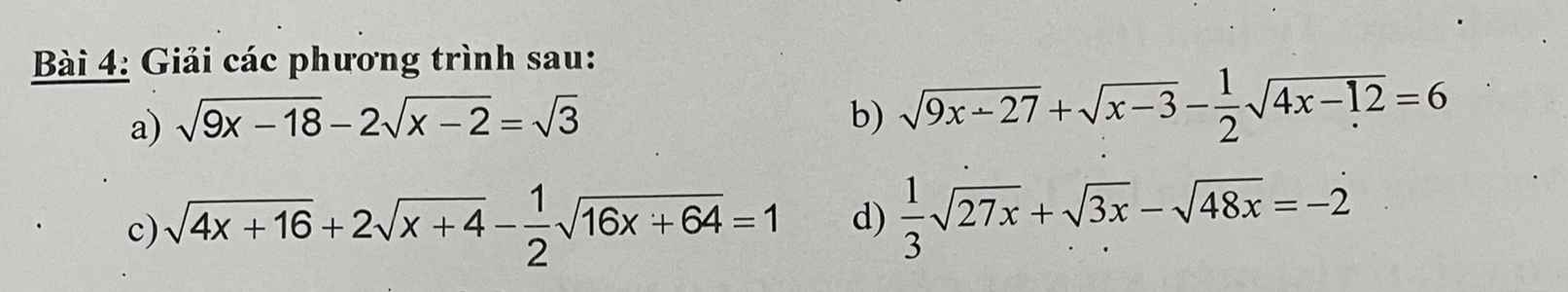
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 1:
\(54\left(\dfrac{km}{h}\right)=15\left(\dfrac{m}{s}\right);9\left(\dfrac{m}{s}\right)=32,4\left(\dfrac{km}{h}\right)\)
Baì 2:
\(t'=s':v'=5:\left(5.3,6\right)=\dfrac{5}{18}h\)
\(\Rightarrow v_{tb}=\dfrac{s'+s''}{t'+t''}=\dfrac{5+3,8}{\dfrac{5}{18}+\left(\dfrac{15}{60}\right)}\simeq16,67\left(\dfrac{km}{h}\right)\)


Câu 2:
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(10x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=-\dfrac{3}{10}\end{matrix}\right.\)



Áp dụng bất đẳng thức Cosi ta có :
\(x^4+1\ge2x^2;x^2+1\ge\left|x\right|\Rightarrow x^4+3\ge4\left|x\right|\)
Tương tự : \(y^4+3\ge4\left|y\right|\)
\(\Rightarrow x^4+y^4+6\ge4\left(\left|x\right|+\left|y\right|\right)\left(1\right)\)
Từ (1) suy ra \(x^4+y^4+6\ge4\left(x-y\right)\Rightarrow P\le\dfrac{1}{4}\)
Dấu = xảy ra \(x=1;y=-1\)
Từ (1) suy ra \(x^4+y^4+6\ge4\left(y-x\right)\Rightarrow P\ge-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
Dấu = xảy ra \(x=-1;y=1\)

Bài 1.
a)Điện trở tương đương: \(R_m=R_1+R_2=12+8=20\Omega\)
b)\(I_A=I_1=I_2=\dfrac{U_{AB}}{R_m}=\dfrac{18}{20}=0,9A\)
c)\(U_1=I_1\cdot R_1=0,9\cdot12=10,8V\)
\(U_2=I_2\cdot R_2=0,9\cdot8=7,2V\)
d)\(R_Đ=\dfrac{U_Đ^2}{P_Đ}=\dfrac{12^2}{6}=6\Omega\)
\(\Rightarrow R_m=R_1+R_Đ=12+6=18\Omega\)
\(I_m=\dfrac{U}{R}=\dfrac{18}{18}=1A\)
\(I_{Đđm}=\dfrac{P_Đ}{U_Đ}=\dfrac{6}{12}=0,5A< I_m=1A\)
Vậy đèn sáng yếu hơn bình thường.
Bài 2:
a. \(R=\dfrac{R1.R2}{R1+R2}=\dfrac{20.30}{20+30}=12\Omega\)
\(U=U1=U2=IR=12.2=24V\left(R1\backslash\backslash\mathbb{R}2\right)\)
b. \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}I1=U1:R1=24:20=1,2A\\I2=U2:R2=24:30=0,8A\end{matrix}\right.\)
c. \(I=I12=I3=0,5A\left(R12ntR3\right)\)
\(U3=U-U12=24-\left(0,5.12\right)=18V\)
d. \(P=UI'=24.0,5=12\)W

1 more difficult
2 warmer
3 the most intelligent
4 the hottest
5 cheaper than
6 luckiest
7 more comfortable than
8 the most boring
9 the luckiest
10 simper

Bài 1:
\((n+1)^n-1=n[(n+1)^{n-1}+(n+1)^{n-2}+....+(n+1)+1]\)
Giờ ta chỉ cần cmr \((n+1)^{n-1}+(n+1)^{n-2}+...+(n+1)+1\vdots n\)
Thật vậy:
\((n+1)^{n-1}+(n+2)^{n-2}+...+(n+1)+1\equiv 1^{n-1}+1^{n-2}+...+1^1+1=n\equiv 0\pmod n\)
Do đó ta có đpcm.
Bài 2 em xem lại. Số $2^{n(2^n-1)}$ chỉ toàn ước có dạng $2^k$ với $k=0,1,..., n(2^n-1)$ trong khi đó $(2^n-1)^2$ là số lẻ.


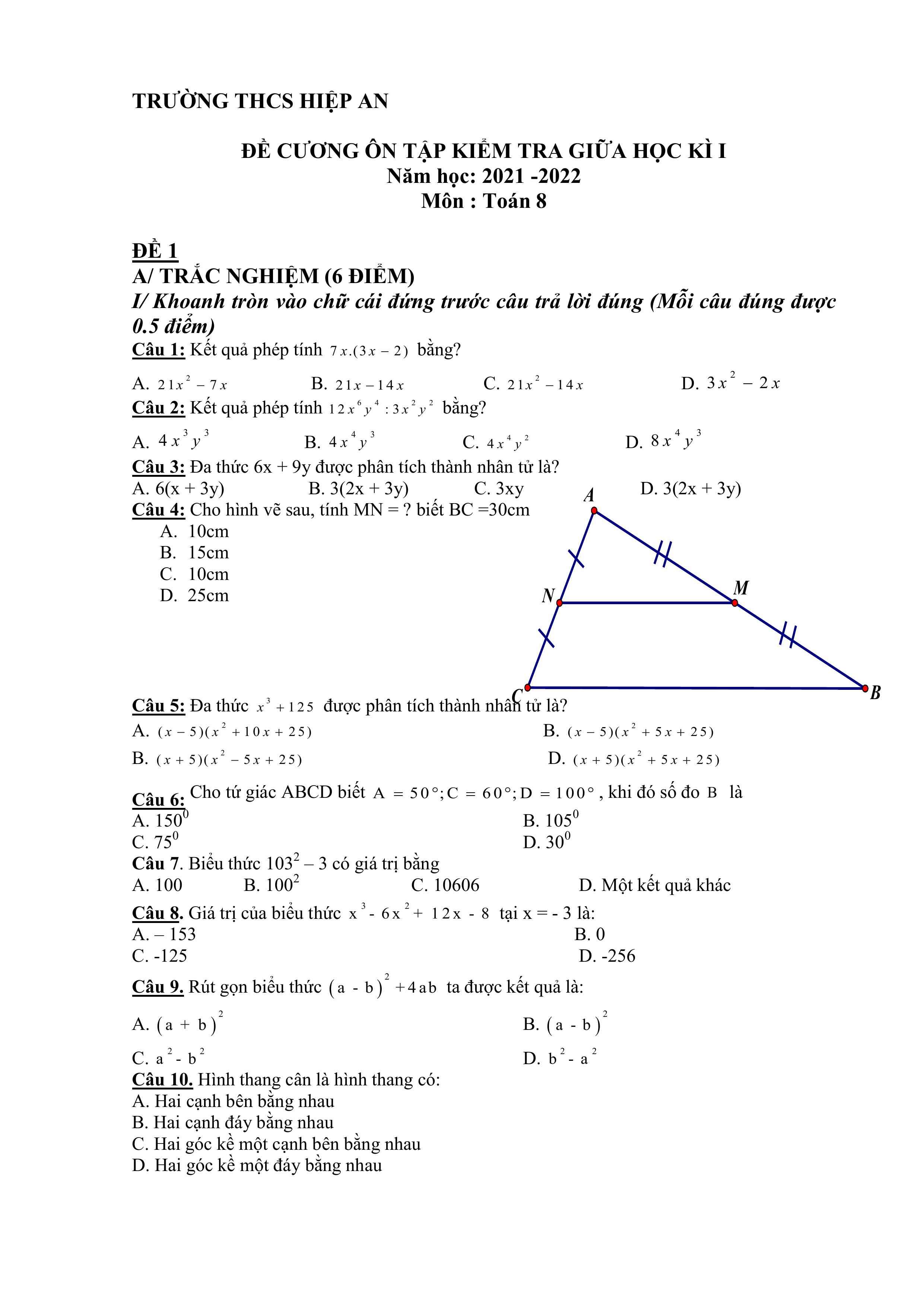





\(a,ĐK:x\ge2\\ PT\Leftrightarrow3\sqrt{x-2}-2\sqrt{x-2}=\sqrt{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-2}=\sqrt{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow x-2=3\\ \Leftrightarrow x=5\left(tm\right)\\ b,ĐK:x\ge3\\ PT\Leftrightarrow3\sqrt{x-3}+\sqrt{x-3}-\sqrt{x-3}=6\\ \Leftrightarrow3\sqrt{x-3}=6\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-3}=2\\ \Leftrightarrow x-3=4\Leftrightarrow x=7\left(tm\right)\\ c,ĐK:x\ge-4\\ PT\Leftrightarrow4\sqrt{x+4}+2\sqrt{x+4}-2\sqrt{x+4}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow4\sqrt{x+4}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x+4}=\dfrac{1}{4}\Leftrightarrow x+1=\dfrac{1}{16}\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{15}{16}\left(tm\right)\\ d,ĐK:x\ge0\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{3x}+\sqrt{3x}-4\sqrt{3x}=-2\\ \Leftrightarrow-2\sqrt{3x}=-2\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{3x}=1\Leftrightarrow3x=1\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}\left(tm\right)\)