
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


2: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+x\right)^2-5\left(x^2+x\right)-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-6=0\)
=>(x+3)(x-2)=0
=>x=-3 hoặc x=2
5: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-2;1;-1\right\}\)

Ta có \(2y^2⋮2\Rightarrow x^2\equiv1\left(mod2\right)\Rightarrow x^2\equiv1\left(mod4\right)\Rightarrow2y^2⋮4\Rightarrow y⋮2\Rightarrow x^2\equiv5\left(mod8\right)\) (vô lí).
Vậy pt vô nghiệm nguyên.
2: \(PT\Leftrightarrow3x^3+6x^2-12x+8=0\Leftrightarrow4x^3=\left(x-2\right)^3\Leftrightarrow\sqrt[3]{4}x=x-2\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{-2}{\sqrt[3]{4}-1}\).

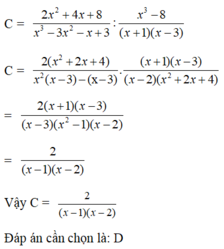
Bài làm
x³ - 8 = 2x² - 4x
<=> x³ - 2x² + 4x - 8 = 0
<=> x²( x - 2 ) + 4( x - 2 ) = 0
<=> ( x - 2 )( x² + 4 ) = 0
<=> x - 2 = 0 hoặc x² + 4 = 0
<=> x = 2 hoặc x² = -4 ( vô lí )
Vậy x = 2 là nghiệp phương trình.
"nghiệp" :v