
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\Delta'=9-\left(2n-3\right)=12-2n>0\Rightarrow n< 6\)
Khi đó theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=6\\x_1x_2=2n-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do \(x_1\) là nghiệm của pt nên:
\(x_1^2-6x_1+2n-3=0\Leftrightarrow x_1^2-5x_1+2n-4=x_1-1\)
Tương tự ta có: \(x_2^2-5x_2+2n-4=x_2-1\)
Thế vào bài toán:
\(\left(x_1-1\right)\left(x_2-1\right)=-4\Leftrightarrow x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1=-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2n-3-6+1=-4\Rightarrow n=2\)

\(x^2-6x+2m-3=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac=36-4\left(2m-3\right)=36-8m+12=48-8m\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì \(\Delta>0\)\(< =>48-8m>0< =>48>8m< =>6>m\)
Theo Vi-ét ta có :\(\hept{\begin{cases}x_1x_2=\frac{c}{a}=2m-3\\x_1+x_2=\frac{-b}{a}=6\end{cases}}\)là
\(x_1\)là nghiệm phương trình \(x_1^2-6x_1+2m-3=0\)
\(=>x_1^2=3-2m+6x_1\)
\(x_2\)là nghiệm phương trình \(x_2^2-6x_2+2m-3=0\)
\(=>x_2^2=3-2m+6x_2\)
Mà \(\left(x_1^2-5x_1+2m-4\right)\left(x_2^2-5x_2+2m-4\right)=2\)
\(\left(3-2m+6x_1-5x_1+2m-4\right)\left(3-2m+6x_2-5x_2+2m-4\right)=2\)
\(\left(3+x_1-4\right)\left(3+x_2-4\right)=2\)
\(\left(x_1-1\right)\left(x_2-1\right)=2\)
\(x_1x_2-x_1-x_2+1=2\)
\(x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)=1\)
\(2m-3-6=1\)
\(2m-9=1\)
\(m=5\)
Vậy m=5

Thay n = 4 vào pt (1) ta có
\(x^2-6x+5=0\\ ta.có.a+b+c=1-6+5=0\\ Vậy.pt.có.n_o:\\ x_1=1;x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=5\)
\(Ta.có:\Delta=b^2-4ac=....=-8n+48\\ Để.pt.\left(1\right).có.1.n_o.phân.biệt.thì.\Delta>0\\ \Leftrightarrow n< 6\)
Vậy m < 6 thì pt (1) có nghiệm phân biệt \(x_1;x_2\) nên theo Vi ét ta có
\(x_1+x_2=\dfrac{-b}{a}=6\\ x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=2n-3\)
Ta có
\(x^2-6x+2n-3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+2n-4=x-1\)
Vì x1 x2 là nghiệm pt \(x^2-6x+2n-3=0\) nên x1 x2 là nghiệm PT \(x^2-5x+2n-4=x-1\) nên ta có
\(x_1^2-5x+2x-4=x_1-1.và\\ x_2^2-5x_2+2n-4=x_2-1\\ \Rightarrow\left(x_1^2-5x_1+2n-4\right)\left(x_2^2-5x_2+2n-4\right)=\left(x_1-1\right)\left(x_2-1\right)\)
\(Mà\\ \left(x_1^2-5x_1+2n-4\right)\left(x_2^2-5x_2+2n-4\right)=-4\\ Nên\left(x_1-1\right)\left(x_2-1\right)=-4\\ \Leftrightarrow x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1=-4\\ \Leftrightarrow2n-3-6+1=-4\\ \Leftrightarrow2n=4\Rightarrow n=2\left(tm\right)\\ ......\left(kl\right)\)

\(\Delta'=9-\left(2n-3\right)>0\Leftrightarrow n< 6\)
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=6\\x_1x_2=2n-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do \(x_1;x_2\) là nghiệm nên:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1^2-6x_1+2n-3=0\\x_2^2-6x_2+2n-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1^2-5x_1+2n-4=x_1-1\\x_2^2-5x_2+2n-4=x_2-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay vào bài toán:
\(\left(x_1-1\right)\left(x_2-1\right)=-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2n-3-6+5=0\Leftrightarrow n=2\)

\(\Delta=m^2-4\left(m-4\right)=\left(m^2-4m+4\right)+12=\left(m-2\right)^2+12>0;\forall m\)
Suy ra pt luôn có hai nghiệm pb với mọi m
Theo viet có:\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=m\\x_1.x_2=m-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(5x_1-1\right)\left(5x_2-1\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow25x_1x_2-5\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow25\left(m-4\right)-5m+1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{99}{20}\)
Vậy...
\(\Delta=m^2-4m+16=\left(m-2\right)^2+12>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) pt luôn có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
Áp dụng hệ thức Vi-ét: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=m\\x_1x_2=m-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có: \(\left(5x_1-1\right)\left(5x_2-1\right)=25x_1x_2-5\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1\)
\(=25\left(m-4\right)-5m+1=20m-99\)
\(\Rightarrow20m-99< 0\Rightarrow m< \dfrac{99}{20}\)

xét ptr \(2x^2-x-3+0\)
△=\(\left(-1\right)^2-4.2.\left(-3\right)=25>0\)
⇒ptr có 2 ngh phân biệt \(x_1;x_2\)
Theo hệt thức viet \(x_1+x_2=\dfrac{1}{2};x_1x_2=\dfrac{-3}{2}\)
Xét A = \(x_1^2+x_2^2-x_1^2x_2^2=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2-x_1^2x_2^2\)
=\(\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2-2\left(-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)-\left(-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2=\dfrac{1}{4}+3-\dfrac{9}{4}=3-2=1\)
Của cậu đây ạ, kh hiểu j thì hỏi tớ nha <3

a) 2 x 2 – 17 x + 1 = 0
Có a = 2; b = -17; c = 1
Δ = b 2 – 4 a c = ( - 17 ) 2 – 4 . 2 . 1 = 281 > 0 .
Theo hệ thức Vi-et: phương trình có hai nghiệm x1; x2 thỏa mãn:
x 1 + x 2 = − b / a = 17 / 2 x 1 x 2 = c / a = 1 / 2
b) 5 x 2 – x – 35 = 0
Có a = 5 ; b = -1 ; c = -35 ;
Δ = b 2 – 4 a c = ( - 1 ) 2 – 4 . 5 . ( - 35 ) = 701 > 0
Theo hệ thức Vi-et, phương trình có hai nghiệm x1; x2 thỏa mãn:
x 1 + x 2 = − b / a = 1 / 5 x 1 ⋅ x 2 = c / a = − 35 / 5 = − 7
c) 8 x 2 – x + 1 = 0
Có a = 8 ; b = -1 ; c = 1
Δ = b 2 – 4 a c = ( - 1 ) 2 – 4 . 8 . 1 = - 31 < 0
Phương trình vô nghiệm nên không tồn tại x1 ; x2.
d) 25 x 2 + 10 x + 1 = 0
Có a = 25 ; b = 10 ; c = 1
Δ = b 2 – 4 a c = 10 2 – 4 . 25 . 1 = 0
Khi đó theo hệ thức Vi-et có:
x 1 + x 2 = − b / a = − 10 / 25 = − 2 / 5 x 1 x 2 = c / a = 1 / 25


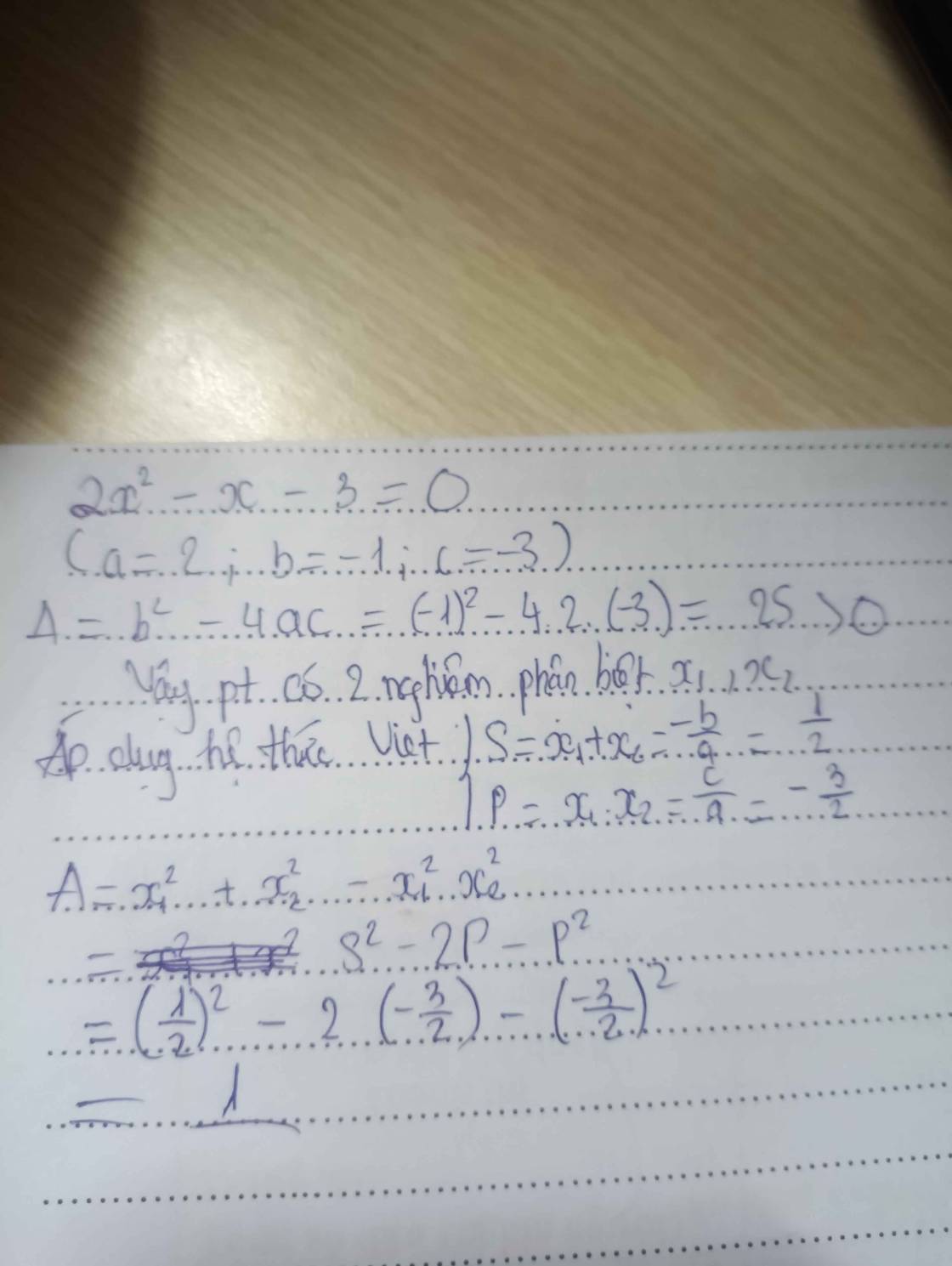
\(A=\dfrac{5x_1-x_2}{x_1}+\dfrac{5x_2-x_1}{x_2}\)
\(=\dfrac{5x_1\cdot x_2-x_2^2+5x_1x_2-x_1^2}{x_1x_2}\)
\(=\dfrac{10x_1x_2-\left[\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2\right]}{x_1x_2}\)
\(=\dfrac{10\cdot4-\left[5^2-2\cdot4\right]}{4}=\dfrac{40-25+8}{4}=\dfrac{23}{4}\)