Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Ta có : 2xy - x - y = 2
<=> 2xy - x = 2 + y
<=> x(2y - 1) = y + 2
=> x = \(\frac{y+2}{2y-1}\)
Vì x nguyên nên \(\frac{y+2}{2y-1}\) nguyên
Ta có ; \(\frac{y+2}{2y-1}=\frac{2y+4}{2y-1}=\frac{\left(2y-1\right)+5}{2y-1}=\frac{2y-1}{2y-1}+\frac{5}{2y-1}=1+\frac{5}{2y-1}\)
Để \(\frac{y+2}{2y-1}\) nguyên thì \(\frac{5}{2y-1}\) nguyên
Suy ra : 2y - 1 \(\in\) Ư(5) = {-5;-1;1;5}
Ta có bảng :
| 2y - 1 | -5 | -1 | 1 | 5 |
| 2y | -4 | 0 | 2 | 6 |
| y | -2 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| x | 0 | -2 | 3 | 1 |
Cảm ơn bạn nhá ![]()
Nhưng mà \(\dfrac{y+2}{2y-1}\) làm sao mà bằng \(\dfrac{2y+4}{2y-1}\)
Phải \(2x\) mới bằng \(\dfrac{2y+4}{2y-1}\) được chứ ![]()

a/ \(\left|2x-1,6\right|-2,3=1,4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x-1,6\right|=3,7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1,6=3,7\\2x-1,6=-3,7\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=5,3\\2x=-2,1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2,65\\x=-1,05\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ....
b/ \(5,4-\left|3x-1,2\right|=5,5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|3x-1,2\right|=-0,1\)
Mà \(\left|3x-1,2\right|\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\varnothing\)
c/ \(\left|x+1,3\right|+\left|x+2,4\right|=4x\)
Mà \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|x+1,3\right|\ge0\\\left|x+2,4\right|\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow4x\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1,3+x+2,4=4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+3,7=4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3,7=4x-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=3,7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1,85\)
Vậy ....
d/ \(\left|x-1,2\right|+\left|2,5-x\right|=0\)
Mà \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|x-1,2\right|\ge0\\\left|2,5-x\right|\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left|x-1,2\right|=0\\\left|2,5-x\right|=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1,2=0\\2,5-x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1,2\\x=2,5\end{matrix}\right.\) (loại)
Vậy ..
a, \(\left|2x-1,6\right|-2,3=1,4\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|2x-1,6\right|=3,7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1,6=3,7\\2x-1,6=-3,7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2,65\\x=-1,05\end{matrix}\right.\)
b,\(5,4-\left|3x-1,2\right|=5,5\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|3x-1,2\right|=-0,1\) (vô lí)
Vì \(\left|x\right|\ge0\) mà \(\left|3x-1,2\right|< 0\)
Vậy, không có giá trị của x thỏa mãn.
c, \(\left|x+1,3\right|+\left|x+2,4\right|=4x\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|x+1,3\right|\ge0\\\left|x+2,4\right|\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow4x\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1,3+x+2,4=4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+x+1,3+2,4=4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+3,7=4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-4x=-3,7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x=-3,7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3,7}{2}\)
d, \(\left|x-1,2\right|+\left|2,5-x\right|=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|x-1,2\right|\ge0\\\left|2,5-x\right|\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left|x-1,2\right|=0\\\left|2,5-x\right|=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1,2=0\\2,5-x=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1,2\\x=2,5\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) Ta có: \(\left|2x-1\right|=\left|2x+3\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=2x+3\left(loại\right)\\2x-1=-2x-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow2x+2x=-3+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=-2\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)

A) \(\frac{7}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+10\right)}+\frac{11}{\left(x+10\right)\left(x+21\right)}+\frac{13}{\left(x+21\right)\left(x+34\right)}\)
\(=\frac{\left(x+10\right)-\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+10\right)}+\frac{\left(x+21\right)-\left(x+10\right)}{\left(x+10\right)\left(x+21\right)}+\frac{\left(x+34\right)-\left(x+21\right)}{\left(x+21\right)\left(x+34\right)}\)
\(=\frac{1}{x+3}-\frac{1}{x+10}+\frac{1}{x+10}-\frac{1}{x+21}+\frac{1}{x+21}-\frac{1}{x+34}\)
\(=\frac{1}{x+3}-\frac{1}{x+34}\)
\(=\frac{\left(x+34\right)-\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+34\right)}\)\(=\frac{x}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+34\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+34\right)-\left(x+3\right)=x\)
\(\Rightarrow x=31\)
Vậy, x = 31
Bạn áp dụng: \(\frac{k}{x\cdot\left(x+k\right)}=\frac{1}{x}-\frac{1}{x+k}\) với \(x,k\inℝ;x\ne0;x\ne-k\)
Chứng minh: \(\frac{1}{x}-\frac{1}{x+k}=\frac{x+k}{x\left(x+k\right)}-\frac{x}{x\left(x+k\right)}=\frac{x+k-x}{x\left(x+k\right)}=\frac{k}{x\left(x+k\right)}\)

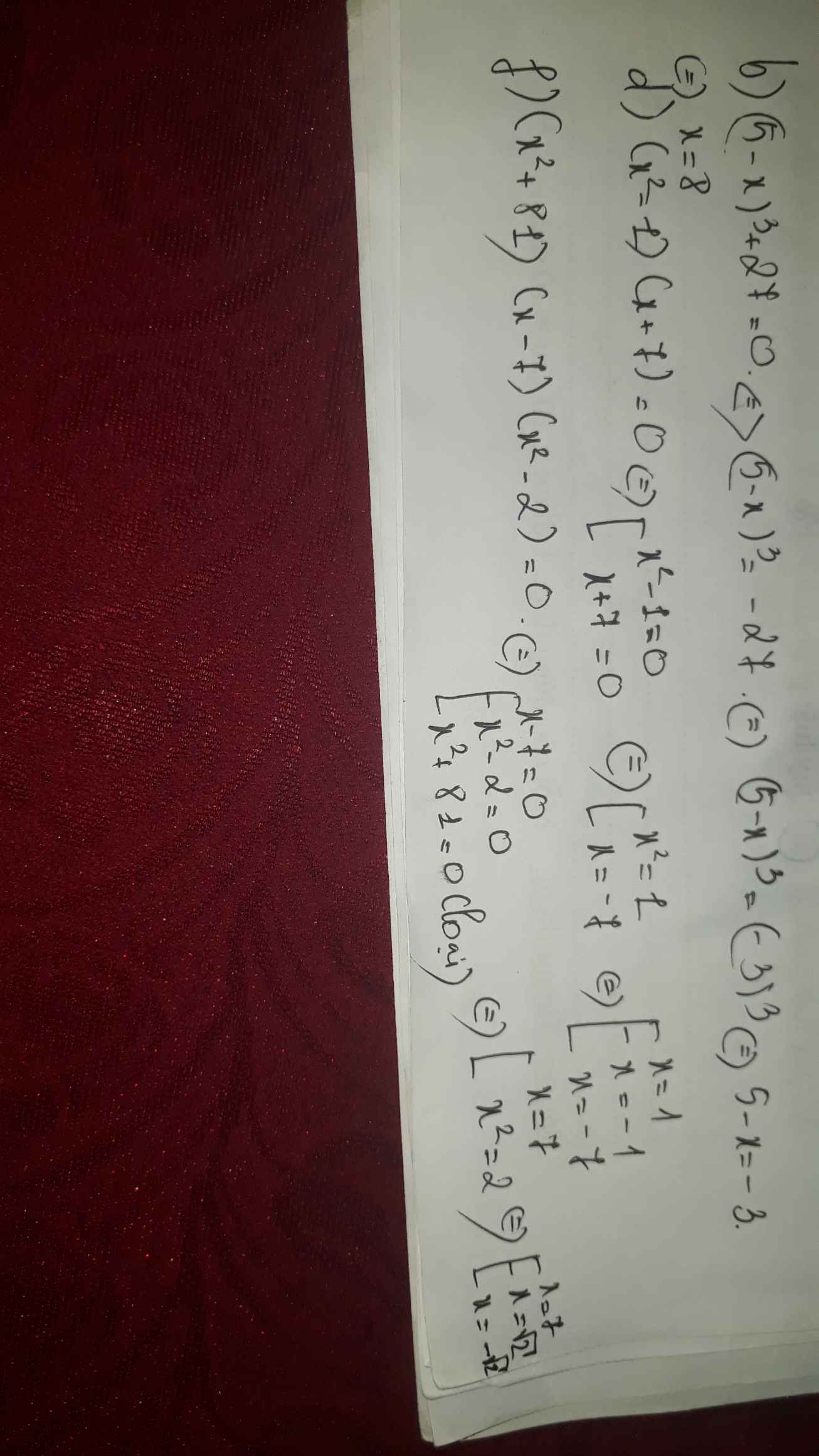
a) \(\left|x\left(x-7\right)\right|=x\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x\left(x-7\right)=x\\x\left(x-7\right)=-x\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-7=1\\x-7=-1\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x=8\\x=6\end{cases}}}\)
b) \(\left|x-1,1\right|+\left|x+1,2\right|+\left|x+1,3\right|+\left|x+1,4\right|=5x\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1,1+x+1,2+x+1,3+x+1,4=5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+2,8=5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2,8\)
\(a.\)\(\left|x.\left(x-7\right)\right|=x\)( Đk: \(x\ge0\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x.\left(x-7\right)=x\\x.\left(x-7\right)=-x\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-7=x:x\\x-7=-x:x\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-7=1\\x-7=-1\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1+7\\x=-1+7\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=8\\x=6\end{cases}}\)
\(b.\)\(\left|x-1,1\right|+\left|x+1,2\right|+\left|x+1,3\right|+\left|x+1,4\right|=5x\)( Đk: \(5x\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\ge0\))
\(\Rightarrow x-1,1+x+1,2+x+1,3+x+1,4=5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+x+x+x\right)+\left(-1,1+1,2+1,3+1,4\right)=5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+2,8=5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2,8=5x-4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2,8\)
\(c.\)\(7^{x+2}+2.7^{x-1}=345\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7^{x-1}.7^{x+3}+2.7^{x-1}=345\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7^{x-1}.\left(7^{x+3}+2\right)=345\)
\(......................\)
Đến đây mk ko bt làm nữa, tự lm nhé !