
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a, | x + 1,3 | = 3,3
TH1 : x + 1,3 = 3,3
x = 3,3 - 1,3
x = 2
TH2 : x + 1,3 = -3,3
x = -3,3 - 1,3
x = -4,6

Mình làm rồi nhớ chọn Đúng đấy :
a) |2,5 - x| = 1,3
=> hoặc 2,5 - x = 1,3 hoặc 2,5 - x = -1,3
=> hoặc x = 1,2 hoặc x = 3,8
a,
Ta co :
|2,5-x|=1,3
Ta thấy đây trên có 2 trườg hợp
suy ra :|2,5-x|=-+1,3
TH1:
2,5-x=-1,3
x = 2,5 - (-1,3)
x = 3,8
TH2:
2,5-x=1,3
x = 2,5-1,3
x = 1,2
Vậy :s=1,2 và 3,8
b,
Ta co :
16-|x-0,2|=0
|x-0,2| =16-0
|x-0,2| = 16
Ta thay day tren co 2 t/h
suy ra : |x-0,2|=-+16
TH1:
x-0,2=-16
x = -16 + 0,2
x = -15,8
TH2:
x-0,2=16
x = 16 + 0,2
x = 16,2
Vậy s=16,2 và -15,8

Ta có : |2,5 - x| = 1,3
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2,5-x=1,3\\2,5-x=-1,3\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2,5-1,3\\x=2,5+1,3\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1,2\\x=3,8\end{cases}}\)
b) Ta có : 1,6 - |x - 0,2| = 0
=> |x - 0,2| = 1,6
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-0,2=1,6\\x-0,2=-1,6\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1,6+0,2\\x=-1,6+0,2\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1,8\\x=-1,4\end{cases}}\)
c) Ta có : \(\left|x-1,5\right|+\left|2,5-x\right|\ge\left|x-1,5+2,5-x\right|\forall x\)
\(\left|x-1,5\right|+\left|2,5-x\right|\ge\left|x-1,5+2,5-x\right|=1\forall x\)
Vậy sai đề : D
a, Th1: X = 2,5 - 1,3 = 1,2
TH2: X = -2,5 - 1,3 = -3,8
b, và c, bạn cx làm 2 trường hợp tương tự như vậy

c: Ta có: \(\left|\dfrac{1}{2}x-2\right|-\left|x+3\right|=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|\dfrac{1}{2}x-2\right|=\left|x+3\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{2}x-2=x+3\\\dfrac{1}{2}x-2=-x-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\cdot\dfrac{-1}{2}=5\\x\cdot\dfrac{3}{2}=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-10\\x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a./2.5-x/=1,3 hay /5/2-x/=13/10. => 5/2-x= 13/10 hoặc -13/10
* 5/2-x=13/10 => x=6/5 * 5/2-x= -13/10 => x=19/5
b giải tương tự
c./x-1,5/+/2,5-x/=0
vì /x-1,5/> hoặc =0, /2,5-x/> hoặc =0
=> x-1,5=0 và 2,5-x=0
* x-1,5=0 => x=1,5 2,5-x=0 => x= 2,5
minh cũng làm tương tự như bạn Tiên nha
k tui nha
thanks

c) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|x-1,5\right|\ge0\forall x\in Q\\\left|2,5-x\right|\ge0\forall x\in Q\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|x-1,5\right|+\left|2,5-x\right|\ge0\forall x\in Q\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|x-1,5\right|=0\\\left|2,5-x\right|=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1,5\\x=2,5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x=\left\{{}\begin{matrix}1,5\\2,5\end{matrix}\right.\).
e) \(\left(x-2\right)^2=1\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=\sqrt{1}\\x-2=-\sqrt{1}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\).
Mấy câu kia dễ rồi.
sửa lại ý c của N.Anh
Áp dụng bđt \(\left|a\right|+\left|b\right|\ge\left|a+b\right|\) có:
\(\left|x-1,5\right|+\left|2,5-x\right|\ge\left|x-1,5+2,5-x\right|=1\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|x-1,5\right|+\left|2,5-x\right|\ge1>0\)
mà theo đề thì \(\left|x-1,5\right|+\left|2,5-x\right|=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) k có gt \(x\) nào tm yêu cầu đề bài


a) | 2,5 - x | = 1,3
=> 2,5 - x = 1,3 hoặc 2,5 - x = -1,3
Hay: x = 1,3 + 2,5 hoặc x = (-1,3) + 2,5
=> x = 3,8 hoặc x = 1,2
b) 1,6 - | x - 0,2 | = 0
| x - 0,2 | = 1,6 - 0 = 1,6
=> x - 0,2 = 1,6 hoặc x - 0,2 = -1,6
Hay: x = 1,6 + 0,2 hoặc x = (-1,6) + 0,2
=> x = 1,8 hoặc x = -1,4
c) | x - 1,5 | + | 2,5 - x | = 0
Vì giá trị tuyệt đối luôn > hoặc = 0
=> | x - 1,5 | = 0 và | 2,5 - x | = 0
=> x - 1,5 = 0 và 2,5 - x = 0
=> x = 1,5 và x = 2,5
Mà 1,5 khác 2,5
=> Không thỏa mãn x sao cho | x - 1,5 | + | 2,5 - x | = 0
x + x : 0,2 = 1,35
x * 1 + x * 5 = 1,35
x * ( 1 + 5 ) = 1,35
x * 6 = 1,35
x = 1,35 : 6
x = 0,225
hok tốt nha ^_^

a.\(\Rightarrow\begin{cases}2,5-x=1,3\\2,5-x=-1,3\end{cases}\)\(\Rightarrow\begin{cases}x=1,2\\x=3,8\end{cases}\)
b.\(\Rightarrow\begin{cases}x-1,5=0\\2,5-x=0\end{cases}\)\(\Rightarrow\begin{cases}x=1,5\\x=2,5\end{cases}\)
c.\(\left|x-0,2\right|=1,6\)
\(\Rightarrow\begin{cases}x-0,2=1,6\\x-0,2=-1,6\end{cases}\)\(\Rightarrow\begin{cases}x=1,8\\x=-1,4\end{cases}\)
tick cho mk nhé![]()
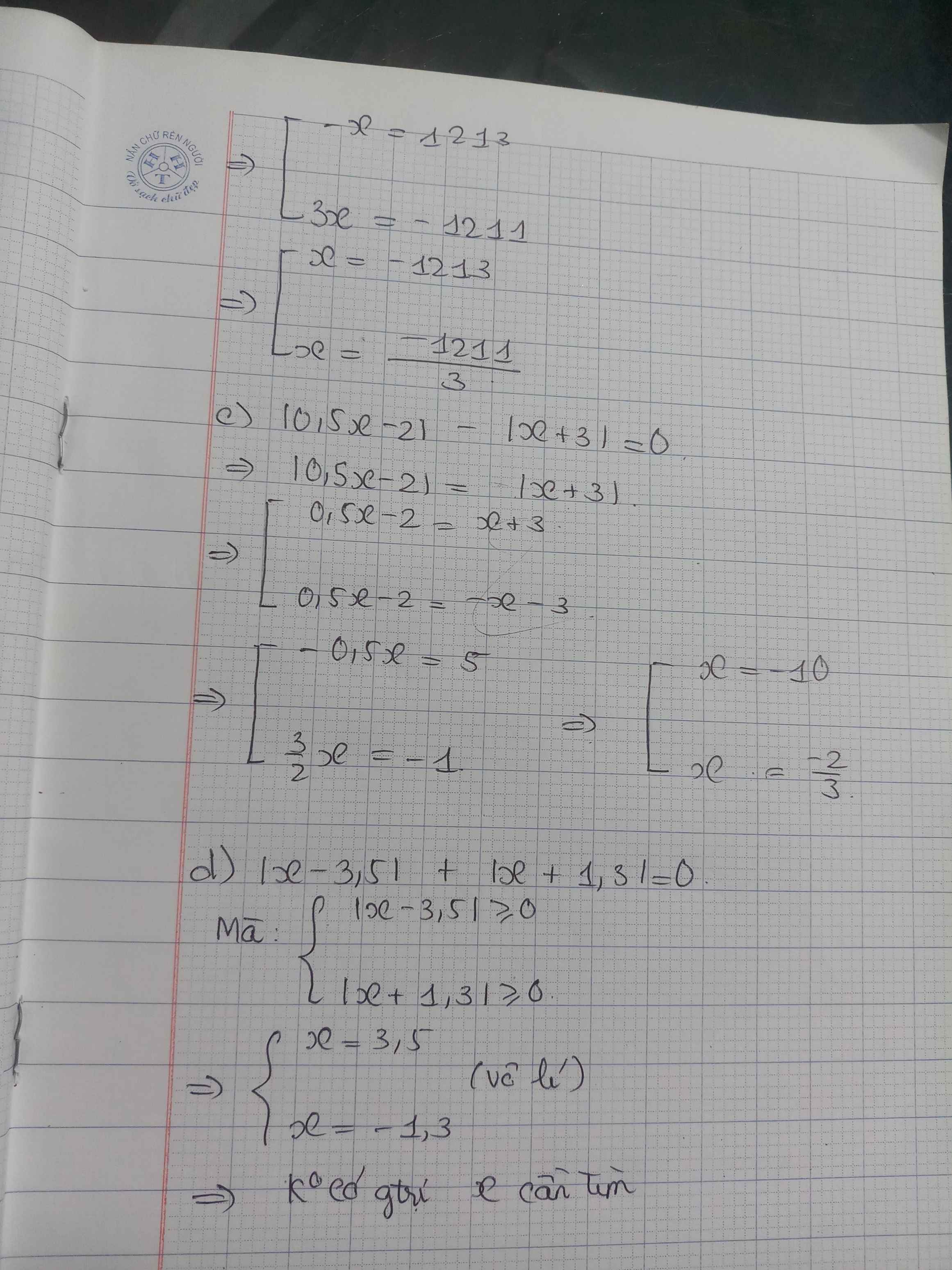
Giải:
a) \(\left|x\right|=1,3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1,3\\x=-1,3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...
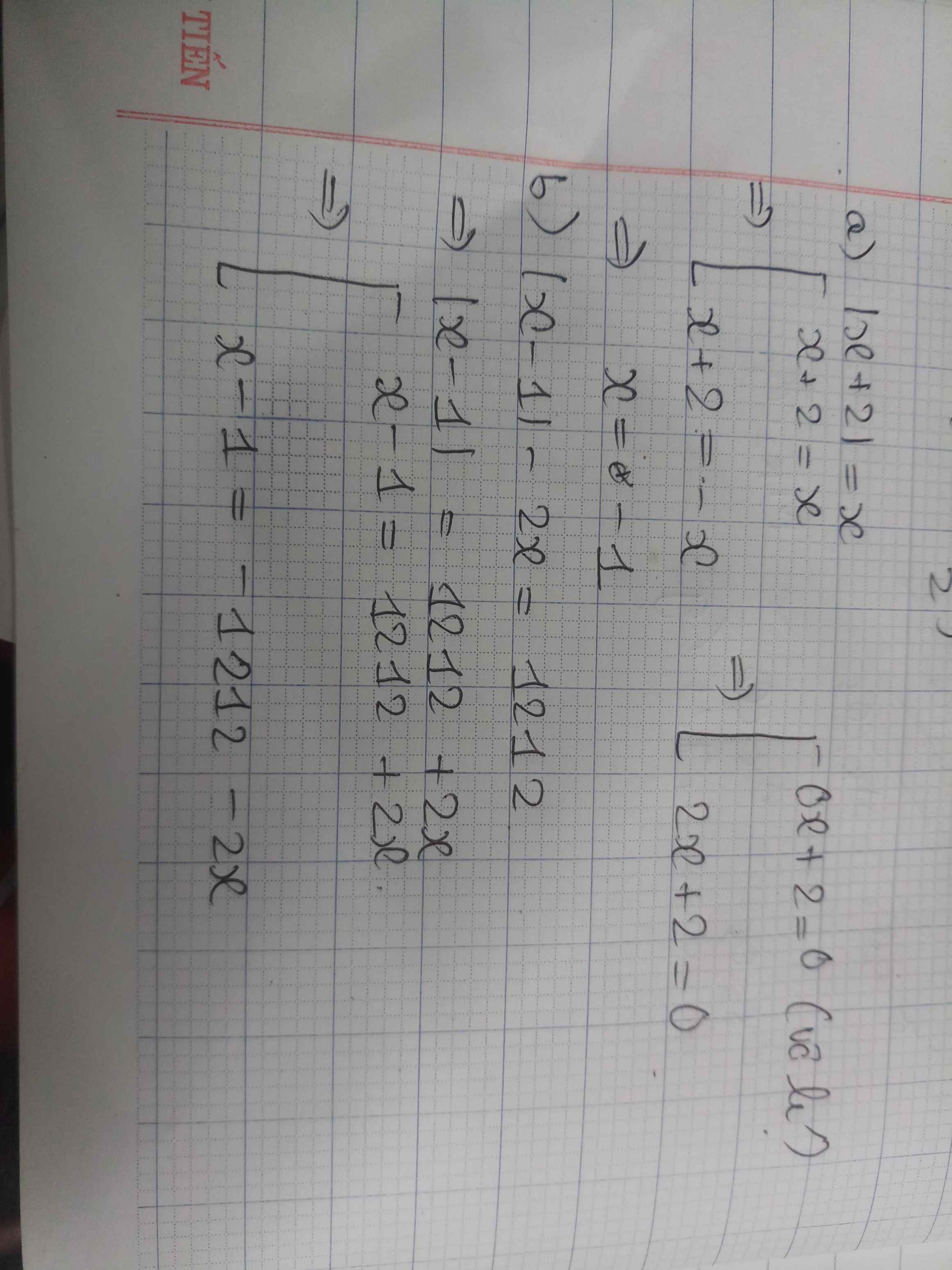
b) \(\left|x+1,3\right|=3,3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1,3=3,3\\x+1,3=-3,3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-4,6\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...
c) \(\left|5,6-x\right|=4,6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5,6-x=4,6\\5,6-x=-4,6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=10,2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...
d) \(\left|3x-5\right|+\left|x-2\right|=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-5=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{3}\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=> Phương trình vô nghiệm
Vậy ...
* Trả lời:
\(a.\left|x\right|=1,3\)
\(\Rightarrow x=1,3\) hoặc \(x=-1,3\)
Vậy \(x=\pm1,3\)
\(b.\left|x+1,3\right|=3,3\)
\(\Rightarrow x+1,3=3,3\) hoặc \(x+1,3=-3,3\)
\(\Rightarrow x=3,3-1,3\) | \(x=-3,3-1,3\)
\(\Rightarrow x=2\) | \(x=-4,6\)
Vậy \(x=2\) ; \(x=-4,6\)
\(c.\left|5,6-x\right|=4,6\)
\(\Rightarrow5,6-x=4,6\) hoặc \(5,6-x=-4,6\)
\(\Rightarrow-x=4,6-5,6\) | \(-x=-4,6-5,6\)
\(\Rightarrow-x=-1\) | \(-x=-10,2\)
\(\Rightarrow x=1\) | \(x=10,2\)
Vậy \(x=1\) ; \(x=10,2\)
\(d.\left|3x-5\right|+\left|x-2\right|=0\)
Lý luận: giá trị tuyệt đối luôn lớn hơn hoặc bằng 0
Nên \(\left|3x-5\right|+\left|x-2\right|\ne0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Không có giá trị \(x\)