
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(a)7x-21=0.\\ \Leftrightarrow x=3.\)
\(b)3x-5=2x+7.\\ \Leftrightarrow x=12.\)
\(c)6x+18=0.\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-3.\\ d)5x+2=4x-1.\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-3.\)
Bài 1:
a: 7x-21=0
=>7x=21
hay x=3
b: 3x-5=2x+7
=>3x-2x=7+5
=>x=12
c: 6x+18=0
=>6x=-18
hay x=-3
d: 5x+2=4x-1
=>5x-4x=-1-2
=>x=-3

do tam giác ABC có góc A=90\(^o\)=>\(\Delta ABC\) vuông tại A
\(\Delta ABH\sim\Delta CBA\left(g.g\right)\)( vì góc B chung, góc AHB=góc BAC)
\(=>\dfrac{AB}{BC}=\dfrac{BH}{BA}=>AB^2=BH.BC\)(1)
b,dựa vào (1)\(=>AB=\sqrt{BH.BC}=\sqrt{BH\left(BH+HC\right)}=\sqrt{4.\left(4+9\right)}=2\sqrt{13}cm\)
theo pytago\(=>AC=\sqrt{BC^2-AB^2}=\sqrt{13^2-\left(2\sqrt{13}\right)^2}=3\sqrt{13}cm\)
c,theo tính chất phan giác=>\(\dfrac{AB}{BC}=\dfrac{AD}{DC}=>\dfrac{AD}{DC}=\dfrac{2}{3}\)\(=>DC=\dfrac{3}{2}AD\)
có: \(AD+DC=AC=>AD+\dfrac{3}{2}AD=3\sqrt{13}=>AD=\dfrac{6\sqrt{13}}{5}cm\)
\(=>S\left(\Delta DBA\right)=\dfrac{AB.AD}{2}=15,6cm^2\)
có: tam giac BDA đồng dạng tam giác BEH(g.g)(do góc B1=góc B2, góc A=góc H=90 độ)
=>góc E2= góc D1
mà góc E2=góc E1(đối đỉnh)=>góc D1=góc E1=>tam giác AED cân tại A
=>AE=AD=\(\dfrac{6\sqrt{13}}{5}cm\),
theo pytago=>AH=\(\sqrt{AB^2-BH^2}=\sqrt{ \left(2\sqrt{13}\right)^2-4^2}=6cm\)
=>EH=AH-AE=\(6-\dfrac{6\sqrt{13}}{5}cm\)
=>\(S\left(\Delta EBH\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}BH.EH\) rồi tự tính ra rồi lập tỉ số 2 S tam giác (mỏi tay)

11)\(\dfrac{3x+1}{x-5}+\dfrac{2x}{x-5}=\dfrac{3x+2x+1}{x-5}=\dfrac{5x+1}{x-5}\)
12)\(\dfrac{4-x^2}{x-3}+\dfrac{2}{x^2-9}=\dfrac{4-x^2}{x-3}+\dfrac{2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{\left(4-x^2\right)\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\dfrac{2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{2+\left(2-x\right)\left(2+x\right)\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
13)
\(\dfrac{3}{4x-2}+\dfrac{2x}{4x^2-1}=\dfrac{3}{2\left(2x-1\right)}+\dfrac{2x}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}=\dfrac{3\left(2x+1\right)}{2\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}+\dfrac{2.2x}{2\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}=\dfrac{6x+3+4x}{2\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}=\dfrac{10x+3}{2\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}\)
14)
\(\dfrac{2x+1}{2x-4}+\dfrac{5}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{2x+1}{2\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{5}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{\left(2x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}{2\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\dfrac{5.2}{2\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{2x^2+5x+12}{2\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)

Cách 1: \(5x^2-60x-5600=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-12x-1120=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-40x+28x-1120=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-40\right)+28\left(x-40\right)=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-40\right)\left(x+28\right)=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-40=0\\x+28=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=40\\x=-28\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=40\\x=-28\end{cases}}\)
Cách 2: \(5x^2-60x-5600=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-12x-1120=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x.6+6^2-1156=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)^2-34^2=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6-34\right)\left(x-6+34\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-40\right)\left(x+28\right)=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-40=0\\x+28=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=40\\x=-28\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=40\\x=-28\end{cases}}\)



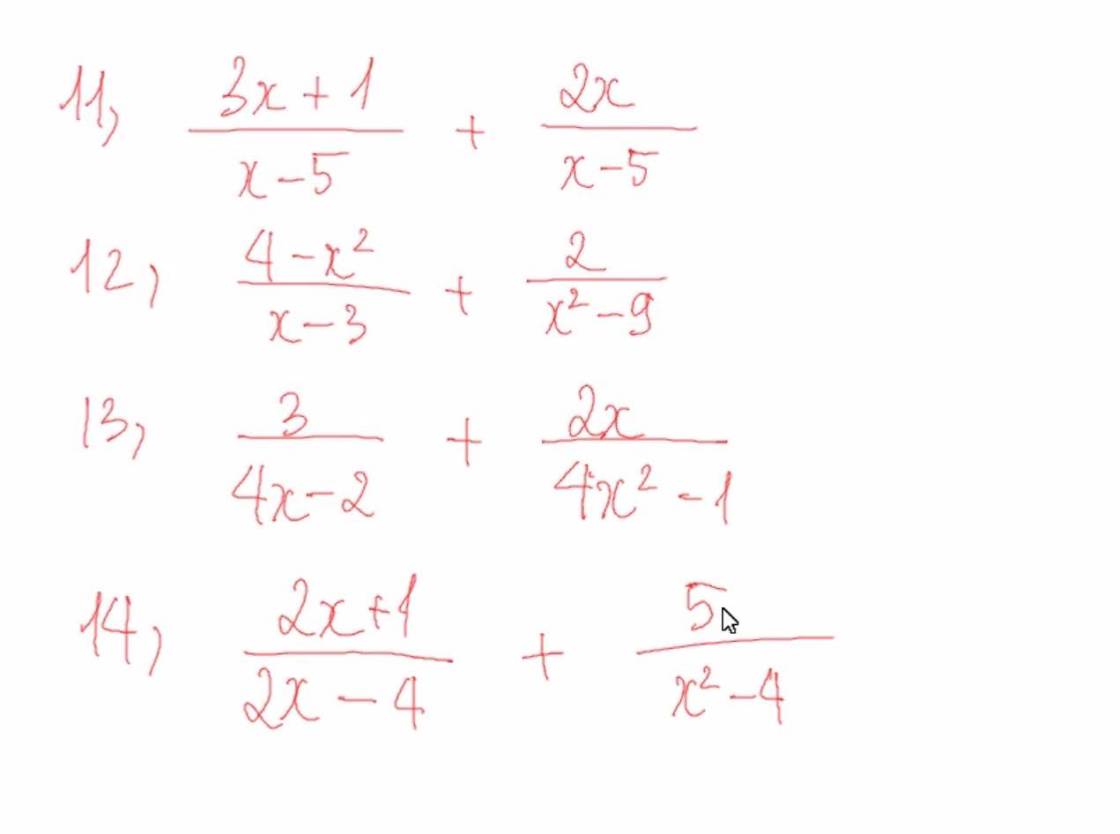
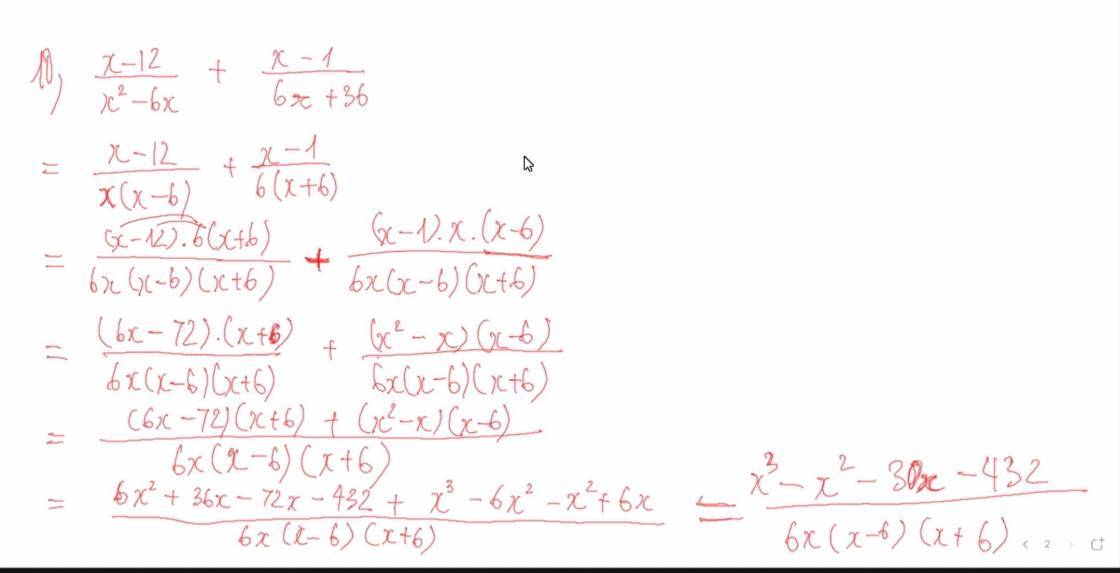
a: Xét tứ giác OAMD có
OA//MD
OD//AM
Do đó: OAMD là hình bình hành
mà \(\widehat{AOD}=90^0\)
nên OAMD là hình chữ nhật