Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


f: Ta có: \(\sqrt{2-x}=\sqrt{x^2-2x+4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+4=2-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\varnothing\)

\(1,\\ a,=\dfrac{12\left(3+\sqrt{3}\right)}{6}=2\left(3+\sqrt{3}\right)\\ b,=\dfrac{8\left(\sqrt{5}-2\right)}{1}=8\left(\sqrt{5}-2\right)\\ c,=\dfrac{14\left(\sqrt{10}-\sqrt{3}\right)}{7}=2\left(\sqrt{10}-\sqrt{3}\right)\)

4: Ta có: \(\sqrt{3+2\sqrt{2}}+\sqrt{6-4\sqrt{2}}\)
\(=\sqrt{2}+1+2-\sqrt{2}\)
=3
5: Ta có: \(2+\sqrt{17-4\sqrt{9}+4\sqrt{5}}\)
\(=2+\sqrt{5+4\sqrt{5}}\)
6: Ta có: \(2\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{18-8\sqrt{2}}\)
\(=2\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{2}+4-\sqrt{2}\)
\(=4+2\sqrt{3}\)


a) (d) cắt trục hoành tại điểm có hoành độ bằng 2
\(\Rightarrow\) tọa độ điểm đó là \(\left(2;0\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow0=2a-3\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{3}{2}\Rightarrow\left(d\right):y=\dfrac{3}{2}x-3\)
b) Vì (d) song song với đồ thị của hàm \(y=2x+1\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2\\-3\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow a=2\Rightarrow\left(d\right):y=2x-3\)
c) Gọi A là giao điểm của (d) và (d')
\(\Rightarrow x_A=1\Rightarrow y_A=2+3=5\Rightarrow A\left(1;5\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow5=a-3\Rightarrow a=8\Rightarrow\left(d\right):y=8x-3\)

a) Thay a=3 vào (d), ta được:
y=3x+b
Vì (d): y=3x+b cắt trục hoành tại điểm có hoành độ bằng 2 nên
Thay x=2 và y=0 vào (d), ta được:
\(3\cdot2+b=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow b=-6\)
Vậy: (d): y=3x-6
b) Thay a=2 vào (d), ta được:
y=2x+b
Thay x=1 và y=6 vào (d), ta được:
\(b+2\cdot1=6\)
hay b=4
Vậy: (d): y=2x+4

a) Ta có: \(\sqrt{12+2\sqrt{35}}-\sqrt{12-2\sqrt{35}}\)
\(=\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{5}\)
\(=2\sqrt{5}\)
b) Ta có: \(\left(\dfrac{5+\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{5}+1}+2\right)\left(\dfrac{5-\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{5}-1}-2\right)\)
\(=\left(\sqrt{5}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{5}-2\right)\)
=1
c) Ta có: \(\dfrac{7\sqrt{2}+2\sqrt{7}}{\sqrt{14}}-\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{2}}\)
\(=\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{2}\)
\(=2\sqrt{2}\)

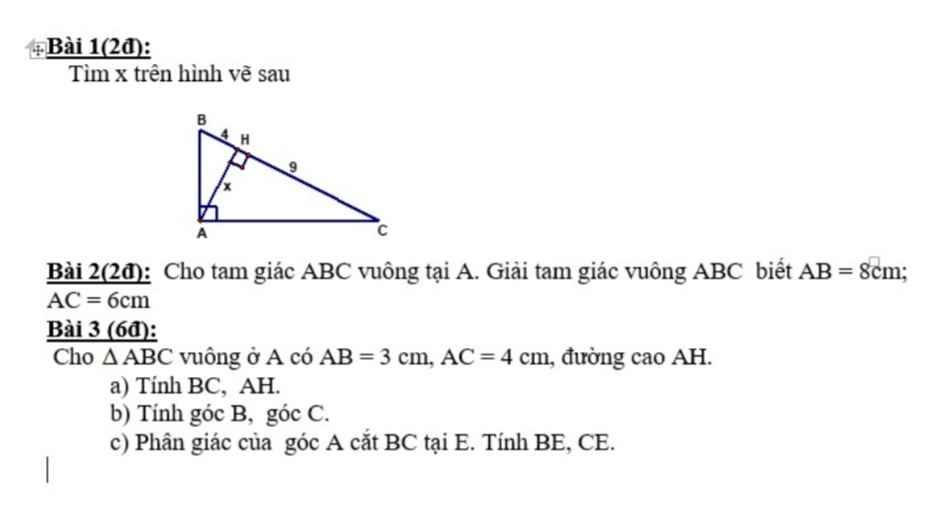
Bài 1:
Áp dụng HTL trong tam giác vuông:
$AH^2=BH.CH$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2=4.9=36$
$\Rightarrow x=6$ (do $x>0$)
Bài 2:
Áp dụng định lý Pitago:
$BC=\sqrt{AB^2+AC^2}=\sqrt{6^2+8^2}=10$ (cm)
$\sin B=\frac{AC}{BC}=\frac{6}{10}=\frac{3}{5}$
$\Rightarrow \widehat{B}=36,87^0$
$\widehat{C}=90^0-\widehat{B}=90^0-36,87^0=53,13^0$