
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 8:
b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(-x+3=3x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x=-4\)
hay x=1
Thay x=1 vào (d), ta được:
y=-1+3=2


Bài 4:
a: Xét tứ giác OBAC có
\(\widehat{OBA}+\widehat{OCA}=180^0\)
Do đó: OBAC là tứ giác nội tiếp
hay O,B,A,C cùng thuộc 1 đường tròn
Bài 5:
\(\sqrt{x+2021}-y^3=\sqrt{y+2021}-x^3\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x+2021}-\sqrt{y+2021}\right)+\left(x^3-y^3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-y}{\sqrt{x+2021}+\sqrt{y+2021}}+\left(x-y\right)\left(x^2+xy+y^2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-y\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x+2021}+\sqrt{y+2021}}+x^2+xy+y^2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-y=0\\\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x+2021}+\sqrt{y+2021}}+x^2+xy+y^2=0\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Dễ thấy \(\left(1\right)>0\) với mọi x,y
Do đó \(x-y=0\) hay \(x=y\)
\(\Leftrightarrow M=x^2+2x^2-2x^2+2x+2022=x^2+2x+1+2021\\ \Leftrightarrow M=\left(x+1\right)^2+2021\ge2021\)
Dấu \("="\Leftrightarrow x=y=-1\)

4.
a, \(A=\sqrt[3]{15\sqrt{3}+26}=\sqrt[3]{\left(\sqrt{3}+2\right)^3}=\sqrt{3}+2\)
b, \(B=\sqrt[3]{5+2\sqrt{13}}+\sqrt[3]{5-2\sqrt{13}}\)
\(\Rightarrow2B=\sqrt[3]{40+16\sqrt{13}}+\sqrt[3]{40-16\sqrt{13}}\)
\(=\sqrt[3]{\left(\sqrt{13}+1\right)^3}+\sqrt[3]{\left(\sqrt{13}-1\right)^3}\)
\(=\sqrt{13}+1+\sqrt{13}-1=2\sqrt{13}\)
\(\Rightarrow B=\sqrt{13}\)
c, \(C=\sqrt[3]{182-\sqrt{33125}}+\sqrt[3]{182+\sqrt{33125}}\)
\(\Rightarrow C^3=364+3\sqrt[3]{182-\sqrt{33125}}.\sqrt[3]{182+\sqrt{33125}}\left(\sqrt[3]{182-\sqrt{33125}}+\sqrt[3]{182+\sqrt{33125}}\right)\)
\(=364-3C\)
\(\Rightarrow C^3+3C-364=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow C=7\)

Câu 1:
1) Ta có: \(2x^2+5x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+6x-x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
2) Để hàm số đồng biến trên R thì m-1>0
hay m>1
Câu 1:
3) Ta có: P=a+b-2ab
\(=1+\sqrt{2}+1-\sqrt{2}-2\left(1+\sqrt{2}\right)\left(1-\sqrt{2}\right)\)
\(=2-2\cdot\left(-1\right)=4\)

a: Xét (O) có
ΔABC nội tiếp đường tròn
AB là đường kính
Do đó: ΔABC vuông tại C

\(\frac{4x}{1-x^2}=\sqrt{5}\) ĐKXĐ : x khác 1
\(\Rightarrow4x=\sqrt{5}\left(1-x^2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=\sqrt{5}-x^2\sqrt{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\sqrt{5}-4x-\sqrt{5}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\sqrt{5}-5x+x-\sqrt{5}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\sqrt{5}\left(x-\sqrt{5}\right)+\left(x-\sqrt{5}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\sqrt{5}\right)\left(x\sqrt{5}+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-\sqrt{5}=0\\x\sqrt{5}=-1\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\sqrt{5}\left(tmđk\right)\\x=-\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}}=-\frac{\sqrt{5}}{5}\left(tmđk\right)\end{cases}}}\)
\(4x=\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{5}x^2\)
\(\Rightarrow4x+\sqrt{5}x^2=\sqrt{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(4+\sqrt{5}x\right)=\sqrt{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow x.\sqrt{5}\left(\frac{4}{\sqrt{5}}+x\right)=\sqrt{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow x.\left(\frac{4}{\sqrt{5}}+x\right)=1\)
Với x = 1 \(\Rightarrow\frac{4}{\sqrt{5}}+x=1\Rightarrow x=1-\frac{4}{\sqrt{5}}=\frac{5-4\sqrt{5}}{5}\)
Với x = -1\(\Rightarrow\frac{4}{\sqrt{5}}+x=-1\Rightarrow x=-1-\frac{4}{\sqrt{5}}=-\frac{5+4\sqrt{5}}{5}\)
ko có x thỏa mãn

Câu 15:
Gọi $x_0$ là nghiệm chung của 2 pt thì:
\(\left\{\begin{matrix}
x_0^2+ax_0+1=0\\
x_0^2-x_0-a=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow x_0(a+1)+(a+1)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (x_0+1)(a+1)=0\)
Hiển nhiên $a\neq -1$ để 2 PT không trùng nhau. Do đó $x_0=-1$ là nghiệm chung của 2 PT
Thay vào:
$(-1)^2+a(-1)+1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 1-a+1=0\Rightarrow a=2$
Đáp án C.
Câu 16:
D sai. Trong tam giác vuông tại $A$ là $ABC$, $\cos (90^0-\widehat{B})=\cos \widehat{C}$ và không có cơ sở để khẳng định $\cos \widehat{C}=\sin \widehat{C}$
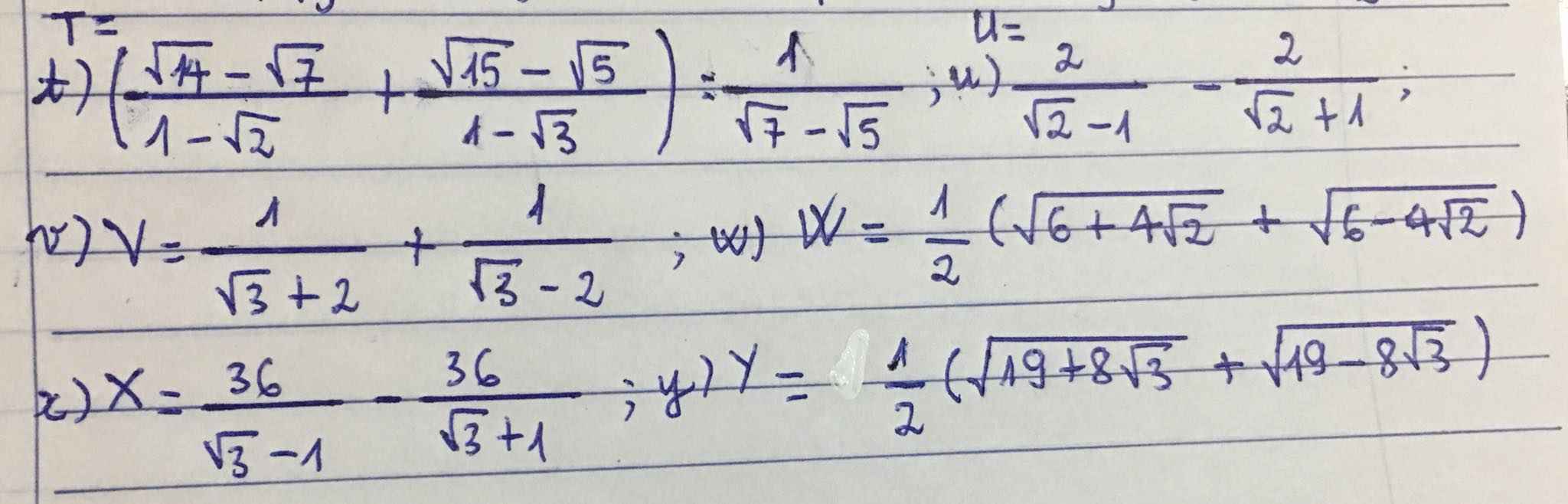

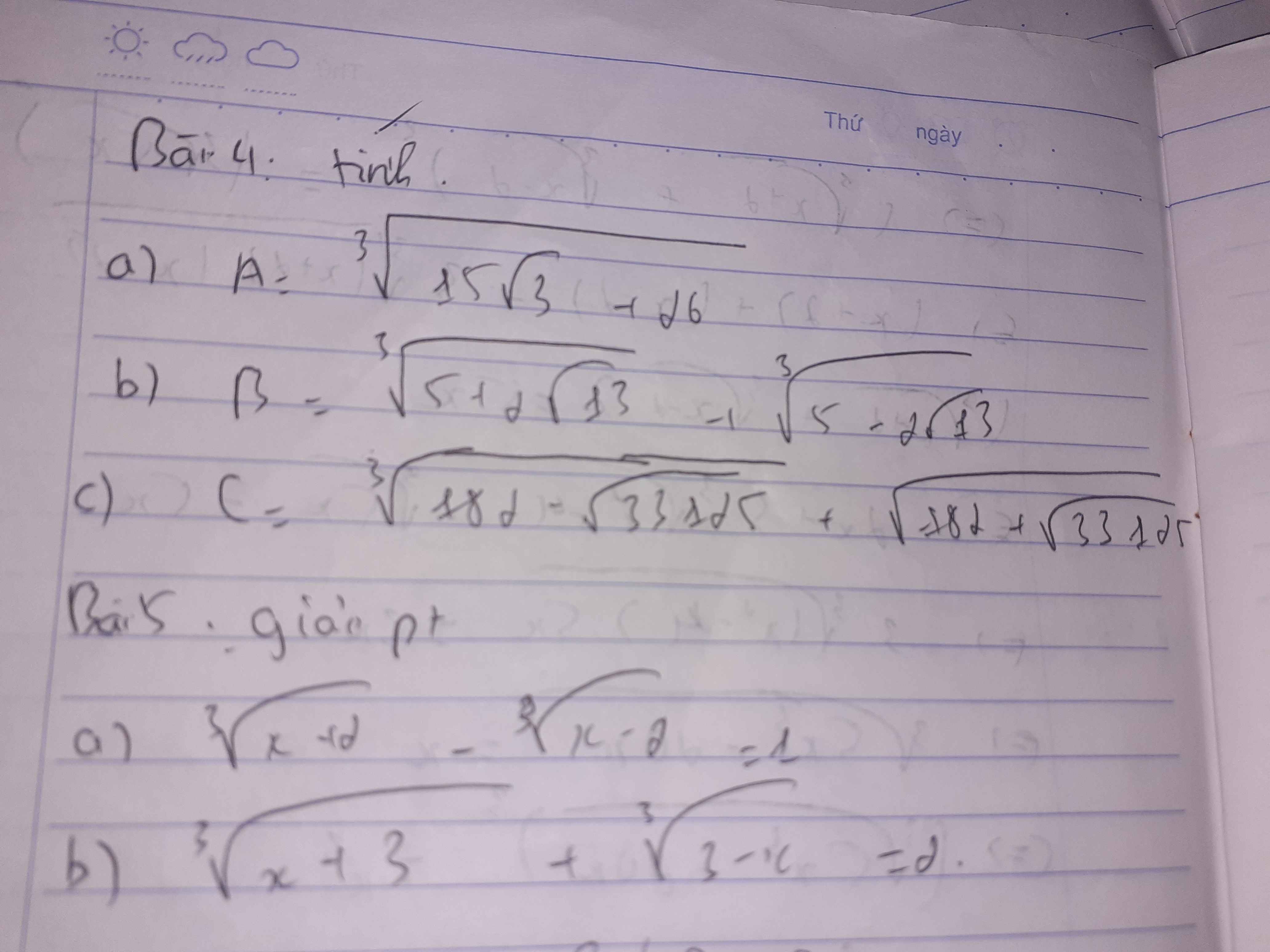



\(W=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\sqrt{\left(2+\sqrt{2}\right)^2}+\sqrt{\left(2-\sqrt{2}\right)^2}\right)\\ W=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(2+\sqrt{2}+2-\sqrt{2}\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot4=2\\ Y=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\sqrt{\left(4+\sqrt{3}\right)^2}+\sqrt{\left(4-\sqrt{3}\right)^2}\right)\\ Y=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(4+\sqrt{3}+4-\sqrt{3}\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot8=4\)