
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 4:
\(A=2x^2+3x-10x-15-2x^2+6x+x+7=-8\\ B=x^3-y^3-5+2y^3-x^3-y^3=-5\\ C=x^3-3x^2+3x-1-x^3-3x^2-3x-1-6x^2+6=4\)


a: Xét tứ giác BFCE có
D là trung điểm của BC
D là trung điểm của FE
Do dó: BFCE là hình bình hành
b: Xét tứ giác ABFE có
AB//FE
AB=FE
Do đó: ABFE là hình bình hành
mà \(\widehat{FAB}=90^0\)
nên ABFE là hình chữ nhật

a, Vì D,M là trung điểm AB,AC nên DM là đtb tg ABC
Do đó \(DM=\dfrac{1}{2}BC=\dfrac{7}{2}\left(cm\right)\) và DM//BC

- Đây có phải là toán lớp 8 nữa không vậy :)? Mình học toán nâng cao nhưng chưa bao giờ thấy dạng này :).
b1:
do x;y thuộc số nguyên N và x,y\(\ge\)2
=>\(-4xy+1< +7x-7y< 4xy+1\)
\(\Rightarrow4x^2y^2-4xy+1< 4x^2y^2+7x-7y< 4x^2y^2+4xy+1\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(2xy-1\right)^2< 4x^2y^2+7x-7y< \left(2xy+1\right)^2\)
mà \(4x^2y^2+7x-7y\) là số chính phương và 1<2xy-1<2xy-1 nên ta có:
\(4x^2y^2+7x-7y-\left(2xy\right)^2\Leftrightarrow x=y\)

Bài 1:
1) \(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
2) \(\Rightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(5x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
3) \(\Rightarrow\left(4x-3\right)\left(7-12x\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{4}\\x=\dfrac{7}{12}\end{matrix}\right.\)
4) \(\Rightarrow x^3+8-x^3+25x=-17\)
\(\Rightarrow25x=-25\Rightarrow x=-1\)
5) \(\Rightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x+2\right)-2\left(3x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x+2-6x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\left(-3x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bài 3:
c: \(x^2+7x+12=\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)\)
d: \(x^3-7x-6\)
\(=x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)-6\left(x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x-6\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)\)

a: \(A=\dfrac{2x^2+x^2-1-2x^2+2x+1}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x+2}{x+1}\)
b: Ta có: \(x^2-2x=0\)
=>x=2
Thay x=2 vào A, ta được:
\(A=\dfrac{2+2}{2+1}=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
(a)
\(A=\dfrac{2x}{x+1}+\dfrac{x-1}{x}-\dfrac{2x^2-2x-1}{x^2+x}\\ =\dfrac{2x}{x+1}+\dfrac{x-1}{x}-\dfrac{2x^2-2x-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x^2}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{x^2-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{2x^2-2x-1}{x\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+x^2-1-2x^2+2x+1}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2+2x+1}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x+1}{x}\)
(b)
\(x^2-2x=0\\ x\left(x-2\right)=0\)
=>x=0 hoặc x=2 mà đk x khác 0 nên thay x=2 vào bt A , ta có:
\(\dfrac{x+1}{x}=\dfrac{2+1}{2}=\dfrac{3}{2}\)

\(a,=x^2+x+4x+4=\left(x+1\right)\left(x+4\right)\\ b,=x^2+2x-3x-6=\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)\\ c,=x^2-2x-3x+6=\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)\\ d,=3\left(x^2-2x+5x-10\right)=3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+5\right)\\ e,=-3x^2+6x-x+2=\left(x-2\right)\left(1-3x\right)\\ f,=x^2-x-6x+6=\left(x-1\right)\left(x-6\right)\\ h,=4\left(x^2-3x-6x+18\right)=4\left(x-3\right)\left(x-6\right)\\ i,=3\left(3x^2-3x-8x+5\right)=3\left(x-1\right)\left(3x-8\right)\\ k,=-\left(2x^2+x+4x+2\right)=-\left(2x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\\ l,=x^2-2xy-5xy+10y^2=\left(x-2y\right)\left(x-5y\right)\\ m,=x^2-xy-2xy+2y^2=\left(x-y\right)\left(x-2y\right)\\ n,=x^2+xy-3xy-3y^2=\left(x+y\right)\left(x-3y\right)\)




 giúp em bài 1 dạng 3 vói em, em cần gấp lắm, em cảm ơn ạ
giúp em bài 1 dạng 3 vói em, em cần gấp lắm, em cảm ơn ạ
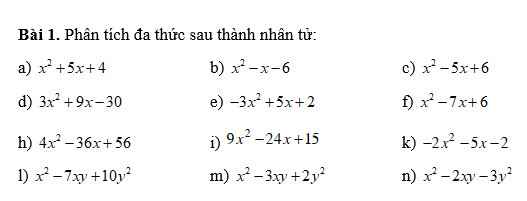
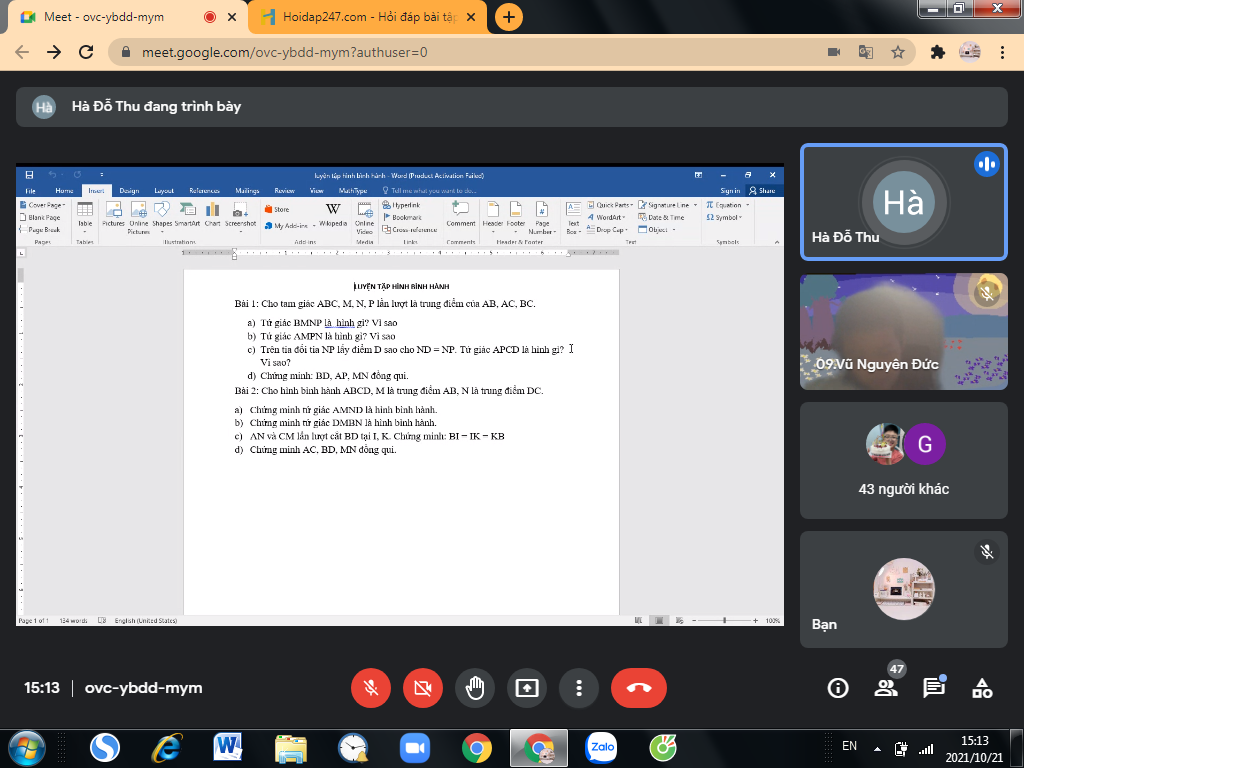
Bài 1:
a: Xét ΔABC có
M là trung điểm của AB
N là trung điểm của AC
Do đó: MN là đường trung bình của ΔABC
Suy ra: MN//BC và \(MN=\dfrac{BC}{2}\)
hay MN//BP và MN=BP
Xét tứ giác BMNP có
MN//BP
MN=BP
Do đó: BMNP là hình bình hành