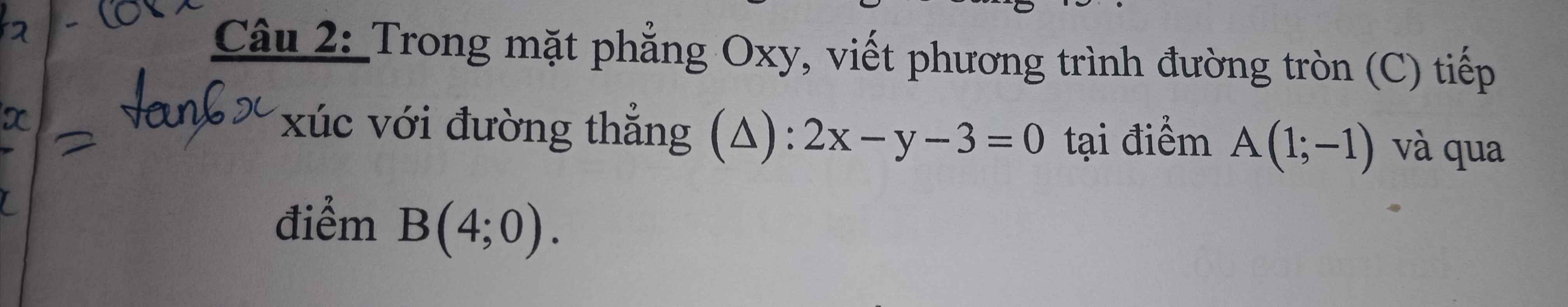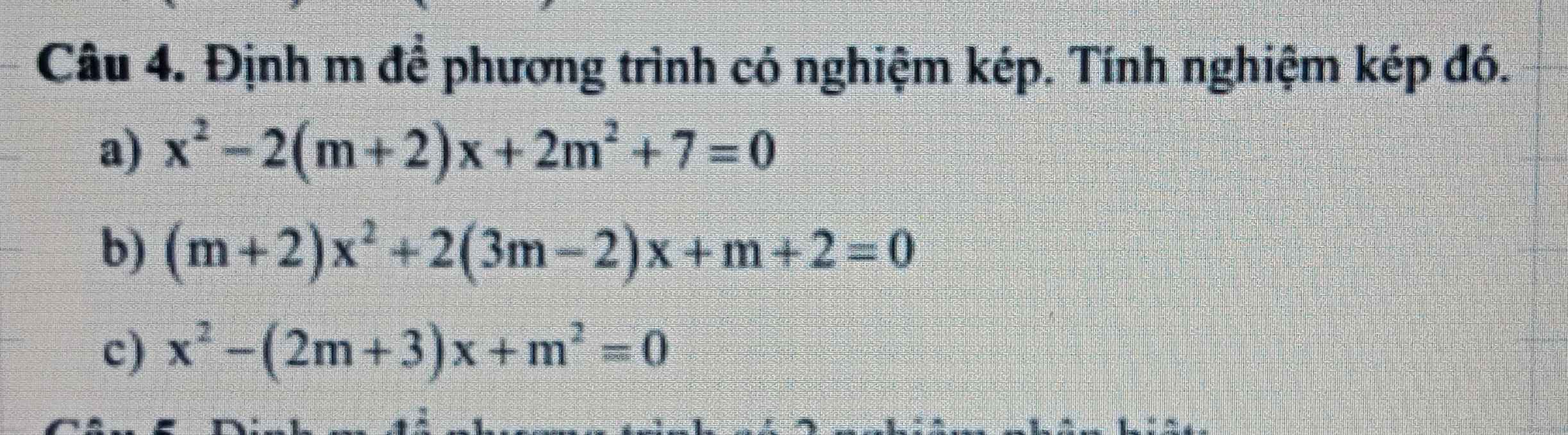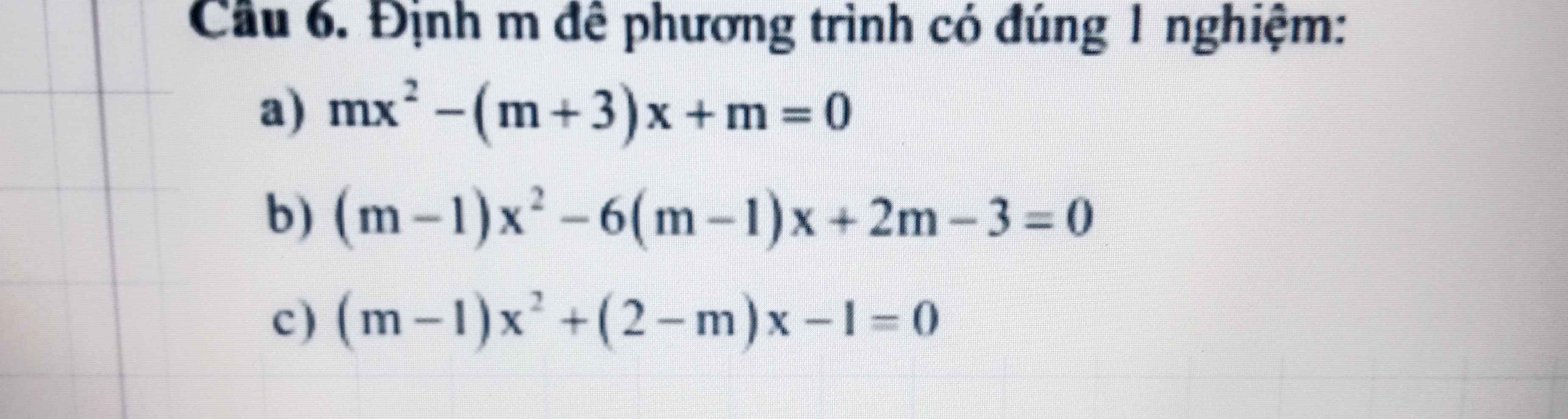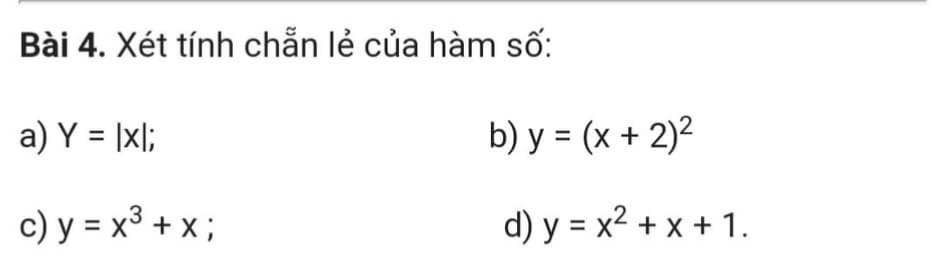Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.






\(a,\Leftrightarrow\Delta=4\left(m+4\right)^2-4\left(m-4\right)\left(m-1\right)>0\\ \Leftrightarrow4m^2+32m+64-4m^2+20m+16>0\\ \Leftrightarrow52m+80>0\Leftrightarrow m>-\dfrac{20}{13}\\ b,\Leftrightarrow\Delta=\left(5m+6\right)^2-12\left(2m+3\right)\left(m+1\right)>0\\ \Leftrightarrow25m^2+60m+36-24m^2-60m-36>0\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2>0\\ \Leftrightarrow m\ne0\\ c,\Leftrightarrow\Delta=4\left(m+3\right)^2-4\left(m-5\right)\left(m-2\right)>0\\ \Leftrightarrow4m^2+24m+36-4m^2+28m-40>0\\ \Leftrightarrow52m-4>0\Leftrightarrow m>\dfrac{1}{13}\)

\(a,\Leftrightarrow\Delta=\left(m+3\right)^2-4m^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(m+3-2m\right)\left(m+3+2m\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3-m=0\\3m+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=3\\m=-1\end{matrix}\right.\\ b,\Leftrightarrow\Delta=36\left(m-1\right)^2-4\left(2m-3\right)\left(m-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow36m^2-72m+36-8m^2+20m-12=0\\ \Leftrightarrow28m^2-52m+24=0\\ \Leftrightarrow7m^2-13m+6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=1\\m=\dfrac{6}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\\ c,\Leftrightarrow\Delta=\left(2-m\right)^2+4\left(m-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2-4m+4+4m-4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2=0\Leftrightarrow m=0\)

a: Để phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất thì m<>2
Để phương trình vô nghiệm thì m=2
Để phương trình có vô số nghiệm thì m\(\in\varnothing\)

Lời giải:
a. TXĐ: $\mathbb{R}$
Với $x\in\mathbb{R}$ thì $-x\in\mathbb{R}$
$f(x)=|x|=|-x|=f(-x)$
$\Rightarrow $ hàm chẵn
b. TXĐ: $\mathbb{R}$
Với $1\in\mathbb{R}$ thì $-1\in\mathbb{R}$
$f(1)=9; -f(1)=-9; f(-1)=1$
$\Rightarrow f(1)\neq f(-1); -f(1)\neq f(-1)$ nên hàm không chẵn không lẻ.
c.
TXĐ: $\mathbb{R}$
Với $x\in\mathbb{R}$ thì $-x\in\mathbb{R}$
$f(-x)=(-x)^3+(-x)=-(x^3+x)=-f(x)$ nên hàm lẻ
d.
TXĐ: $\mathbb{R}$
Với $1\in\mathbb{R}$ thì $-1\in\mathbb{R}$
$f(1)=3; f(-1)=1$
$\Rightarrow f(1)\neq f(-1); -f(1)\neq f(-1)$
Do đó hàm không chẵn không lẻ.