
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.






Câu 69:
Ta có:
\(f(x)+f(y)=1\Leftrightarrow \frac{9^x}{9^x+m^2}+\frac{9^y}{9^y+m^2}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{9^x}{9^x+m^2}=1-\frac{9^y}{9^y+m^2}=\frac{m^2}{9^y+m^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 9^{x+y}=m^4\Leftrightarrow (3^{x+y}-m^2)(3^{x+y}+m^2)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow 3^{x+y}=m^2\) (do \(3^{x+y}>0; m^2\geq 0\Rightarrow 3^{x+y}+m^2>0\) ) (1)
------------------------------------------------
Tiếp theo: \(e^{x+y}\leq e(x+y)\Leftrightarrow e^{x+y-1}\leq x+y\)
Đặt \(x+y=k\Rightarrow e^{k-1}\leq k\Leftrightarrow e^{k-1}-k\leq 0\)
Đặt \(e^{k-1}-k=f(k)\Rightarrow f(k)\leq 0(*)\)
Có: \(f'(k)=e^{k-1}-1=0\Leftrightarrow k=1\)
Lập bảng biến thiên ta thấy rằng \(f(k)_{\min}=f(1)=0\) hay \(f(k)\geq 0(**)\)
Từ \((1);(2)\Rightarrow f(k)=0\) hay \(k=1\Leftrightarrow x+y=1\)
Thay vào (1) ta có \(m^2=3\Leftrightarrow m=\pm \sqrt{3}\)
Vậy có 2 giá trị m thỏa mãn. đáp án D
Câu 70:
Để hai pt lần lượt có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì
\(\Delta _1=\Delta_2=b^2-20a>0\Leftrightarrow b^2> 20a\) (1)
Khi đó, áp dụng hệ thức Viete ta có:
Đối với PT 1: \(\ln x_1+\ln x_2=\frac{-b}{a}\Leftrightarrow \ln (x_1x_2)=\frac{-b}{a}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1x_2=e^{\frac{-b}{a}}\)
Đối với PT 2: \(\log x_1+\log x_2=\frac{-b}{5}\Leftrightarrow \log (x_1x_2)=\frac{-b}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_3x_4=10^{\frac{-b}{5}}\)
Vì \(x_1x_2> x_3x_4\Leftrightarrow e^{\frac{-b}{a}}>10^{\frac{-b}{5}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 10^{\frac{-b}{a\ln 10}}> 10^{\frac{-b}{5}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{-b}{a\ln 10}>\frac{-b}{5}\Leftrightarrow a>\frac{5}{\ln 10}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a> 2,71...\Rightarrow a\geq 3\) (vì a nguyên dương)
Theo (1) ta có: \(b^2>20a\geq 60\Rightarrow b\geq 8\) (do b nguyên dương)
Vậy \(2a+3b\geq 2.3+3.8\Leftrightarrow 2a+3b\geq 30\)
Đáp án A

Lời giải:
\(\log_2^2x+\log_2(\frac{x}{4})=0\)
$\Leftrightarrow \log_2^2x+\log_2x+\log_2(\frac{1}{4})=0$
$\Leftrightarrow \log_2^2x+\log_2x-2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (\log_2x-1)(\log_2x+2)=0$
\Leftrightarrow \log_2x=1$ hoặc $\log_2x=-2$
$\Leftrightarrow x=2$ hoặc $x=\frac{1}{4}$
Tích các nghiệm: $2.\frac{1}{4}=\frac{1}{2}$
Đáp án D

ĐKXĐ:
1.
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-1>0\\log_2\left(x-1\right)-1>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>1\\x-1>2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow x>3\)
2.
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-1>0\\x-1\ne1\\\dfrac{x}{2-x^2}>0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>1\\x\ne2\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< -\sqrt{2}\\0< x< \sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow1< x< \sqrt{2}\)









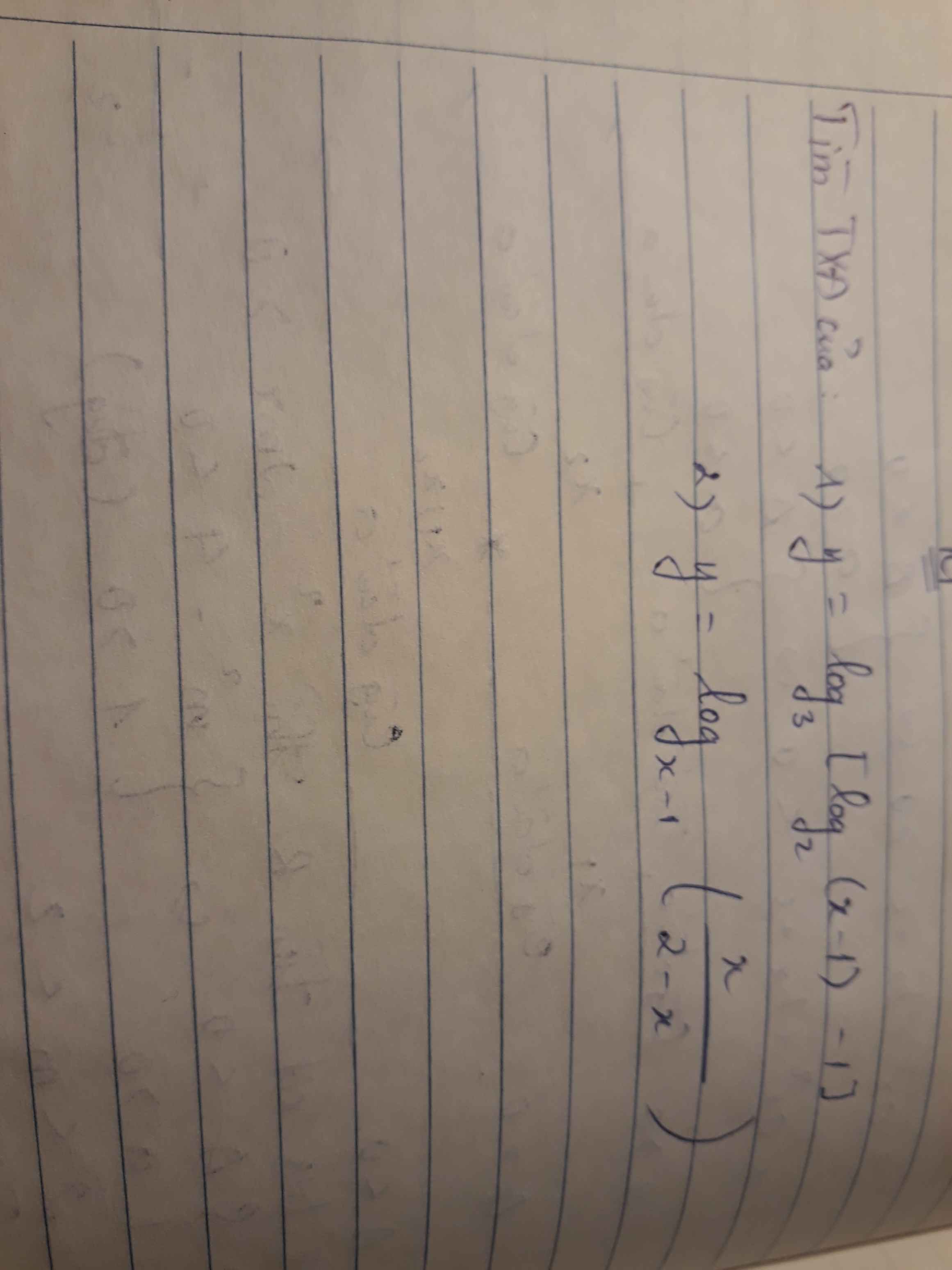
\(\int\left(\dfrac{7}{cos^2x}+cosx-3^x+2\right)dx=7tanx+sinx-\dfrac{3^x}{ln3}+2x+C\)
dạ e cảm ơn