Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Dễ nhận thấy pt này có một nghiệm là 1 nên ta sẽ tạo nhân tử là x-1
Ta có: \(2x^4+4x^3-7x^2-5x+6=0\)
<=> \(\left(2x^4-2x^3\right)+\left(6x^3-6x^2\right)-\left(x^2-x\right)-\left(6x-6\right)=0\)
<=> \(2x^3\left(x-1\right)+6x^2\left(x-1\right)-x\left(x-1\right)-6\left(x-1\right)=0\)
<=> \(\left(x-1\right)\left(2x^3+6x^2-x-6\right)=0\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\2x^3+6x-x-6=0\end{cases}}\)
Bạn có thể giải pt 2x3+6x-x-6=0 bằng pp Cardano nha, cm dài lắm
Ta tách được \(2x^4+4x^3-7x^2-5x+6=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2x^3+6x-x-6\right)=0\)
Vậy pt có 1 nghiệm x= 1.
Ta giải pt bậc ba theo công thức Cardano:
\(2x^3+6x^2-x-6=0\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow x^3+3x^2-\frac{1}{2}x-3=0\)
Đặt \(x=y-1\Rightarrow y^3-\frac{7}{2}y-\frac{1}{2}=0\left(2\right)\)
\(\Delta=27\left(\frac{-1}{2}\right)^2-4\left(\frac{7}{2}\right)^3=-\frac{659}{4}< 0\)
Vậy pt (2) có 3 nghiệm phân biệt thuộc khoảng \(\left(-\frac{\sqrt{42}}{3};\frac{\sqrt{42}}{3}\right)\)
Đặt \(y=\frac{\sqrt{42}}{3}cost\left(t\in\left(0;\pi\right)\right)\). Thay vào pt(2) ta có: \(cos\left(3t\right)=\frac{3\sqrt{42}}{98}\)
Ta tìm được 3 nghiệm t thuộc khoảng \(\left(0;\pi\right)\), sau đó tìm cost rồi suy ra y và x.
Cô tìm một nghiệm để giúp em kiểm chứng nhé. Em có thể thay giá trị nghiệm để kiểm tra.
\(cos\left(3t\right)=\frac{3\sqrt{42}}{98}\Rightarrow t=\frac{arccos\left(\frac{3\sqrt{42}}{98}\right)}{3}\Rightarrow y=\frac{\sqrt{42}}{3}.cos\frac{arccos\left(\frac{3\sqrt{42}}{98}\right)}{3}\)
Vậy \(x=\frac{\sqrt{42}}{3}.cos\frac{arccos\left(\frac{3\sqrt{42}}{98}\right)}{3}-1\). Đó là một nghiệm, em có thể tìm 2 nghiệm còn lại bằng cách tương tự.

22.
ĐKXĐ: \(y\ne1\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-\dfrac{1}{y-1}=2\\2x^2+\dfrac{3}{1-y}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x^2+\dfrac{2}{1-y}=4\\2x^2+\dfrac{3}{1-y}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Trừ pt dưới cho trên:
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{1-y}=-2\)
\(\Rightarrow1-y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Thế vào \(x^2-\dfrac{1}{y-1}=2\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2=4\Rightarrow x=\pm2\)
Vậy nghiệm của hệ là \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(2;\dfrac{3}{2}\right);\left(-2;\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\)
b.
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(Hệ\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2y^2-\dfrac{10}{2x+1}=8\\2y^2-\dfrac{11}{2x+1}=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
Trừ pt trên cho dưới:
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{2x+1}=1\)
\(\Rightarrow2x+1=1\)
\(\Rightarrow x=0\)
Thế vào \(y^2-\dfrac{5}{2x+1}=4\)
\(\Rightarrow y^2=9\Rightarrow y=\pm3\)
Vậy nghiệm của hệ là \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(0;3\right);\left(0;-3\right)\)

`2x+5y=11(1)`
`2x-3y=0(2)`
Lấy (1) trừ (2)
`=>8y=11`
`<=>y=11/8`
`<=>x=(3y)/2=33/16`
a) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+5y=11\\2x-3y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}8y=11\\2x-3y=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{11}{8}\\2x=3y=3\cdot\dfrac{11}{8}=\dfrac{33}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{33}{16}\\y=\dfrac{11}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{33}{16}\\y=\dfrac{11}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x+3y=6\\2x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x+3y=6\\4x+2y=8\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-2\\2x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-2=4\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x=6\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là (x,y)=(3;-2)

Xét \(\Delta=\text{}\)\(\left(-4m\right)^2-4\left(3m^2-3\right)\)\(=4m^2+12>0\forall m\)
=> Pt luôn có hai nghiệm pb
Theo viet \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=4m\\x_1x_2=3m^2-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(P=\dfrac{2019}{\left|x_1-x_2\right|}\)\(\Leftrightarrow P^2=\dfrac{2019^2}{\left(x_1-x_2\right)^2}\)\(=\dfrac{2019^2}{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2}\)\(=\dfrac{2019^2}{16m^2-4\left(3m^2-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2019^2}{4m^2+12}\le\dfrac{2019^2}{12}\)
\(\Rightarrow P\le\dfrac{2019}{\sqrt{12}}\)
\(\Rightarrow P_{max}=\dfrac{2019\sqrt{12}}{12}\Leftrightarrow m=0\)
Vậy m=0

=>16x+9y=840 và 210/x-210/y=7/4
=>16x=840-9y và 30/x-30/y=1/4
=>x=-9/16y+52,5 và (30y-30x)=xy/4
=>xy=120y-120x
=>y(-9/16y+52,5)=120y-120(-9/16y+52,5)
=>-9/16y^2+52,5y-120y+120(-9/16y+52,5)=0
=>-9/16y^2-67,5y-67,5y+6300=0
=>y=40 hoặc y=-280
=>x=30 hoặc x=210

\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{\sqrt{x}-1}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
\(=\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{x}=2\sqrt{x}\)

\(x=\sqrt[3]{9+4\sqrt{5}}+\sqrt[3]{9-4\sqrt{5}}\)
\(\Rightarrow x^3=9+4\sqrt{5}+9-4\sqrt{5}+3\sqrt[3]{\left(9+4\sqrt[]{5}\right)\left(9-4\sqrt{5}\right)}\left(\sqrt[3]{9+4\sqrt{5}}+\sqrt[3]{9-4\sqrt{5}}\right)\)
\(=18+3\sqrt{81-80}.x=18+3x\)\(\Rightarrow x^3-3x=18\left(1\right)\)
\(y=\sqrt[3]{3+2\sqrt{2}}+\sqrt[3]{3-2\sqrt{2}}\)
\(\Rightarrow y^3=3+2\sqrt{2}+3-2\sqrt{2}+3\sqrt[3]{\left(3+2\sqrt{2}\right)\left(3-2\sqrt{2}\right)}\left(\sqrt[3]{3+2\sqrt{2}}+\sqrt[3]{3-2\sqrt{2}}\right)\)
\(=6+3\sqrt[3]{9-8}.y=6+3y\)\(\Rightarrow y^3-3y=6\left(2\right)\)
\(\left(1\right),\left(2\right)\Rightarrow P=x^3+y^3-3\left(x+y\right)+1996=x^3-3x+y^3-3y+1996\)
\(=18+6+1996=2020\)

bạn tự vẽ hình giúp mik nha
a. xét \(\Delta ADN\) và \(\Delta BAM\) có
AB=AD(gt)
\(\widehat{ADN}=\widehat{BAM}=90^o\)
DN=MA(N,M là trung điểm của cạnh DC,AD)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta ADN\sim\Delta BAM\left(c.g.c\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{DNA}=\widehat{AMB}\)
mà:\(\widehat{DNA}+\widehat{DAN}=90^o\Rightarrow\widehat{BMA}+\widehat{DAN}=90^o\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta MAI\) vuông tại I
\(\Rightarrow AI\perp MI\) hay \(MB\perp AN\)
b.ta có M là trung điểm của AD\(\Rightarrow AM=\dfrac{1}{2}AD=\sqrt{5}\)
trong \(\Delta MAB\) vuông tại A có
\(MB=\sqrt{AM^2+AB^2}=\sqrt{\sqrt{5^2}+\left(2\sqrt{5}\right)^2}=5\)
\(AM^2=MB.MI\Rightarrow MI=\dfrac{AM^2}{MB}=\dfrac{\sqrt{5^2}}{5^5}=0,2\)
\(AI.MB=AM.AB\Rightarrow AI=\dfrac{AM.AB}{MB}=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}.2\sqrt{5}}{5}\)=2
c.IB=MB-MI=5-0,2=4,8
\(S_{\Delta AIB}=\dfrac{AI.IB}{2}=\)\(\dfrac{2.4,8}{2}=4,8\)
\(S_{\Delta ADN}=\dfrac{AD.DN}{2}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{5}.\sqrt{5}}{2}=5\)
\(S_{\Delta ABCD}=\left(2\sqrt{5}\right)^2=20\)
\(S_{BINC}=S_{ABCD}-S_{\Delta AIB}-S_{\Delta DAN}\)=20-4,8-5=10,2



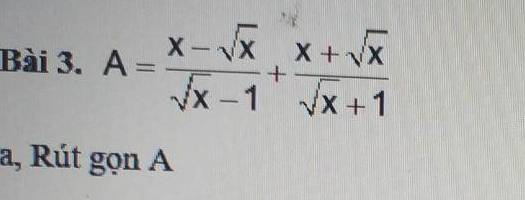
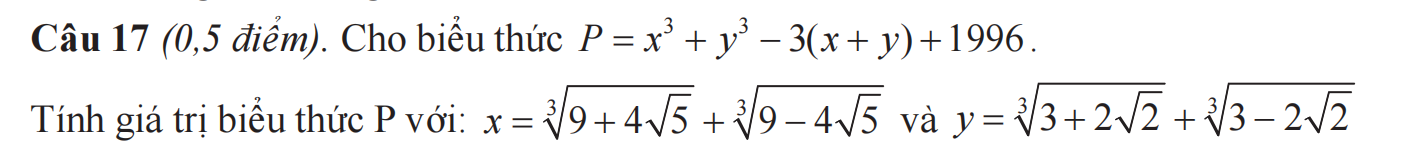 cảm ơn
cảm ơn 
`x^2+\sqrt{x^2+20}=22`
`<=>x^2+20+\sqrt{x^2+20}-42=0`
Đặt `\sqrt{x^2+20}=t` `(t > 0)` khi đó ta có ptr:
`t^2+t-42=0`
`<=>t^2+7t-6t-42=0`
`<=>t(t+7)-6(t+7)=0`
`<=>(t+7)(t-6)=0`
`<=>` $\left[\begin{matrix} t=-7\text{ (ko t/m)}\\ t=6\text{ (t/m)}\end{matrix}\right.$
`@ t=6=>\sqrt{x^2+20}=6`
`<=>x^2+20=36`
`<=>x^2=16`
`<=>x=+-4`
Vậy `S={+-4}`