
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


ĐK \(x\ge0\)
Đặt \(x=a,x+1=b\)
\(PT\Leftrightarrow a^4+b^4=\left(a+b\right)^4\)
<=> 4a3b+6a2b2+4ab3=0
<=> ab(2a2+3ab+2b2)=0
=>ab=0 (vì 2a2+3ab+2b2>0)
=>\(\orbr{\begin{cases}a=0\\b=0\end{cases}}\)<=>\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=-1\end{cases}}\)
Vậy.............................

Đặt \(\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{4x-1}}=a\)
Theo đề, ta có phương trình:
a+1/a=2
\(\Leftrightarrow a+\dfrac{1}{a}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{a^2+1-2a}{a}=0\)
=>a=1
=>\(x=\sqrt{4x-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2=4x-1\\x>=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-2\right)^2=3\\x>=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{2+\sqrt{3};2-\sqrt{3}\right\}\)

Đặt \(u=\sqrt{x+1};t=\sqrt{1-x};\text{đ}k:-1\le x\le1\)
Phương trình trở thành:
\(u+2u^2=-t^2+t+3ut\Leftrightarrow\left(u-t\right)^2+u\left(u-t\right)+\left(u-t\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(u-t\right)\left(2u-t+1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}u=t\\2u+1=t\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\sqrt{x+1}=\sqrt{1-x}\\2\sqrt{x+1}+1=\sqrt{1-x}\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\frac{-24}{25}\end{cases}}}\)
mình dùng cách khác nhé :((
\(\sqrt{x+1}+2\left(x+1\right)=x-1+\sqrt{1-x}+3\sqrt{1-x^2}\left(đk:-1\le x\le1\right)\)
\(< =>\sqrt{x+1}-1+2x+2-3=x-1+\sqrt{1-x}-1+3\sqrt{1-x^2}-3\)
\(< =>\frac{x}{\sqrt{x+1}+1}+2x-1-x+1=-\frac{x}{\sqrt{1-x}+1}+\frac{9\left(1-x^2-1\right)}{3\sqrt{1-x^2}+3}\)
\(< =>\frac{x}{\sqrt{x+1}+1}+x+\frac{x}{\sqrt{1-x}+1}+\frac{9x^2}{3\sqrt{1-x^2}+3}=0\)
\(< =>x\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{x+1}+1}+1+\frac{1}{\sqrt{1+x}+1}+\frac{9x}{3\sqrt{1-x^2}+3}\right)=0< =>x=0\)
rồi đến đây dùng đk đánh giá cái ngoặc khác 0 là ok

a) 2 x 2 − 2 x 2 + 3 x 2 − 2 x + 1 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt x 2 – 2 x = t ,
(1) trở thành : 2 t 2 + 3 t + 1 = 0 ( 2 ) .
Giải (2) :
Có a = 2 ; b = 3 ; c = 1
⇒ a – b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có nghiệm t 1 = - 1 ; t 2 = - c / a = - 1 / 2 .
+ Với t = -1 ⇒ x 2 − 2 x = − 1 ⇔ x 2 − 2 x + 1 = 0 ⇔ ( x − 1 ) 2 = 0 ⇔ x = 1
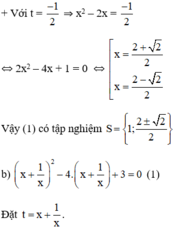
(1) trở thành: t 2 – 4 t + 3 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2):
Có a = 1; b = -4; c = 3
⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có nghiệm t 1 = 1 ; t 2 = c / a = 3 .
+ t = 1 ⇒ x + 1/x = 1 ⇔ x 2 + 1 = x ⇔ x 2 – x + 1 = 0
Có a = 1; b = -1; c = 1 ⇒ Δ = ( - 1 ) 2 – 4 . 1 . 1 = - 3 < 0
Phương trình vô nghiệm.
