
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 5:
a: 2x-(3-5x)=4(x+3)
=>2x-3+5x=4x+12
=>7x-3=4x+12
=>3x=15
=>x=5
b: =>5/3x-2/3+x=1+5/2-3/2x
=>25/6x=25/6
=>x=1
c: 3x-2=2x-3
=>3x-2x=-3+2
=>x=-1
d: =>2u+27=4u+27
=>u=0
e: =>5-x+6=12-8x
=>-x+11=12-8x
=>7x=1
=>x=1/7
f: =>-90+12x=-45+6x
=>12x-90=6x-45
=>6x-45=0
=>x=9/2

1.\(x^2+4x+4=\left(x+2\right)^2\)
2.\(x^2-8x+16=\left(x-4\right)^2\)
3.\(\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)=x^2-25\)
4.\(x^3+12x+48x+64=\left(x+4\right)^3\)
5.\(x^3-6x^2+12x-8=\left(x-2\right)^3\)
6.\(\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)=x^3+8\)
7.\(\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+3x+9\right)=x^3-27\)
8.\(4x^4-15=\left(2x^2\right)^2-\left(\sqrt{15}\right)^2=\left(2x^2-\sqrt{15}\right)\left(2x^2+\sqrt{15}\right)\)

1) \(A=25x^2+10x+1\)
\(A=5x^2+2.5.10x+1\)
\(A=5x^2+100x+1\)
\(A=\left(5x+1\right)^2\)
Thay \(x=\dfrac{1}{5}\) vào biểu thức \(\left(5x+1\right)^2\)
\(\left(5x+1\right)^2\)
= \(\left(5.\dfrac{1}{5}+1\right)^2\)
= \(2^2=4\)
Nếu sai thì cho mình xin lỗi nhé
2) Bài này mình không biết làm

Gọi độ dài quãng đường AB là x
Theo đề, ta có phương trình:
\(\dfrac{x}{40}-\dfrac{x}{50}=\dfrac{7}{20}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\cdot\dfrac{1}{200}=\dfrac{7}{20}\)
hay x=70

a: Ta có: \(5-3x< 8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x>-3\)
hay x>-1
b: Ta có: \(\dfrac{2x-5}{4}\ge\dfrac{3-x}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(2x-5\right)\ge4\left(3-x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-15\ge12-4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow10x\ge27\)
hay \(x\ge\dfrac{27}{10}\)
c: Ta có: \(2x+5< x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-x< 7-5\)
hay x<2
d: Ta có: \(4\left(x-3\right)\ge x+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-12-x-2\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\ge14\)
hay \(x\ge\dfrac{14}{3}\)
e: Ta có: \(\dfrac{2x+2}{3}< 2+\dfrac{x-2}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+4< 12+3x-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-3x< 6-4\)
hay x<2
f: Ta có: \(x-\dfrac{5x+2}{6}>\dfrac{7-3x}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-2\left(5x+2\right)>3\left(7-3x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-4>21-9x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow11x>25\)
hay \(x>\dfrac{25}{11}\)

a: Ta có: \(2x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=3\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
b: Ta có: \(\left(2x+7\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+7=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: Ta có: \(2x+7=32-3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x=25\)
hay x=5
d: Ta có: \(\left(3x-2\right)\left(4x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-2=0\\4x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=-\dfrac{5}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
e: Ta có: \(3x-5=x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=12\)
hay x=6
f: Ta có: \(\dfrac{3}{x-2}=\dfrac{2}{x+1}\)
Suy ra: \(3x+3=2x-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-7\left(nhận\right)\)

k có j bn bè nên thật tình giúp nhau mà, đúng cho mk chứ hjhj
9x2 - 4y2 = (3x)2 - (2y)2 =(3x+2y)(3x-2y) =0
mà 3x-2y =0 => 9x2 -4y2 = 0


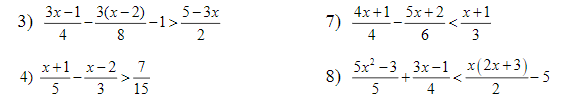

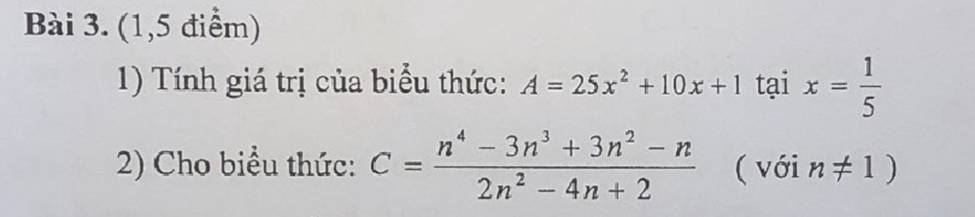 Giải dùm mình với ạ! Mình cần gấp
Giải dùm mình với ạ! Mình cần gấp





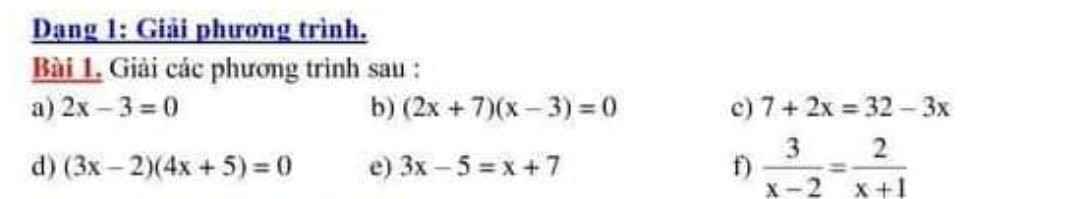

5/ \(10x+3-5x\le14x+12\)
<=>\(10x-5x-14x\le12-3\)
<=>\(-9x\le9\)
<=>\(x\ge-1\)
Vậy bất phương trình có nghiệm là \(x\ge-1\)
6/\(\left(3x-1\right)< 2x+4\)
<=>\(3x-2x< 4+1\)
<=> x<5
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là x<5