Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) ( x - 3)4 + ( x - 5)4 = 82
Đặt : x - 4 = a , ta có :
( a + 1)4 + ( a - 1)4 = 82
⇔ a4 + 4a3 + 6a2 + 4a + 1 + a4 - 4a3 + 6a2 - 4a + 1 = 82
⇔ 2a4 + 12a2 - 80 = 0
⇔ 2( a4 + 6a2 - 40) = 0
⇔ a4 - 4a2 + 10a2 - 40 = 0
⇔ a2( a2 - 4) + 10( a2 - 4) = 0
⇔ ( a2 - 4)( a2 + 10) = 0
Do : a2 + 10 > 0
⇒ a2 - 4 = 0
⇔ a = + - 2
+) Với : a = 2 , ta có :
x - 4 = 2
⇔ x = 6
+) Với : a = -2 , ta có :
x - 4 = -2
⇔ x = 2
KL.....
b) ( n - 6)( n - 5)( n - 4)( n - 3) = 5.6.7.8
⇔ ( n - 6)( n - 3)( n - 5)( n - 4) = 1680
⇔ ( n2 - 9n + 18)( n2 - 9n + 20) = 1680
Đặt : n2 - 9n + 19 = t , ta có :
( t - 1)( t + 1) = 1680
⇔ t2 - 1 = 1680
⇔ t2 - 412 = 0
⇔ ( t - 41)( t + 41) = 0
⇔ t = 41 hoặc t = - 41
+) Với : t = 41 , ta có :
n2 - 9n + 19 = 41
⇔ n2 - 9n - 22 = 0
⇔ n2 + 2n - 11n - 22 = 0
⇔ n( n + 2) - 11( n + 2) = 0
⇔ ( n + 2)( n - 11) = 0
⇔ n = - 2 hoặc n = 11
+) Với : t = -41 ( giải tương tự )
@Giáo Viên Hoc24.vn
@Giáo Viên Hoc24h
@Giáo Viên
@giáo viên chuyên
@Akai Haruma

a) 3x(x - 1) + 2(x - 1) = 0
<=> (3x + 2)(x - 1) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x+2=0\\x-1=0\end{cases}}\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{2}{3}\\x=1\end{cases}}\)
Vậy S = {-2/3; 1}
b) x2 - 1 - (x + 5)(2 - x) = 0
<=> x2 - 1 - 2x + x2 - 10 + 5x = 0
<=> 2x2 + 3x - 11 = 0
<=> 2(x2 + 3/2x + 9/16 - 97/16) = 0
<=> (x + 3/4)2 - 97/16 = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+\frac{3}{4}=\frac{\sqrt{97}}{4}\\x+\frac{3}{4}=-\frac{\sqrt{97}}{4}\end{cases}}\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{\sqrt{97}-3}{4}\\x=-\frac{\sqrt{97}-3}{4}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy S = {\(\frac{\sqrt{97}-3}{4}\); \(-\frac{\sqrt{97}-3}{4}\)
d) x(2x - 3) - 4x + 6 = 0
<=> x(2x - 3) - 2(2x - 3) = 0
<=> (x - 2)(2x - 3) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-2=0\\2x-3=0\end{cases}}\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=\frac{3}{2}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy S = {2; 3/2}
e) x3 - 1 = x(x - 1)
<=> (x - 1)(x2 + x + 1) - x(x - 1) = 0
<=> (x - 1)(x2 + x + 1 - x) = 0
<=> (x - 1)(x2 + 1) = 0
<=> x - 1 = 0
<=> x = 1
Vậy S = {1}
f) (2x - 5)2 - x2 - 4x - 4 = 0
<=> (2x - 5)2 - (x + 2)2 = 0
<=> (2x - 5 - x - 2)(2x - 5 + x + 2) = 0
<=> (x - 7)(3x - 3) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-7=0\\3x-3=0\end{cases}}\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=7\\x=1\end{cases}}\)
Vậy S = {7; 1}
h) (x - 2)(x2 + 3x - 2) - x3 + 8 = 0
<=> (x - 2)(x2 + 3x - 2) - (x- 2)(x2 + 2x + 4) = 0
<=> (x - 2)(x2 + 3x - 2 - x2 - 2x - 4) = 0
<=> (x - 2)(x - 6) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-2=0\\x-6=0\end{cases}}\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=6\end{cases}}\)
Vậy S = {2; 6}
\(a,3x\left(x-1\right)+2\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(3x.x-3x+2x-2=0\)
\(2x-2=0\)
\(2x=2\)
\(x=1\)

e: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=1\\\dfrac{3}{x}+\dfrac{4}{y}=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{x}-\dfrac{3}{y}=3\\\dfrac{3}{x}+\dfrac{4}{y}=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{-7}{y}=-2\\\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{7}{2}\\\dfrac{1}{x}=1+\dfrac{2}{7}=\dfrac{9}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=\dfrac{7}{9}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+4y=-11\\5x-4y=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6x=-10\\x+4y=-11\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-5}{3}\\y=\dfrac{-11-x}{4}=\dfrac{-11+\dfrac{5}{3}}{4}=-\dfrac{7}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-y=7\\3x+5y=-22\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6x-3y=21\\6x+15y=-66\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-18y=78\\2x-y=7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{-13}{3}\\x=\dfrac{y+7}{2}=\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) => 5x^2 - 3 = 2 hoặc 5x^2 - 3 = -2
=> 5x^2 = 5 hoặc 5x^2 = 1
b) pt <=> l(x-1)^2l = x + 2
VÌ ( x - 1 )^2 >= 0 => l( x - 1 )^2 l = ( x- 1 )^2
pt <=> x^2 - 2x + 1 = x + 2 <=>
x^2 - 3x - 1 = 0
c) l2x-5l - l2x^2 - 7x + 5 l = 0
<=> l2x-5l - l ( 2x-5)(x-1) l = 0
<=> l2x-5l ( 1 - l x - 1 l = 0
<=> l 2x - 5 l = 0 hoặc 1 - l x - 1 l = 0
d); e lập bảng xét dấu sau đó xét ba trường hợ p ra

a: Ta có: \(\sqrt{4x+20}-3\sqrt{x+5}+\dfrac{4}{3}\sqrt{9x+45}=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{x+5}-3\sqrt{x+5}+4\sqrt{x+5}=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\sqrt{x+5}=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+5=4\)
hay x=-1
b: Ta có: \(\dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt{x-1}-\dfrac{3}{2}\sqrt{9x-9}+24\sqrt{\dfrac{x-1}{64}}=-17\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt{x-1}-\dfrac{9}{2}\sqrt{x-1}+3\sqrt{x-1}=-17\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-1}=17\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=289\)
hay x=290

a, \(2\left(x+3\right)\left(x-4\right)=\left(2x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)-27\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2-4x+3x-12\right)=2x^2+4x-x-2-27\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-2x-24=2x^2+3x-29\Leftrightarrow-5x+5=0\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
b, \(\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)-x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=26\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-8-x\left(x^2-9\right)=26\Leftrightarrow-8+9x=26\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x=18\Leftrightarrow x=2\)

1.
ĐKXĐ: \(x< 5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\dfrac{42}{5-x}}-3+\sqrt{\dfrac{60}{7-x}}-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\dfrac{42}{5-x}-9}{\sqrt{\dfrac{42}{5-x}}+3}+\dfrac{\dfrac{60}{7-x}-9}{\sqrt{\dfrac{60}{7-x}}+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{9x-3}{\left(5-x\right)\left(\sqrt{\dfrac{42}{5-x}}+3\right)}+\dfrac{9x-3}{\left(7-x\right)\left(\sqrt{\dfrac{60}{7-x}}+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(9x-3\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{\left(5-x\right)\left(\sqrt{\dfrac{42}{5-x}}+3\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(7-x\right)\left(\sqrt{\dfrac{60}{7-x}}+3\right)}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
b.
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge2\)
\(\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-1\right)}+\sqrt{x+3}=\sqrt{x-2}+\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-1\right)}-\sqrt{x-2}+\sqrt{x+3}-\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-2}\left(\sqrt{x-1}-1\right)-\sqrt{x+3}\left(\sqrt{x-1}-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x-1}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x-2}-\sqrt{x+3}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x-1}-1=0\\\sqrt{x-2}-\sqrt{x+3}=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=1\\x-2=x+3\left(vn\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x=2\)
a)
5 x 2 − 3 x + 1 = 2 x + 11 ⇔ 5 x 2 − 3 x + 1 − 2 x − 11 = 0 ⇔ 5 x 2 − 5 x − 10 = 0
Có a = 5; b = -5; c = -10 ⇒ a - b + c = 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm: x 1 = - 1 v à x 2 = - c / a = 2 .
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-1; 2}.
⇔ 6 x 2 − 20 x = 5 ( x + 5 ) ⇔ 6 x 2 − 20 x − 5 x − 25 = 0 ⇔ 6 x 2 − 25 x − 25 = 0
Có a = 6; b = -25; c = -25
⇒ Δ = ( - 25 ) 2 – 4 . 6 . ( - 25 ) = 1225 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm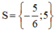
⇔ x 2 = 10 − 2 x ⇔ x 2 + 2 x − 10 = 0
Có a = 1; b = 2; c = -10 ⇒ Δ ’ = 1 2 – 1 . ( - 10 ) = 11 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm
Cả hai nghiệm đều thỏa mãn điều kiện xác định.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm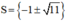
⇔ ( x + 0 , 5 ) ⋅ ( 3 x − 1 ) = 7 x + 2 ⇔ 3 x 2 + 1 , 5 x − x − 0 , 5 = 7 x + 2 ⇔ 3 x 2 − 6 , 5 x − 2 , 5 = 0
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm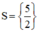
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm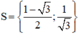
Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm