Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Từ giả thiết ta suy ra
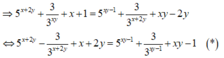
Xét hàm số f ( t ) = 5 t - 1 3 t + t với t ∈ ℝ , f ' ( t ) = 5 t . ln 5 + 3 - t . ln 3 + 1 > 0 ; ∀ t ∈ ℝ
Suy ra y= f( t) là hàm số đồng biến trên R mà từ ( * ) suy ra
f (x+ 2y) =f( xy-1) hay x+ 2y= xy-1
![]()
với x>0 suy ra y>1.
Khi đó
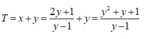
Xét hàm số
f ( y ) = y 2 + y + 1 y - 1 t r ê n 1 ; + ∞ f ' y = y 2 - 2 y - 2 y - 1 2 = 0 ⇔ y = ± 1 + 3 f 1 + 3 = 3 + 2 3 ; lim y → 1 f ( y ) = lim y → + ∞ f ( y ) = + ∞
Do đó, giá trị nhỏ nhất của hàm số là 3 + 2 3 .
Vậy kết quả là 3 + 2 3
Chọn B.

Đáp án C.
Ta có: GT
<=> 5x+2y + x + 2y – 3–x–2y = 5xy–1 – 31–xy + xy – 1.
X é t h à m s ố f t = 5 t + t - 3 - t
⇒ f t = 5 t ln 5 + 1 + 3 - t ln 3 > 0 ∀ t ∈ ℝ
Do đó hàm số đồng biến trên ℝ suy ra
f(x+2y) = f(xy – 1) <=> x+ 2y = xy – 1
⇔ x = 2 y + 1 y - 1 ⇒ T = 2 y + 1 y - 1 + y .
Do x > 0 => y > 1.
Ta có:
T = 2 + y + 3 y - 1 = 3 + y - 1 + 3 y - 1 ≥ 3 + 2 3 .

Do \(x^2+y^2=1\), đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=sina\\y=cosa\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(P=\left(3-sina\right)\left(3-cosa\right)=9-3\left(sina+cosa\right)+sina.cosa\)
Đặt \(sina+cosa=t\Rightarrow t\in\left[-\sqrt{2};\sqrt{2}\right]\)
\(t^2=1+2sina.cosa\Rightarrow sina.cosa=\dfrac{t^2-1}{2}\)
\(P=9-3t+\dfrac{t^2-1}{2}=\dfrac{1}{2}t^2-3t+\dfrac{17}{2}\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(t\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}t^2-3t+\dfrac{17}{2}\) trên \(\left[-\sqrt{2};\sqrt{2}\right]\)
\(f'\left(t\right)=t-3=0\Rightarrow t=3\notin\left[-\sqrt{2};\sqrt{2}\right]\)
\(f\left(-\sqrt{2}\right)=\dfrac{19+6\sqrt{2}}{2}\) ; \(f\left(\sqrt{2}\right)=\dfrac{19-6\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow P_{min}=f\left(\sqrt{2}\right)=\dfrac{19-6\sqrt{2}}{2}\) khi \(t=\sqrt{2}\)

Do \(1\le x\le2\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2\le3x\)
Hoàn toàn tương tự ta có \(y^2+2\le3y\)
Do đó: \(P\ge\dfrac{x+2y}{3x+3y+3}+\dfrac{2x+y}{3x+3y+3}+\dfrac{1}{4\left(x+y-1\right)}\)
\(P\ge\dfrac{x+y}{x+y+1}+\dfrac{1}{4\left(x+y-1\right)}\)
Đặt \(a=x+y-1\Rightarrow1\le a\le3\)
\(\Rightarrow P\ge f\left(a\right)=\dfrac{a+1}{a+2}+\dfrac{1}{4a}\)
\(f'\left(a\right)=\dfrac{3a^2-4a-4}{4a^2\left(a+2\right)^2}=\dfrac{\left(a-2\right)\left(3a+2\right)}{4a^2\left(a+2\right)^2}=0\Rightarrow a=2\)
\(f\left(1\right)=\dfrac{11}{12}\) ; \(f\left(2\right)=\dfrac{7}{8}\) ; \(f\left(3\right)=\dfrac{53}{60}\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(a\right)\ge\dfrac{7}{8}\Rightarrow P_{min}=\dfrac{7}{8}\) khi \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(1;2\right);\left(2;1\right)\)

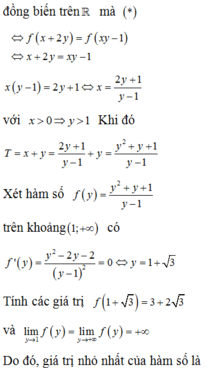
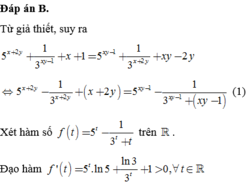
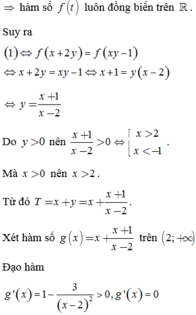

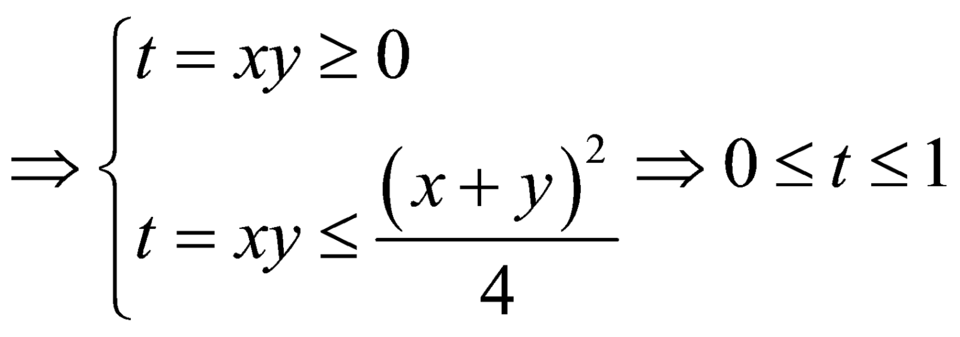

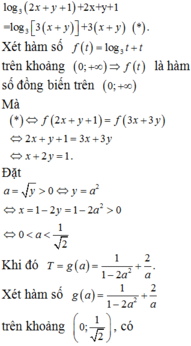


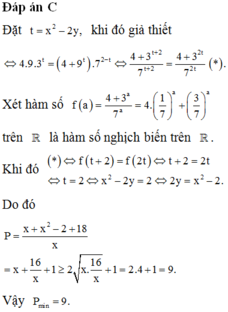
Đáp án B.
Từ giả thiết, suy ra
Xét hàm số f ( t ) = 5 t - 1 3 t + t trên ℝ .
Đạo hàm f ' ( t ) = 5 t . ln 5 - ln 3 3 t + 1 > 0 , ∀ t ∈ ℝ ⇒ hàm số f ( t ) luôn đồng biến trên ℝ .
Suy ra
Do y > 0 nên x + 1 x - 2 > 0 ⇔ [ x > 2 x < - 1 . Mà x > 0 nên x > 2 .
Từ đó T = x + y = x + x + 1 x - 2 . Xét hàm số g ( x ) = x + x + 1 x - 2 trên 2 ; + ∞ .
Đạo hàm
Lập bảng biến thiên của hàm số trên 2 ; + ∞ , ta thấy min g ( x ) = g ( 2 + 3 ) = 3 + 2 3 .
Vậy T m i n = 3 + 2 3 khi x = 2 + 3 và x = 1 + 3 .