

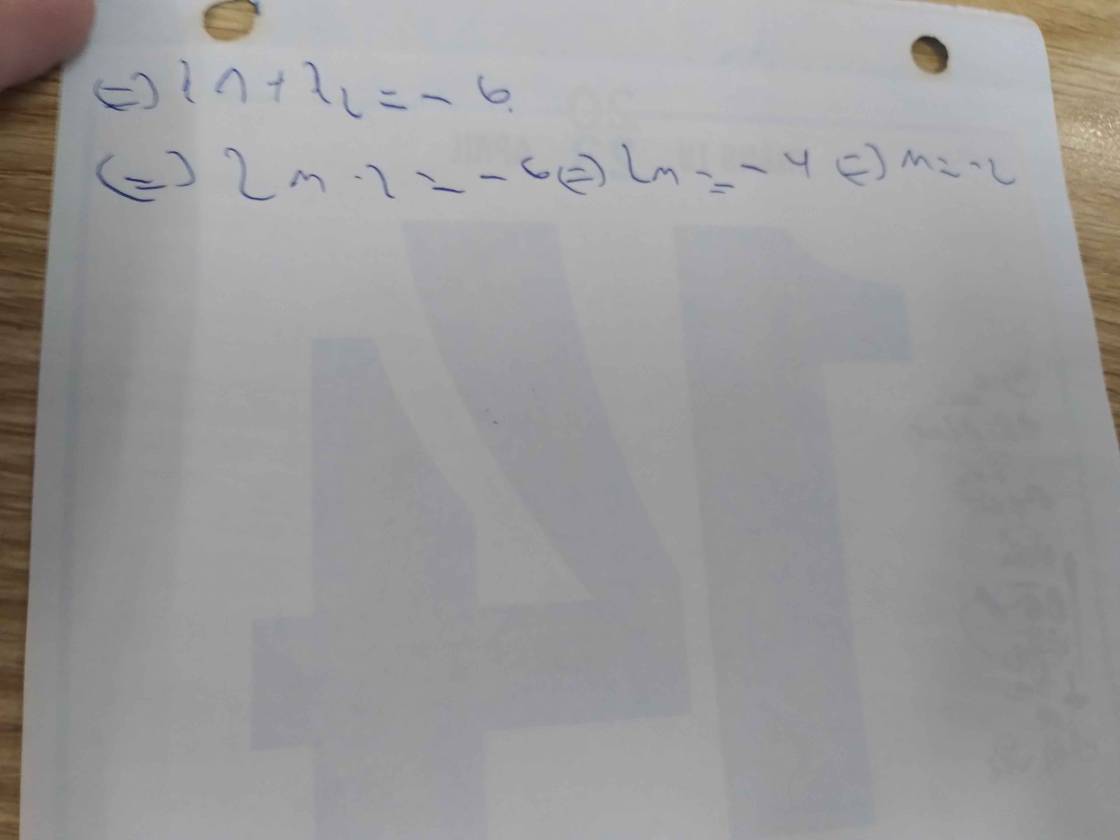
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


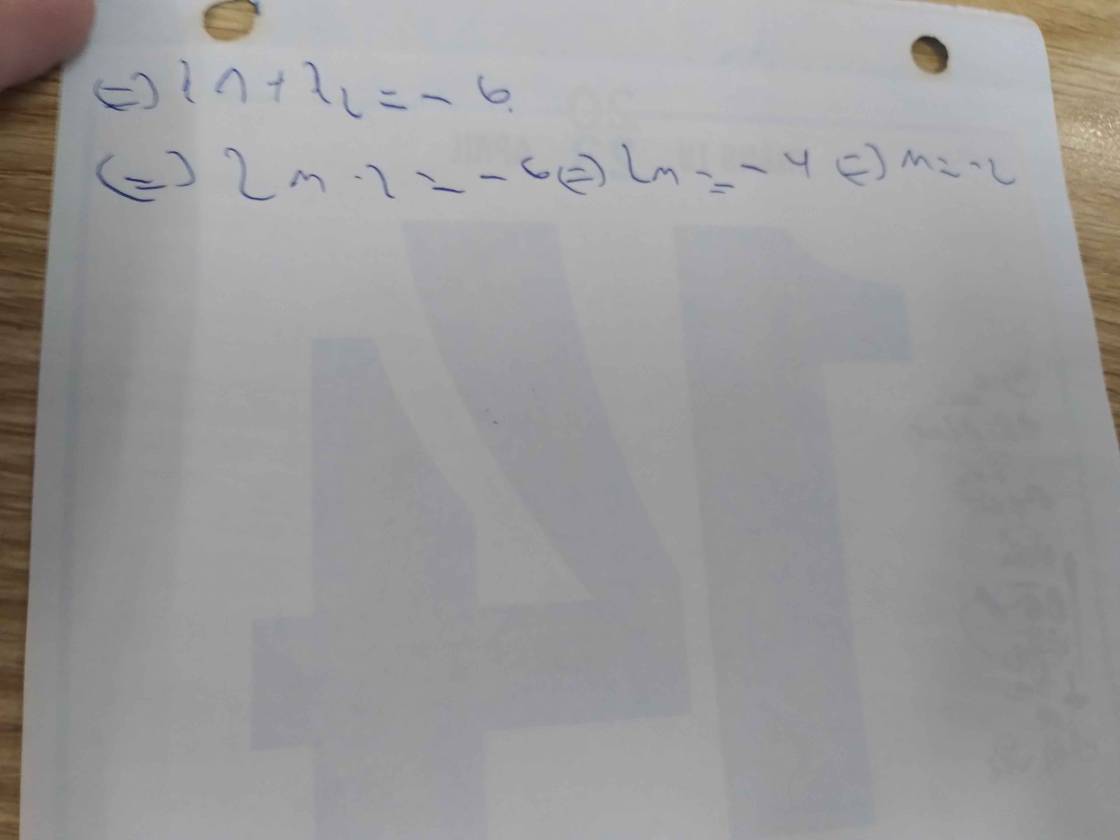

2 nghiệp pt phải:
(2m - 1)2-4(m2 - 1)≥0
Vì x1 là nghiệm nên
x21−(2m−1)x1+m2−1=0
<=> x12−(2m−1)x1+m2−1=0
<=>x12−2mx1+m2=x1+1
<=> 9m2=0 <=>m=0
#YQ

Ptr có nghiệm `<=>\Delta' > 0`
`<=>(-m)^2-2m+1 > 0`
`<=>(m-1)^2 > 0<=>m-1 ne 0<=>m ne 1`
`=>` Áp dụng Viét có: `{(x_1+x_2=-b/a=2m),(x_1.x_2=c/a=2m-1):}`
Ta có: `(x_1 ^2-2mx_1 +3)(x_2 ^2-2mx_2 -2)=50`
`<=>[x_1 ^2-(x_1+x_2)x_1+3][x_2 ^2-(x_1+x_2)x_2 -2]=50`
`<=>(-x_1.x_2+3)(-x_1.x_2-2)=50`
`<=>(1-2m+3)(1-2m-2)=50`
`<=>(4-2m)(-1-2m)=50`
`<=>-4-8m+2m+4m^2=50`
`<=>4m^2-6m-54=0`
`<=>4m^2+12m-18m-54=0`
`<=>(m+3)(4m-18)=0<=>[(m=-3),(m=9/2):}` (t/m)


b: \(\text{Δ}=\left(2m+3\right)^2-4\left(4m+2\right)\)
\(=4m^2+12m+9-16m-8\)
\(=4m^2-4m+1=\left(2m-1\right)^2>=0\)
Do đó: Phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm
Theo đề, ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x_1-5x_2=6\\x_1+x_2=2m+3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x_1-5x_2=6\\2x_1+2x_2=4m+6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-7x_2=-4m\\2x_1=5x_2+6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_2=\dfrac{4}{7}m\\2x_1=\dfrac{20}{7}m+6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_2=\dfrac{4}{7}m\\x_1=\dfrac{10}{7}m+3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Theo đề, ta có: \(x_1x_2=4m+2\)
\(\Rightarrow4m+2=\dfrac{40}{49}m^2+\dfrac{12}{7}m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2\cdot\dfrac{40}{49}-\dfrac{16}{7}m-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow40m^2-112m-98=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow40m^2-140m+28m-98=0\)
=>\(20m\left(2m-7\right)+14\left(2m-7\right)=0\)
=>(2m-7)(20m+14)=0
=>m=7/2 hoặc m=-7/10

Bài 1:
$2x^4-3x^2-5=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (2x^4+2x^2)-(5x^2+5)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x^2(x^2+1)-5(x^2+1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x^2+1)(2x^2-5)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x^2-5=0$ (do $x^2+1\geq 1>0$ với mọi $x\in\mathbb{R}$)
$\Leftrightarrow x^2=\frac{5}{2}$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\pm \sqrt{\frac{5}{2}}$
Bài 2:
a. Khi $m=1$ thì pt trở thành:
$x^2-6x+5=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x^2-x)-(5x-5)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x(x-1)-5(x-1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-1)(x-5)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-1=0$ hoặc $x-5=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=1$ hoặc $x=5$
b.
Để pt có 2 nghiệm $x_1,x_2$ thì:
$\Delta=(m+5)^2-4(-m+6)\geq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow m^2+14m+1\geq 0(*)$
Áp dụng định lý Viet:
$x_1+x_2=m+5$
$x_1x_2=-m+6$
Khi đó:
$x_1^2x_2+x_1x_2^2=18$
$\Leftrightarrow x_1x_2(x_1+x_2)=18$
$\Leftrightarrow (m+5)(-m+6)=18$
$\Leftrightarrow -m^2+m+12=0$
$\Leftrightarrow m^2-m-12=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (m+3)(m-4)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow m=-3$ hoặc $m=4$
Thử lại vào $(*)$ thấy $m=4$ thỏa mãn.

a) Ta có: \(\Delta=\left[-2\left(m-1\right)\right]^2-4\cdot1\cdot\left(2m-5\right)\)
\(=\left(2m-2\right)^2-4\left(2m-5\right)\)
\(=4m^2-8m+4-8m+20\)
\(=4m^2-16m+24\)
\(=4m^2-2\cdot2m\cdot4+16+8\)
\(=\left(2m-4\right)^2+8>0\forall m\)
Vậy: Phương trình (1) luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt \(x_1;x_2\)