
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


(Dòng khoanh đỏ ở dấu tương đương đầu tiên)Có nghĩa là chia cả hai vế cho \(\dfrac{5\pi}{3}\) ấy
(Dòng khoanh đỏ ở dấu tương đương thứ hai) Xét \(cos\pi x=\dfrac{1}{10}+k\dfrac{6}{5}\) (*)
Do \(-1\le cos\pi x\le1\)\(\Leftrightarrow-1\le\dfrac{1}{10}+k\dfrac{6}{5}\le1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{11}{12}\le k\le\dfrac{3}{4}\) mà k nguyên \(\Rightarrow k=0\)
Thay k=0 vào (*)\(\Rightarrow cos\pi x=\dfrac{1}{10}\)
Làm tương tự với cái bên dưới \(-1\le\dfrac{1}{2}+k\dfrac{6}{5}\le1\) \(\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{5}{4}\le k\le\dfrac{5}{12}\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}k=0\\k=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay k=0 với k=-1 sẽ ra được \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}cos\pi x=\dfrac{1}{2}\\cos\pi x=-\dfrac{7}{10}\end{matrix}\right.\)
(Với mỗi \(cos\pi x\) sẽ nhận được hai họ nghiệm => Tổng tất cả là 6 họ nghiệm)
Vì \(cosx\in\left[-1;1\right]\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-1\le\dfrac{1}{10}+k\dfrac{6}{5}\le1\left(1\right)\\-1\le\dfrac{1}{2}+k\dfrac{6}{5}\le1\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{11}{12}\le k\le\dfrac{9}{12}\Leftrightarrow k=0\Rightarrow cosx=\dfrac{1}{10}\)
\(\left(2\right)\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{15}{12}\le k\le\dfrac{5}{12}\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}k=0\\k=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cosx=\dfrac{1}{2}\\cosx=-\dfrac{7}{10}\end{matrix}\right.\)

TXĐ: `D=RR\\{π/2+kπ ; -π/4 +kπ}`
Mà `-π/2+k2π` và `π/2+k2π \in π/2 +kπ`
`=>` Không nằm trong TXĐ.

Đồng nhất hệ số 2 vế thôi, hệ số các vecto bên vế trái bằng với vế phải (bên vế trái ko có \(\overrightarrow{c}\) nên coi như hệ số của nó bằng 0, do đó \(-\left(2m+n\right)=0\Rightarrow2m+n=0\))


\(\sqrt{2}cos\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{15}\right)-3=0\Leftrightarrow cos\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{15}\right)=\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{2}}\)
Do \(\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{2}}>1\) \(\Rightarrow\) phương trình vô nghiệm
A đúng

Ta có : \(f\left(2\right)=2a+b-6\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2^+}\dfrac{x-\sqrt{x+2}}{x^2-4}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2^+}\dfrac{x^2-x-2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+\sqrt{x+2}\right)}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2^+}\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+\sqrt{x+2}\right)}=\dfrac{3}{16}\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2^-}x^2+ax+3b=4+2a+3b\)
H/s liên tục tại điểm x = 2 \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{16}=2a+3b+4=2a+b-6\)
Suy ra : \(a=\dfrac{179}{32};b=-5\) => t = a + b = 19/32 . Chọn C
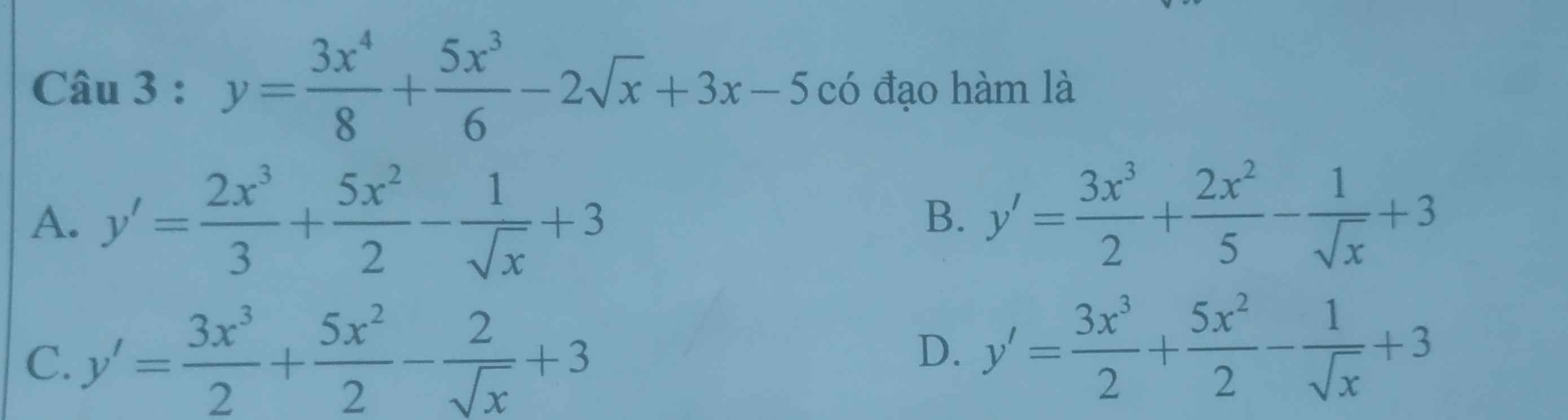 cho đáp án và giải thích giùm mình với ạ
cho đáp án và giải thích giùm mình với ạ



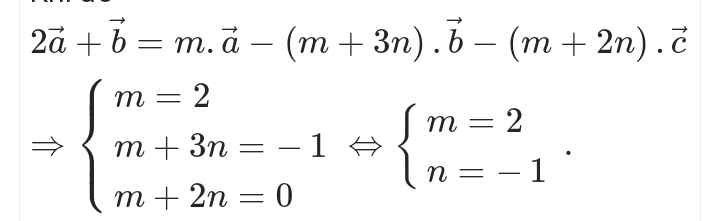





\(y'=\dfrac{4.3}{8}.x^3+\dfrac{5.3}{6}x^2-\dfrac{2}{2\sqrt{x}}+3=\dfrac{3x^3}{2}+\dfrac{5x^2}{2}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}+3\)