Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Đặt 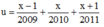
Suy ra 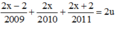
Phương trình đã cho trở thành:
0,05.2u = 3,3 − u ⇔ 0,1u = 3,3 – u ⇔ 1,1u = 3,3 ⇔ u = 3.
Do đó: 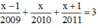
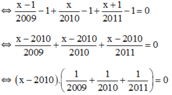
⇔ x – 2010 = 0
⇔ x = 2010.

Đặt ![]() ta có phương trình 6u – 8 = 3u + 7.
ta có phương trình 6u – 8 = 3u + 7.
Giải phương trình này:
6u – 8 = 3u + 7
⇔ 6u – 3u = 7 + 8
⇔ 3u = 15 ⇔ u = 5
Vậy (16x + 3)/7 = 5 ⇔ 16x + 3 = 35
⇔ 16x = 32 ⇔ x = 2
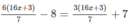
⇔ (16x + 3)/7 = 5 ⇔ 16x + 3 = 35
⇔ 16x = 32 ⇔ x = 2

a/ \(\dfrac{6\left(16x+3\right)}{7}-8=\dfrac{3\left(16x+3\right)}{7}+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6\left(16x+3\right)-56=3\left(16x+3\right)+49\)
\(\Leftrightarrow96x+18-56-48x-9-49=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow48x=96\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm x=2
a) Đặt u = \(\dfrac{16x+3}{7}\), ta có:
\(\dfrac{6\left(16x+3\right)}{7}\) - 8 = \(\dfrac{3\left(16x+3\right)}{7}\) + 7
<=> 6.u - 8 = 3.u + 7
=> 6.u - 3.u = 8 + 7
=> 3.u = 15
=> u = 15 / 3
=> u = 5
<=> \(\dfrac{16x+3}{7}\) = 5
=> 16x + 3 = 5 . 7
=> 16x = 35 - 3
=> 16x = 32
=> x = 32 / 16
=> x = 2
Vậy S = { 2 }.

a: =>(x^2-2x+1-1)^2+2(x-1)^2=1
=>(x-1)^4-2(x-1)^2+1+2(x-1)^2=1
=>(x-1)^4=0
=>x-1=0
=>x=1
b: =>(x^2+2)^2+3x(x^2+2)+2x^2-20x^2=0
=>(x^2+2)^2+3x(x^2+2)-18x^2=0
=>(x^2+2+6x)(x^2-3x+2)=0
=>\(x\in\left\{-3\pm\sqrt{7};1;2\right\}\)

\(\Leftrightarrow4\left|x-2\right|=\left(x-2\right)^2+4\)
Đặt \(\left|x-2\right|=t\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow4t=t^2+4\Rightarrow t^2-4t+4=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(t-2\right)^2=0\Rightarrow t=2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|x-2\right|=2\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=2\\x-2=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)

2/ (x2 + x + 1) (x2+ x + 2) = 12
đặt x2 + x = t
thay vào đc:
(t + 1) (t + 2) = 12
<=> t2 + 3t + 2 = 12
<=> t2 + 3t - 10 = 0
<=> t2 - 2t + 5t - 10 = 0
<=> t (t - 2) + 5 (t - 2) = 0
<=> (t + 5) (t - 2) = 0
=> {
t=−5 |
t=2 |
thay t đc:
*) x2 + x = -5 => x loại
*) x2 + x = 2 = x2 + x - 2 = x2 - 1 + x - 1 = (x - 1) (x + 1) + (x - 1) = (x - 1) (x + 2)
=> x = 1 hoặc x = - 2
S = {-2 ; 1}
3/ (x2 - 6x + 4)2 - 15(x2 - 6x + 10) = 1
đặt x2 - 6x + 4 = t
có: t2 - 15(t + 6) = 1
<=> t2 - 15t - 91 = 0
Câu 2 đặt ẩn phụ là x^2+x+2= a là đc
Câu 3 đặt ẩnphụ là x^2-6x+4= b là đc

Bài 1 :
Mình nghĩ phải sửa đề ntn :
\(4\left(2x+7\right)^2-9\left(x+3\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[2\left(2x+7\right)\right]^2-\left[3\left(x+3\right)\right]^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[2\left(2x+7\right)-3\left(x+3\right)\right]\left[2\left(2x+7\right)+3\left(x+3\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+14-3x-9\right)\left(4x+14+3x+9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(7x+23\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+5=0\\7x+23=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-5\\x=\frac{-23}{7}\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy....
b) \(A=\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+2\right)-12\)
Đặt \(q=x^2+x+1\)ta có :
\(A=q\left(q+1\right)-12\)
\(A=q^2+q-12\)
\(A=q^2+4q-3q-12\)
\(A=q\left(q+4\right)-3\left(q+4\right)\)
\(A=\left(q+4\right)\left(q-3\right)\)
Thay \(q=x^2+x+1\)ta có :
\(A=\left(x^2+x+1+4\right)\left(x^2+x+1-3\right)\)
\(A=\left(x^2+x+5\right)\left(x^2+x-2\right)\)
\(A=\left(x^2+x+5\right)\left(x^2+2x-x-2\right)\)
\(A=\left(x^2+x+5\right)\left[x\left(x+2\right)-\left(x+2\right)\right]\)
\(A=\left(x^2+x+5\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\)

2/ (x2 + x + 1) (x2+ x + 2) = 12
đặt x2 + x = t
thay vào đc:
(t + 1) (t + 2) = 12
<=> t2 + 3t + 2 = 12
<=> t2 + 3t - 10 = 0
<=> t2 - 2t + 5t - 10 = 0
<=> t (t - 2) + 5 (t - 2) = 0
<=> (t + 5) (t - 2) = 0
=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}t=-5\\t=2\end{cases}}\)
thay t đc:
*) x2 + x = -5 => x loại
*) x2 + x = 2 = x2 + x - 2 = x2 - 1 + x - 1 = (x - 1) (x + 1) + (x - 1) = (x - 1) (x + 2)
=> x = 1 hoặc x = - 2
S = {-2 ; 1}
3/ (x2 - 6x + 4)2 - 15(x2 - 6x + 10) = 1
đặt x2 - 6x + 4 = t
có: t2 - 15(t + 6) = 1
<=> t2 - 15t - 91 = 0
....
....
số xấu, xem lại đề ~0~
câu 2, a=x2 +x+1 . PHƯƠNG TRÌNH TRỞ THÀNH a x (a +1)=12. giải binh thương
câu 3, tương tự a= x2 - 6x + 4 .PHƯƠNG TRÌNH TRỞ THÀNH a2 - 15x(a+6)=1. giải bình thương
Nếu đặt u = x 2 − 1 thì x 2 = u + 1 nên phương trình có dạng
( 2 + 2)u = 2(u + 1) − 2 (1)
Ta giải phương trình (1):
(1) ⇔ 2 u + 2u = 2u + 2 − 2
⇔ 2 u = 2 − 2
⇔ 2 u = 2 ( 2 − 1) ⇔ u = 2 − 1
⇔ x 2 − 1 = 2 − 1
⇔ x 2 = 2
⇔ x = 1