
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Câu 1:
Ta có: \(\left(3x+7\right)\left(2x+3\right)-\left(3x-5\right)\left(2x+11\right)\)
\(=6x^2+9x+14x+21-\left(6x^2+33x-10x-55\right)\)
\(=6x^2+23x+21-6x^2-23x+55\)
=76

8) \(\dfrac{x+7}{3}+\dfrac{x+5}{4}=\dfrac{x+3}{5}+\dfrac{x+1}{6}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x+7}{3}+\dfrac{x+5}{4}-\dfrac{x+3}{5}-\dfrac{x+1}{6}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x+7}{3}+2+\dfrac{x+5}{4}+2-\dfrac{x+3}{5}-2-\dfrac{x+1}{6}-2=0+2+2-2-2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(\dfrac{x+7}{3}+2\right)+\left(\dfrac{x+5}{4}+2\right)-\left(\dfrac{x+3}{5}+2\right)-\left(\dfrac{x+1}{6}+2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(\dfrac{x+7}{3}+\dfrac{6}{3}\right)+\left(\dfrac{x+5}{4}+\dfrac{8}{4}\right)-\left(\dfrac{x+3}{5}+\dfrac{10}{5}\right)-\left(\dfrac{x+1}{6}+\dfrac{12}{2}\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+13\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{5}-\dfrac{1}{6}\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+13=0\\\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{6}=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x+13=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-13\)
\(\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{6}=0\)
\(\dfrac{13}{60}=0\) (vô lí)
Vậy \(x=-13\)
9) Bạn chuyển vế rồi cộng 3 vào từng mỗi số

a: Ta có: \(x^2-x+1\)
\(=x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
d: Ta có: \(x^2-2x+\left|y+1\right|+5\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)^2+\left|y+1\right|+4\ge4\forall x,y\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=1 và y=-1

Bài 15:
\(P=\dfrac{x+y-1}{x\left(x+y\right)}+\dfrac{x-y}{2xy}\cdot\dfrac{xy+y^2+xy-y^2}{x\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{x}\)


3) \(\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}\) thì (x-2)(x+1)>0
=> x2 -x-2>0
=> x2 - x - \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)- \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)>0
= (x+\(\dfrac{1}{4}\))2 - 3/2 >0
=> x+ 1/4>3/2
=> x>5/4
4) Có x đâu mà tìm bạn??


Bài 6:
a: Xét tứ giác DEBF có
DE//BF
DE=BF
Do đó: DEBF là hình bình hành
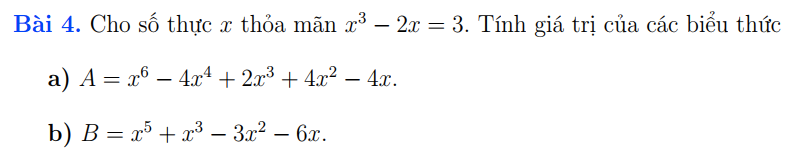






\(A=x^6-2x^4-2x^4+4x^2+2x^3-4x\\ A=x^3\left(x^3-2x\right)-2x\left(x^3-2x\right)+2\left(x^3-2x\right)\\ A=\left(x^3-2x\right)\left(x^3-2x+2\right)=3\left(3+2\right)=3\cdot5=15\\ B=x^5-2x^3+3x^3-6x-3x^2\\ =x^2\left(x^3-2x\right)+3\left(x^3-2x\right)-3x^2\\ =\left(x^3-2x\right)\left(x^2+3\right)-3x^2=3\left(x^2+3\right)-3x^2\\ =3x^2-3x^2+9=9\)