Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

1: =>x^2+3x-4=0
=>(x+4)(x-1)=0
=>x=1 hoặc x=-4
2: =>2x-3y=1 và 3x=4y+2
=>2x-3y=1 và 3x-4y=2
=>x=2 và y=1

a) Ta có: \(\dfrac{1}{2}x^2+\dfrac{3}{4}x+1=0\)(1)
\(\Delta=\dfrac{9}{16}-4\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot1=\dfrac{9}{16}-2=-\dfrac{23}{16}\)
Vì \(\Delta< 0\) nên phương trình (1) vô nghiệm
Vậy: \(S=\varnothing\)
b) Ta có: \(x^2-\left(2+\sqrt{5}\right)x+2\sqrt{5}=0\)(2)
\(\Delta=\left(2+\sqrt{5}\right)^2-4\cdot1\cdot2\sqrt{5}=9+4\sqrt{5}-8\sqrt{5}=9-4\sqrt{5}>0\)
Vì \(\Delta>0\) nên phương trình (2) có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{2+\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{9-4\sqrt{5}}}{2\cdot1}=\dfrac{2+\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{5}+2}{2\cdot1}=\dfrac{4}{2}=2\\x_2=\dfrac{2+\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{9-4\sqrt{5}}}{2\cdot1}=\dfrac{2+\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{5}-2}{2\cdot1}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{5}}{2}=\sqrt{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{2;\sqrt{5}\right\}\)


TA CÓ : \(x^4+\left(x^2+1\right)\sqrt{x^2+1}-1=0\)
ĐẶT \(\sqrt{x^2+1}=y\left(y>0\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x^4=\left(y^2-1\right)^2\)
Từ Đó Ta Có pt mới : \(\left(y^2-1\right)^2+y^3-1=0\left(y>0\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow y^4+y^3-2y^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow y^2\left(y^2+y-2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow y^2\left(y-1\right)\left(y+2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow y=1\left(y>0\Rightarrow y\notin\left(-2;0\right)\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x^2+1}=1\Rightarrow x=0\)
VẬY PT trên có nghiệm duy nhất X = 0

Bài 1: ĐKXĐ: $2\leq x\leq 4$
PT $\Leftrightarrow (\sqrt{x-2}+\sqrt{4-x})^2=2$
$\Leftrightarrow 2+2\sqrt{(x-2)(4-x)}=2$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(4-x)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-2=0$ hoặc $4-x=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=2$ hoặc $x=4$ (tm)
Bài 2:
PT $\Leftrightarrow 4x^3(x-1)-3x^2(x-1)+6x(x-1)-4(x-1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-1)(4x^3-3x^2+6x-4)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=1$ hoặc $4x^3-3x^2+6x-4=0$
Với $4x^3-3x^2+6x-4=0(*)$
Đặt $x=t+\frac{1}{4}$ thì pt $(*)$ trở thành:
$4t^3+\frac{21}{4}t-\frac{21}{8}=0$
Đặt $t=m-\frac{7}{16m}$ thì pt trở thành:
$4m^3-\frac{343}{1024m^3}-\frac{21}{8}=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 4096m^6-2688m^3-343=0$
Coi đây là pt bậc 2 ẩn $m^3$ và giải ta thu được \(m=\frac{\sqrt[3]{49}}{4}\) hoặc \(m=\frac{-\sqrt[3]{7}}{4}\)
Khi đó ta thu được \(x=\frac{1}{4}(1-\sqrt[3]{7}+\sqrt[3]{49})\)
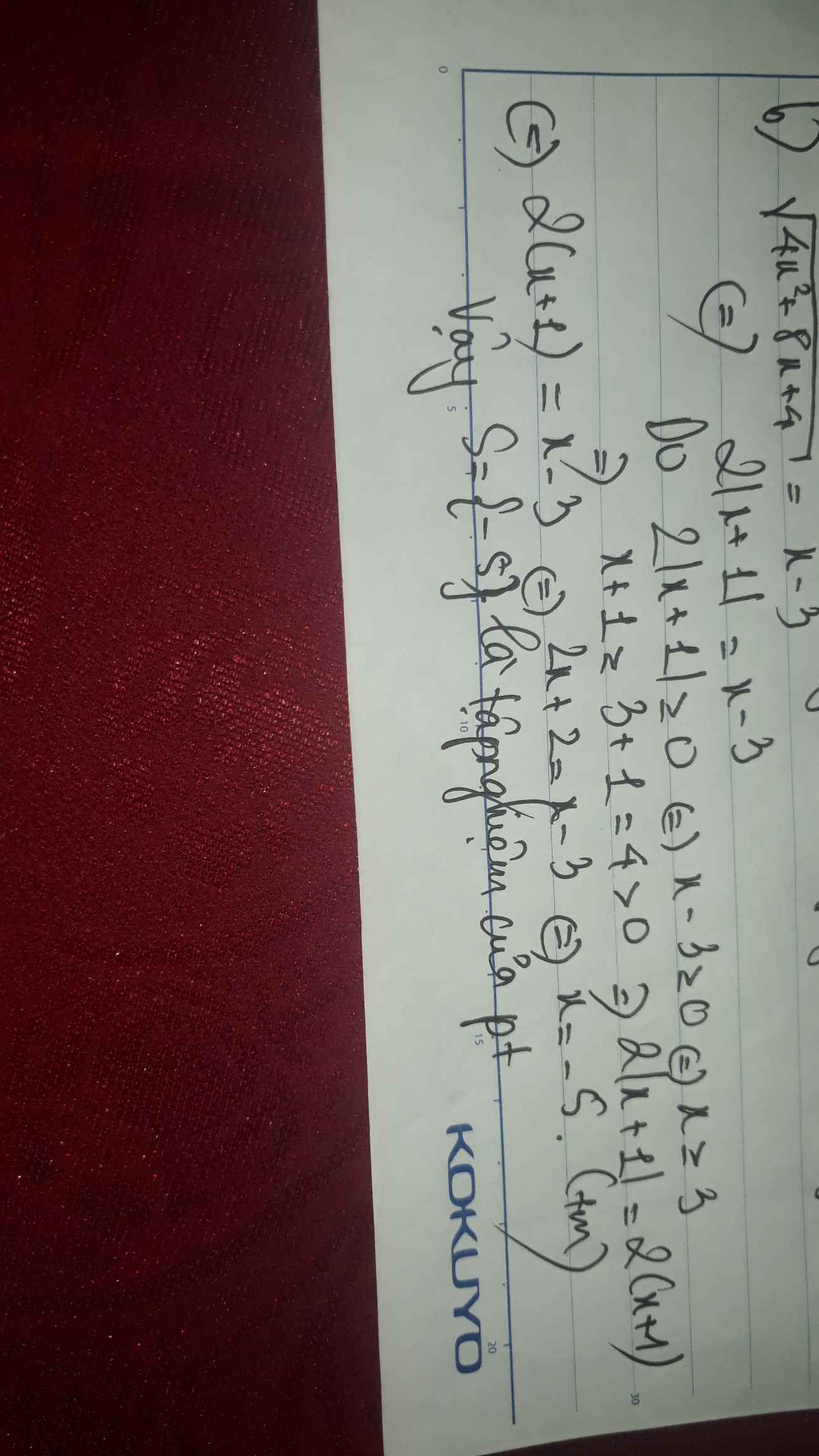

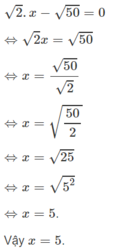
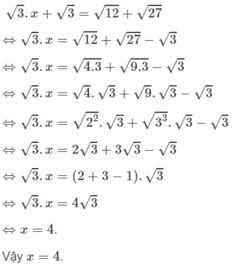
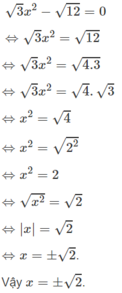
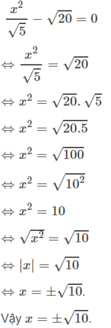
a: =>(x^2+x)^2-2(x^2+x)+(x^2+x)-2=0
=>(x^2+x-2)(x^2+x+1)=0
=>(x+2)(x-1)=0
=>x=-2 hoặc x=1
b: ĐKXĐ: x<>4; x<>1
PT =>\(\dfrac{x+3+3x-12}{x-4}=\dfrac{6}{1-x}\)
=>(4x-9)(1-x)=6(x-4)
=>4x-4x^2-9+9x=6x-24
=>-4x^2+13x-9-6x+24=0
=>-4x^2+7x+15=0
=>x=3(nhận) hoặc x=-5/4(nhận)