
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Phân thức 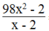 = 0 khi
98
x
2
+
2
=
0
và x – 2
≠
0
= 0 khi
98
x
2
+
2
=
0
và x – 2
≠
0
Ta có: x – 2 ≠ 0 ⇔ x ≠ 2
98 x 2 + 2 = 0 ⇔ 2 49 x 2 - 1 = 0 ⇔ (7x + 1)(7x – 1) = 0
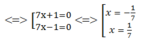
Ta có: 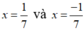 thỏa mãn điều kiện x
≠
2
thỏa mãn điều kiện x
≠
2
Vậy ![]() thì phân thức
thì phân thức ![]() có giá trị bằng 0.
có giá trị bằng 0.

\(x^3-6x^2-25x-18=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+1\right)-7x\left(x+1\right)-18\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-7x-18\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+2x-9x-18\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left[x\left(x+2\right)-9\left(x+2\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x-9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}x+1=0\\x+2=0\\x-9=0\end{array}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}x=-1\\x=-2\\x=9\end{array}\right.\)
Vậy nghiệm nhỏ nhất của phương trình là \(-2\)

Phân thức 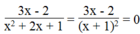 khi 3x – 2 = 0 và
x
+
1
2
≠
0
khi 3x – 2 = 0 và
x
+
1
2
≠
0
Ta có: x + 1 2 ≠ 0 ⇔ x + 1 ≠ 0 ⇔ x ≠ - 1
3x – 2 = 0 ⇔ 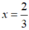
Ta có: 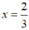 thỏa mãn điều kiện x
≠
- 1
thỏa mãn điều kiện x
≠
- 1
Vậy 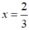 thì phân thức
thì phân thức 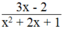 có giá trị bằng 0.
có giá trị bằng 0.

ĐKXĐ : \(x^2+10x+25\ne0\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)^2\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne-5\)
Để \(M=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^3-25x}{x^2+10x+25}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-25x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-25\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x^2-25=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\pm5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\) ( đối chiếu theo đkxđ : \(x\ne-5\) )
Vậy ...
ĐKXĐ:
\(x^2+10x+25\ne0\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)^2\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne-5\)
\(M=\dfrac{x^3-25x}{\left(x+5\right)^2}=\dfrac{x\left(x^2-25\right)}{\left(x+5\right)^2}=\dfrac{x\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)}{\left(x+5\right)^2}=\dfrac{x\left(x-5\right)}{x+5}\)
\(\Rightarrow M=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(thoa\right)\\x=5\left(thoa\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy x = 0 hoặc x = 5

a) \(25x^2-2=0\)
\(=>\left(5x\right)^2-\left(\sqrt{2}\right)^2=0\)
\(=>\left(5x-\sqrt{2}\right)\left(5x+\sqrt{2}\right)=0\)
\(=>\hept{\begin{cases}5x-\sqrt{2}=0\\5x+\sqrt{2}=0\end{cases}}\)
\(=>\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{5}\\x=-\frac{\sqrt{2}}{5}\end{cases}}\)
b) \(10x-x^2-25=0\)
\(=>-x^2-5x-5x-25=0\)
\(=>-x\left(x+5\right)-5\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(=>\left(x+5\right)\left(-x-5\right)=0\)
\(=>\hept{\begin{cases}x+5=0\\-x-5=0\end{cases}}\)
\(=>\hept{\begin{cases}x=-5\\x=-5\end{cases}}\)

a: =>2x(x-4)=0
=>x=4 hoặc x=0
b: =>x^2*(x+1)-25(x+1)=0
=>(x+1)(x-5)(x+5)=0
hay\(x\in\left\{-1;5;-5\right\}\)

Ta có: \(x=-24\Leftrightarrow-x=24\Leftrightarrow1-x=25\)
Thay vào E ta được:
\(E=x^{20}+\left(1-x\right)x^{19}+\left(1-x\right)x^{18}+...+\left(1-x\right)x^2+\left(1-x\right)x+\left(1-x\right)\)
\(E=x^{20}+x^{19}-x^{20}+x^{18}-x^{19}+...+x^2-x^3+x-x^2+1-x\)
\(E=1\)

25(x2-1)=0
x2-1=0:25
x2-1=0
x2=1
x=\(\sqrt{1}\)
25-25x2=0
⇔25(1-x2)=0
⇔25(1-x)(1+x)=0
⇔1-x=0 hay 1+x=0
⇔x=1 hay x=-1