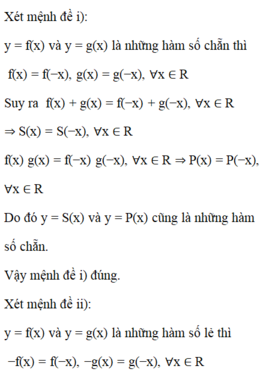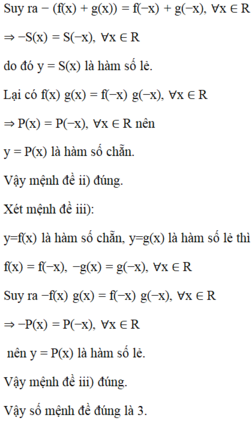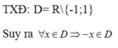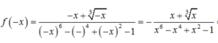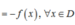Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Đặt y = f(x) = x2 + x + 1.
+ TXĐ: D = R nên với ∀x ∈ D thì –x ∈ D.
+ f(–x) = (–x)2 + (–x) + 1 = x2 – x + 1 ≠ x2 + x + 1 = f(x)
+ f(–x) = (–x)2 + (–x) + 1 = x2 – x + 1 ≠ –(x2 + x + 1) = –f(x)
Vậy hàm số y = x2 + x + 1 không chẵn, không lẻ.

Bài 1:
\(f\left(-x\right)=\left|\left(-x\right)^3+x\right|=\left|-x^3+x\right|=\left|-\left(x^3-x\right)\right|=\left|x^3-x\right|=f\left(x\right)\)
Vậy hàm số chẵn
Bài 2:
\(f\left(4\right)=4-3=1\\ f\left(-1\right)=2.1+1-3=0\\ b,\text{Thay }x=4;y=1\Leftrightarrow4-3=1\left(\text{đúng}\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow A\left(4;1\right)\in\left(C\right)\\ \text{Thay }x=-1;y=-4\Leftrightarrow2\left(-1\right)^2+1-3=-4\left(\text{vô lí}\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow B\left(-1;-4\right)\notin\left(C\right)\)

a: \(f\left(-x\right)=-2\cdot\left(-x\right)^3+3\cdot\left(-x\right)\)
\(=2x^3-3x\)
\(=-\left(-2x^3+3x\right)\)
=-f(x)
Vậy: f(x) là hàm số lẻ
c: TXĐ: D=[-2;2]
Nếu \(x\in D\Leftrightarrow-x\in D\)
\(f\left(-x\right)=\sqrt{6-3\cdot\left(-x\right)}-\sqrt{6+3\cdot\left(-x\right)}\)
\(=\sqrt{6+3x}-\sqrt{6-3x}\)
\(=-f\left(x\right)\)
Vậy: f(x) là hàm số lẻ