cho phương trình \(x^2-2\left(m+1\right)x+m^2+m-1=0\)
tìm m , biết phương trình có 2 nghiệm x1, x2 thỏa mãn điều kiện \(\dfrac{1}{x_1}+\dfrac{1}{x_2}=4\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

b) phương trình có 2 nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m-1\right)^2-\left(m-1\right)\left(m+3\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-2m+1-m^2-3m+m+3\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4m+4\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\le1\)
Ta có: \(x_1^2+x_1x_2+x_2^2=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=1\)
Theo viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=2\left(m-1\right)\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=m+3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[-2\left(m-1\right)^2\right]-2\left(m+3\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-8m+4-2m-6-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-10m-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m_1=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{37}}{4}\left(ktm\right)\\m_2=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{4}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow m=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{4}\)

a: Thay m=-5 vào (1), ta được:
\(x^2+2\left(-5+1\right)x-5-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-8x-9=0\)
=>(x-9)(x+1)=0
=>x=9 hoặc x=-1
b: \(\text{Δ}=\left(2m+2\right)^2-4\left(m-4\right)=4m^2+8m+4-4m+16=4m^2+4m+20>0\)
Do đó: Phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt
\(\dfrac{x_1}{x_2}+\dfrac{x_2}{x_1}=-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1^2+x_2^2=-3x_1x_2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2+x_1x_2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m+2\right)^2+m-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2+9m=0\)
=>m(4m+9)=0
=>m=0 hoặc m=-9/4

Δ=(m+2)^2-4*2m=(m-2)^2
Để PT có hai nghiệm pb thì m-2<>0
=>m<>2
\(\dfrac{1}{x_1}+\dfrac{1}{x_2}=\dfrac{x_1x_2}{4}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x_1+x_2}{x_1x_2}=\dfrac{x_1x_2}{4}\)
=>\(\dfrac{m+2}{2m}=\dfrac{2m}{4}=\dfrac{m}{2}\)
=>2m^2=2m+4
=>m^2-m-2=0
=>m=2(loại) hoặc m=-1

Để pt có 2 nghiệm trái dấu \(\Leftrightarrow3m-2< 0\Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{2}{3}\)
Nếu \(x_1< 0\) thì \(\dfrac{1}{x_1}-3< 0\) trong khi \(\left|\dfrac{1}{x_2}\right|>0\Rightarrow\) không thỏa mãn
Vậy \(x_1>0;x_2< 0\)
Do đó:
\(\dfrac{1}{x_1}-3=\left|\dfrac{1}{x_2}\right|=-\dfrac{1}{x_2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x_1}+\dfrac{1}{x_2}=3\Leftrightarrow x_1+x_2-3x_1x_2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2\left(m-1\right)-3\left(3m-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=...\)

\(\Delta'=\left(m+1\right)^2-5\ge0\Leftrightarrow m^2+2m-4\ge0\) (1)
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m+1\right)\\x_1x_2=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{1}{\left|x_1\right|}+\dfrac{1}{\left|x_2\right|}=2\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left|x_1\right|+\left|x_2\right|}{\left|x_1x_2\right|}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x_1\right|+\left|x_2\right|=2\left|x_1x_2\right|=10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1^2+x_2^2+2\left|x_1x_2\right|=100\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1^2+x_2^2+10=100\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=90\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(m+1\right)^2-10=90\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m+1\right)^2=25\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=4\\m=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thế vào (1) kiểm tra thấy đều thỏa mãn, vậy...
dạ pt có 2 nghiệm là chỉ lớn hơn không thôi chứ thầy sao có bằng 0 ạ
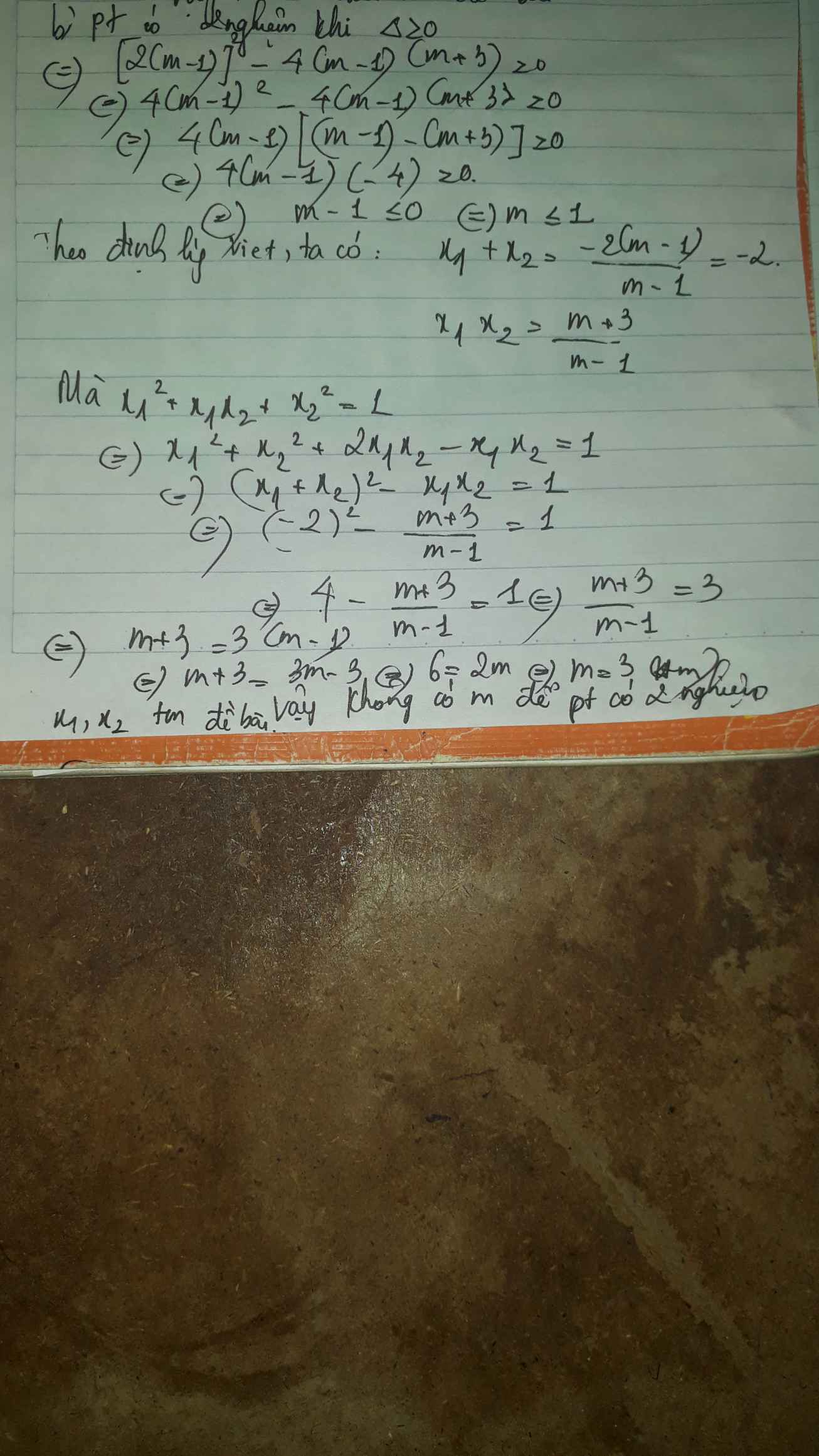


Lời giải:
Để pt có 2 nghiệm thì:
$\Delta'=(m+1)^2-(m^2+m-1)\geq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow m+2\geq 0\Leftrightarrow m\geq -2$
Áp dụng định lý Viet, với $x_1,x_2$ là nghiệm của pt thì ta có:
$x_1+x_2=2(m+1)$
$x_1x_2=m^2+m-1$
Khi đó:
$\frac{1}{x_1}+\frac{1}{x_2}=4$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{x_1+x_2}{x_1x_2}=4$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{2(m+1)}{m^2+m-1}=4$
$\Rightarrow 2m^2+m-3=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (m-1)(2m+3)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow m=1$ hoặc $m=\frac{-3}{2}$ (đều thỏa mãn)