Cho biểu thức P=(\(\dfrac{2a}{a+3}-\dfrac{3}{3-a}-\dfrac{2a^2+3}{a^2-9}\) ) : \(\dfrac{a+1}{a-3}\)
a) Tìm điều kiện của a để P xác định
b) Rút gọn P
c) Tính P khi giá trị tuyệt đối của a=2
d) Tìm a ϵ Z để P ϵ Z
Giúp em giải bài này vs ạ em đag cần lời giải gấp ![]()
![]()
![]() em xin c.ơn trước ạ
em xin c.ơn trước ạ

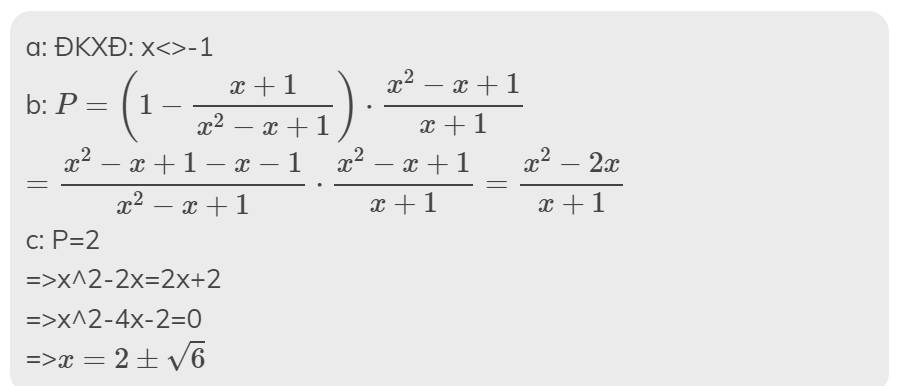
a: ĐKXĐ: a<>3; a<>-3; a<>-1
b: \(P=\dfrac{2a^2-3a+3a+9-2a^2-3}{\left(a-3\right)\left(a+3\right)}\cdot\dfrac{a-3}{a+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{6}{\left(a+3\right)\left(a+1\right)}\)
c: |a|=2
=>a=2 hoặc a=-2
Khi a=-2 thì \(P=\dfrac{6}{\left(-2+3\right)\left(-2+1\right)}=-6\)
Khi a=2 thì \(P=\dfrac{6}{\left(2+3\right)\left(2+1\right)}=\dfrac{6}{5\cdot3}=\dfrac{2}{5}\)