Chứng minh rằng nếu 1 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 3 thì 𝑥 2 + 3 ≤ 4𝑥. Khi nào xảy ra dấu bằng
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


b: Ta có: \(B=x^2\left(11x-2\right)+x^2\left(x-1\right)-3x\left(4x^2-x-2\right)\)
\(=11x^3-2x^2+x^3-x^2-12x^3+3x^2+6x\)
\(=6x\)

Lời giải:
1.
$(x-3)^2=4x^2+20x+25=(2x+5)^2$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-3)^2-(2x+5)^2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-3-2x-5)(x-3+2x+5)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (-x-8)(3x+2)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow -x-8=0$ hoặc $3x+2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=-8$ hoặc $x=-\frac{2}{3}$
2.
$2x(x-4)+x^2-16=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x(x-4)+(x-4)(x+4)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-4)(2x+x+4)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-4)(3x+4)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-4=0$ hoặc $3x+4=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=4$ hoặc $x=-\frac{4}{3}$

\(A=\sqrt{x^2-4x+25}=\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)^2+21}\)
Ta có : \(\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0\) => \(\left(x-2\right)^2+21\ge21\left(\forall x\right)\) => \(\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)^2+21}\ge\sqrt{21}\left(\forall x\right)\)
Dấu " = " xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)^2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x = 2
Vậy giá trị nhỏ nhất của A là : \(\sqrt{21}\) khi x = 2
\(B=\sqrt{x^2-6x+30}=\sqrt{\left(x-3\right)^2+21}\)
Vì \(\sqrt{\left(x-3\right)^2}\ge0\left(\forall x\right)\)=> \(\sqrt{\left(x-3\right)^2+21}\ge\sqrt{21}\left(\forall x\right)\)
Dấu " = " xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\sqrt{\left(x-3\right)^2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x=3\)
Vậy giá trị nhỏ nhất của B là : \(\sqrt{21}\) khi x = 3
\(D=\sqrt{x^2-4x+7}+\sqrt{2}=\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)^2+3}+\sqrt{2}\)
Vì
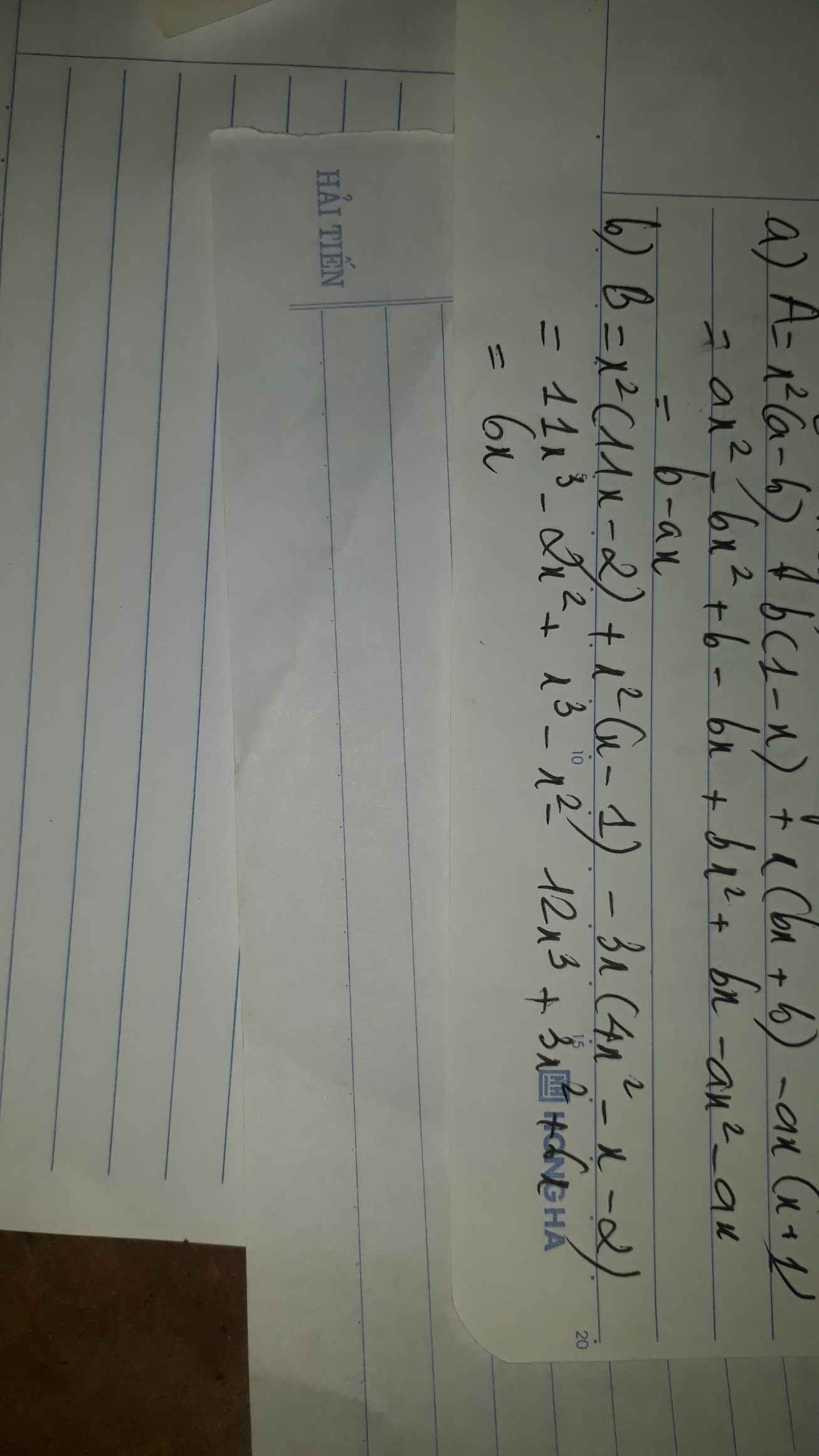
1<=x<=3
=>(x-1)>=0 và (x-3)<=0
=>(x-1)(x-3)<=0
=>x^2-4x+3<=0
=>x^2+3<=4x
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=1 hoặc x=3