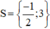Giải phương trình sau bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích: (2x + 1)(3x – 2) = (5x – 8)(2x + 1)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(a,2x\left(x-5\right)+4\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(2x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\2x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\2x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{5;-2\right\}\)
\(b,3x-15=2x\left(x-5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow3\left(x-5\right)-2x\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(-2x+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\-2x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\2x=3\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{5;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
\(c,\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)=\left(5x-8\right)\left(2x+1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)-\left(5x-8\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2-5x+8\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(-2x+6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=0\\-2x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-1\\2x=6\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};3\right\}\)
Câu d xem lại đề

4x2 – 1 = (2x + 1)(3x – 5)
⇔ 4x2 – 1 – (2x + 1)(3x – 5) = 0
⇔ (2x – 1)(2x + 1) – (2x + 1)(3x – 5) = 0
⇔ (2x + 1)[(2x – 1) – (3x – 5)] = 0
⇔ (2x + 1)(2x – 1 – 3x + 5) = 0
⇔ (2x + 1)(4 – x) = 0
⇔ 2x + 1= 0 hoặc 4 – x = 0
+ 2x + 1 = 0 ⇔ 2x = -1 ⇔ x = -1/2.
+ 4 – x = 0 ⇔ x = 4.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 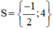

a)(2x+1)(3x-2)=(5x-8)(2x+1)
⇔(2x+1)(3x-2)-(5x-8)(2x+1)=0
⇔(2x+1)(3x-2-5x+8)=0
⇔(2x+1)(-2x+6)=0
⇔2x+1=0 hoặc -2x+6=0
1.2x+1=0⇔2x=-1⇔x=-1/2
2.-2x+6=0⇔-2x=-6⇔x=3
phương trình có 2 nghiệm x=-1/2 và x=3

a, <=> x = -4
b, <=> 6x + 2 = -2x + 5 <=> 8x = 3 <=> x = 3/8
c, <=> 5x + 2x - 2 = 4x + 7 <=> 2x = 9 <=> x = 9 /2
d, <=> 10x^2 - 10x^2 - 15x = 15 <=> x = -1
a, <=> x = -4
b, <=> 6x + 2 = -2x + 5 <=> 8x = 3 <=> x = 3/8
c, <=> 5x + 2x - 2 = 4x + 7 <=> 2x = 9 <=> x = 9 /2
d <=> 10x^2 - 10x^2 - 15x = 15 <=> x = -1

a: =>-x+2x=3-7
=>x=-4
b: =>6x+2+2x-5=0
=>8x-3=0
hay x=3/8
c: =>5x+2x-2-4x-7=0
=>3x-9=0
hay x=3
d: =>10x2-10x2-15x=15
=>-15x=15
hay x=-1

Cách 1:
(x + 1)2 = 4(x2 – 2x + 1)
⇔ (x + 1)2 - 4(x2 – 2x + 1) = 0
⇔ (x + 1)2 - 22. (x -1)2 = 0
⇔ (x + 1)2 – [ 2(x – 1)]2 =0
⇔ [(x+ 1) + 2( x- 1)]. [(x+ 1) - 2( x- 1)]= 0
⇔ ( x+1+ 2x -2) . (x+1 – 2x + 2) =0
⇔ ( 3x- 1).( 3- x) = 0
⇔ 3x – 1 = 0 hoặc 3 – x= 0
+) 3x – 1 = 0 ⇔ 3x = 1 ⇔ x = 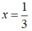
+) 3 – x = 0 ⇔ x= 3
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho là:
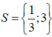
* Cách 2: Ta có:
(x + 1)2 = 4(x2 – 2x + 1)
⇔ (x + 1)2 - 4(x2 – 2x + 1) = 0
⇔ x2 + 2x +1- 4x2 + 8x – 4 = 0
⇔ - 3x2 + 10x – 3 = 0
⇔ (- 3x2 + 9x) + (x – 3) = 0
⇔ -3x (x – 3)+ ( x- 3) = 0
⇔ ( x- 3). ( - 3x + 1) = 0
⇔ x - 3 = 0 hoặc -3x + 1= 0
+) x - 3 = 0 x = 3
+) - 3x + 1 = 0 - 3x = - 1 ⇔ x = 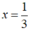
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho là:
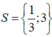
\(\left(x+1\right)^2=4\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\)
\(< =>\left(x+1\right)^2=\left(2x-2\right)^2\)
\(< =>\left(x+1-2x+2\right)\left(x+1+2x-2\right)=0\)
\(< =>\orbr{\begin{cases}-x+3=0\\3x-1=0\end{cases}}\)
\(< =>\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}\)

a) \(9x^2-1=\left(3x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(3x-1\right)=\left(3x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(3x-1\right)-\left(3x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(3x-1-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\3x+1=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\frac{-1}{3}\end{cases}}\)
b) \(\left(4x-3\right)^2=4\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16x^2-24x+9=4x^2-8x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x^2-16x+5=0\)
Ta có \(\Delta=16^2-4.12.5=16,\sqrt{\Delta}=4\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{16+4}{12}=\frac{5}{3}\\x=\frac{16-4}{12}=1\end{cases}}\)

x3 + 3x2 + 2x = 0 ⇔ x(x2 + 3x + 2) = 0
⇔ x = 0 hoặc x2 + 3x + 2 = 0 (1)
Giải phương trình (1) ta được các nghiệm x = -1; x = -2
Vậy phương trình đã cho có 3 nghiệm x = 0; x = -1; x = -2
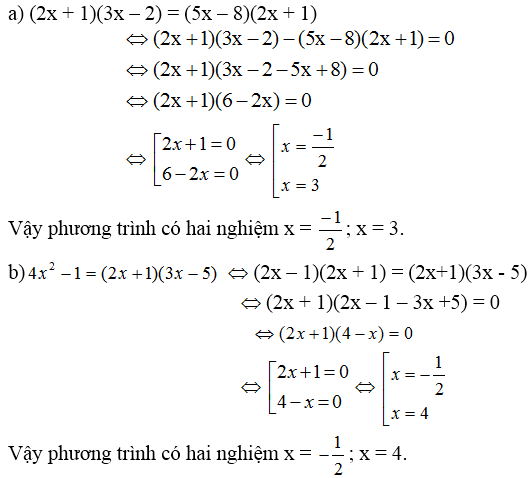
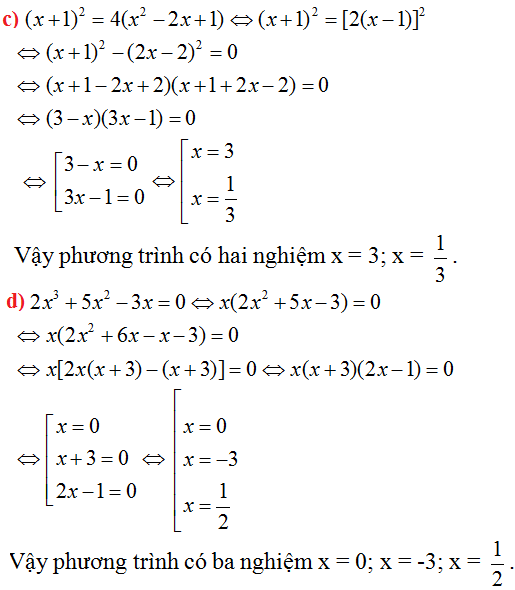
(2x + 1)(3x – 2) = (5x – 8)(2x + 1)
⇔ (2x + 1)(3x – 2) – (5x – 8)(2x + 1) = 0
⇔ (2x + 1).[(3x – 2) – (5x – 8)] = 0
⇔ (2x + 1).(3x – 2 – 5x + 8) = 0
⇔ (2x + 1)(6 – 2x) = 0
⇔ 2x + 1 = 0 hoặc 6 – 2x = 0
+ 2x + 1 = 0 ⇔ 2x = -1 ⇔ x = -1/2.
+ 6 – 2x = 0 ⇔ 6 = 2x ⇔ x = 3.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm