Cho hai hàm số f(x) , g(x) đều có đạo hàm trên ℝ và thỏa mãn: f 3 2 − x − 2 f 2 2 + 3 x + x 2 . g x + 36 x = 0 ∀ x ∈ ℝ . Tính A = 3 f 2 + 4 f ' 2
A. 11
B. 13
C. 14
D. 10
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Chọn đáp án C.
Lấy tích phân hai vế trên đoạn [0;2] có
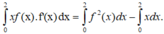
Tích phân từng phần có
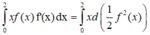
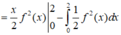
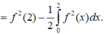
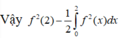
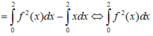
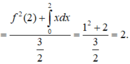

Đáp án D
Ta có y ' = f 1 - x + 2018 x + 2019 ' = 1 - x ' . f ' 1 - x + 2018 = - f ' 1 - x + 2018
= - x 3 - x . g 1 - x - 2018 + 2018 = - x 3 - x . g 1 - x mà g 1 - x < 0 ; ∀ x ∈ ℝ
Nên y ' < 0 ⇔ - x 3 - x . g 1 - x < 0 ⇔ x 3 - x . g 1 - x > 0 ⇔ x 3 - x < 0 ⇔ [ x > 3 x < 0
Khi đó, hàm số y = f 1 - x + 2018 x + 2019 nghịch biến trên khoảng 3 ; + ∞

Đáp án C
Với f x > 0 , ∀ x ∈ ℝ . Xét biểu thức f ' x f x = 2 - 2 x *
Lấy nguyên hàm 2 vế (*), ta được ∫ d f x f x = ∫ 2 - 2 x d x
⇔ ∫ d f x f x = - x 2 + 2 x + C ⇔ ln f x = - x 2 + 2 x + C
Mà f(0) =1 suy ra C = lnf(0) = ln1 = 0. Do đó f x = e - x 2 + 2 x
Xét hàm số f x = e - x 2 + 2 x trên - ∞ ; + ∞ , có f ' x = - 2 x + 2 = 0 ⇔ x = 1
Tính giá trị f 1 = e ; lim x → - ∞ f x = 0 ; lim x → - ∞ f x = 0
Suy ra để phương trình f(x) = m có hai nghiệm thực phân biệt ⇔ 0 < m < e .

1.
\(f'\left(x\right)=3x^2-6mx+3\left(2m-1\right)\)
\(f'\left(x\right)-6x=3x^2-3.2\left(m+1\right)x+3\left(2m-1\right)>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2\left(m+1\right)x+2m-1>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-1>2m\left(x-1\right)\)
Do \(x>2\Rightarrow x-1>0\) nên BPT tương đương:
\(\dfrac{x^2-2x-1}{x-1}>2m\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2-2}{x-1}>2m\)
Đặt \(t=x-1>1\Rightarrow\dfrac{t^2-2}{t}>2m\Leftrightarrow f\left(t\right)=t-\dfrac{2}{t}>2m\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(t\right)\) với \(t>1\) : \(f'\left(t\right)=1+\dfrac{2}{t^2}>0\) ; \(\forall t\Rightarrow f\left(t\right)\) đồng biến
\(\Rightarrow f\left(t\right)>f\left(1\right)=-1\Rightarrow\) BPT đúng với mọi \(t>1\) khi \(2m< -1\Rightarrow m< -\dfrac{1}{2}\)
2.
Thay \(x=0\) vào giả thiết:
\(f^3\left(2\right)-2f^2\left(2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow f^2\left(2\right)\left[f\left(2\right)-2\right]=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}f\left(2\right)=0\\f\left(2\right)=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đạo hàm 2 vế giả thiết:
\(-3f^2\left(2-x\right).f'\left(2-x\right)-12f\left(2+3x\right).f'\left(2+3x\right)+2x.g\left(x\right)+x^2.g'\left(x\right)+36=0\) (1)
Thế \(x=0\) vào (1) ta được:
\(-3f^2\left(2\right).f'\left(2\right)-12f\left(2\right).f'\left(2\right)+36=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f^2\left(2\right).f'\left(2\right)+4f\left(2\right).f'\left(2\right)-12=0\) (2)
Với \(f\left(2\right)=0\) thế vào (2) \(\Rightarrow-12=0\) ko thỏa mãn (loại)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(2\right)=2\)
Thế vào (2):
\(4f'\left(2\right)+8f'\left(2\right)-12=0\Leftrightarrow f'\left(2\right)=1\)
\(\Rightarrow A=3.2+4.1\)

\(f^3\left(2-x\right)-2f^2\left(2+3x\right)+x^2g\left(x\right)+36x=0\) (1)
Thay \(x=0\Rightarrow f^3\left(2\right)-2f^2\left(2\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}f\left(2\right)=0\\f\left(2\right)=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đạo hàm 2 vế của (1):
\(\Rightarrow-3f^2\left(2-x\right).f'\left(2-x\right)-12f\left(2+3x\right).f'\left(2+3x\right)+2x.g\left(x\right)+x^2.g'\left(x\right)+36=0\)
Thay \(x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-3f^2\left(2\right).f'\left(2\right)-12f\left(2\right).f'\left(2\right)+36=0\)
TH1: \(f\left(2\right)=0\Rightarrow36=0\) (ktm)
TH2: \(f\left(2\right)=2\)
\(\Rightarrow-3.2^2.f'\left(2\right)-12.2.f'\left(2\right)+36=0\Rightarrow f'\left(2\right)=1\)
\(\Rightarrow A=3.2+4.1=10\)
Đáp án D
f 3 2 − x − 2 f 2 2 + 3 x + x 2 . g x + 36 x = 0 ∀ x ∈ ℝ 1
− 3 f 2 2 − x . f ' 2 − x − 12 f 2 + 3 x . f ' 2 + 3 x + 2 x . g x + x 2 . g ' x + 36 = 0 ∀ x ∈ ℝ