x-1⋮52 ; x-1⋮35 và 1000 < x < 2000
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


52 x 44 + 84 x 52 + 52 - 52 x 29
= 52 x ( 44 + 84 + 1 - 29 )
= 52 x 100
= 5200
nkớ k nhoa =33

(1 + (1 / 51)) X (1 + (1 / 52)) X (1 + (1 / 53)) =
1.05882352941
( 1+ 1/51 ) x ( 1 + 1/52 ) x ( 1 + 1/53 )
= ( 51/51 + 1/51 ) x ( 52/52 + 1/52 ) x ( 53/53 + 1/53 )
= 52/51 x 53/52 x 54/53
= 52 x 53 x 54/51 x 52 x 53
= 54/51 = 1 3/51 ( hỗn số )

(1 + \(\dfrac{1}{49}\))\(\times\)(1 + \(\dfrac{1}{50}\))\(\times\)(1 + \(\dfrac{1}{51}\))\(\times\)(1 + \(\dfrac{1}{52}\))\(\times\)...\(\times\)(1 + \(\dfrac{1}{60}\))
= \(\dfrac{49+1}{49}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{50+1}{50}\)\(\times\) \(\dfrac{51+1}{51}\)\(\times\)\(\dfrac{52+1}{52}\)\(\times\)...\(\times\)\(\dfrac{61}{60}\)
= \(\dfrac{50}{49}\)\(\times\)\(\dfrac{51}{50}\)\(\times\)\(\dfrac{52}{51}\)\(\times\)...\(\times\)\(\dfrac{61}{60}\)
= \(\dfrac{50\times51\times52\times53\times...\times60}{50\times51\times52\times53\times...\times60}\)\(\times\)\(\dfrac{61}{49}\)
= \(\dfrac{61}{49}\)

a) 3 x 2 − 7 x − 10 ⋅ 2 x 2 + ( 1 − 5 ) x + 5 − 3 = 0
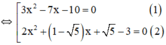
+ Giải (1):
3 x 2 – 7 x – 10 = 0
Có a = 3; b = -7; c = -10
⇒ a – b + c = 0
⇒ (1) có hai nghiệm x 1 = - 1 v à x 2 = - c / a = 10 / 3 .
+ Giải (2):
2 x 2 + ( 1 - √ 5 ) x + √ 5 - 3 = 0
Có a = 2; b = 1 - √5; c = √5 - 3
⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm:
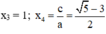
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 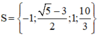
b)
x 3 + 3 x 2 - 2 x - 6 = 0 ⇔ x 3 + 3 x 2 - ( 2 x + 6 ) = 0 ⇔ x 2 ( x + 3 ) - 2 ( x + 3 ) = 0 ⇔ x 2 - 2 ( x + 3 ) = 0
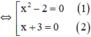
+ Giải (1): x 2 – 2 = 0 ⇔ x 2 = 2 ⇔ x = √2 hoặc x = -√2.
+ Giải (2): x + 3 = 0 ⇔ x = -3.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-3; -√2; √2}
c)
x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = 0 , 6 x 2 + x ⇔ x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = x ⋅ ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) ⇔ x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) − x ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = 0 ⇔ ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) x 2 − 1 − x = 0
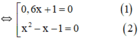
+ Giải (1): 0,6x + 1 = 0 ⇔ 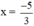
+ Giải (2):
x 2 – x – 1 = 0
Có a = 1; b = -1; c = -1
⇒ Δ = ( - 1 ) 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 1 ) = 5 > 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm 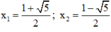
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 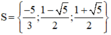
d)
x 2 + 2 x − 5 2 = x 2 − x + 5 2 ⇔ x 2 + 2 x − 5 2 − x 2 − x + 5 2 = 0 ⇔ x 2 + 2 x − 5 − x 2 − x + 5 ⋅ x 2 + 2 x − 5 + x 2 − x + 5 = 0 ⇔ ( 3 x − 10 ) 2 x 2 + x = 0
⇔ (3x-10).x.(2x+1)=0
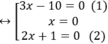
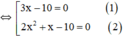
+ Giải (1): 3x – 10 = 0 ⇔ 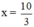
+ Giải (2):
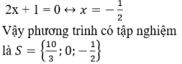
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\in BC\left(52;35\right)=\left\{1820;3640;5460;...\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{1821;3641;5461;...\right\}\)
Mà \(1000< x< 2000\)
\(\Rightarrow x=1821\)