Giải các phương trình sau :
a) \(\tan\left(2x+1\right)\tan\left(3x-1\right)=1\)
b) \(\tan x+\tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=1\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Đặt \(tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=t\)
\(\Rightarrow t^2+\left(\sqrt{3}-1\right)t-\sqrt{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t\left(t-1\right)+\sqrt{3}\left(t-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=1\\t=-\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=1\\tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=-\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}=\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}=-\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{\pi}{12}+k\pi\\x=-\dfrac{2\pi}{3}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)

a1.
$\cot (2x+\frac{\pi}{3})=-\sqrt{3}=\cot \frac{-\pi}{6}$
$\Rightarrow 2x+\frac{\pi}{3}=\frac{-\pi}{6}+k\pi$ với $k$ nguyên
$\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-\pi}{4}+\frac{k}{2}\pi$ với $k$ nguyên
a2. ĐKXĐ:...............
$\cot (3x-10^0)=\frac{1}{\cot 2x}=\tan 2x$
$\Leftrightarrow \cot (3x-\frac{\pi}{18})=\cot (\frac{\pi}{2}-2x)$
$\Rightarrow 3x-\frac{\pi}{18}=\frac{\pi}{2}-2x+k\pi$ với $k$ nguyên
$\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{\pi}{9}+\frac{k}{5}\pi$ với $k$ nguyên.
a3. ĐKXĐ:........
$\cot (\frac{\pi}{4}-2x)-\tan x=0$
$\Leftrightarrow \cot (\frac{\pi}{4}-2x)=\tan x=\cot (\frac{\pi}{2}-x)$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\pi}{4}-2x=\frac{\pi}{2}-x+k\pi$ với $k$ nguyên
$\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{\pi}{4}+k\pi$ với $k$ nguyên.
a4. ĐKXĐ:.....
$\cot (\frac{\pi}{6}+3x)+\tan (x-\frac{\pi}{18})=0$
$\Leftrightarrow \cot (\frac{\pi}{6}+3x)=-\tan (x-\frac{\pi}{18})=\tan (\frac{\pi}{18}-x)$
$=\cot (x+\frac{4\pi}{9})$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\pi}{6}+3x=x+\frac{4\pi}{9}+k\pi$ với $k$ nguyên
$\Rightarrow x=\frac{5}{36}\pi + \frac{k}{2}\pi$ với $k$ nguyên.

a) \(x=-45^0+k90^0,k\in\mathbb{Z}\)
b) \(x=-\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi,k\in\mathbb{Z}\)
c) \(x=\dfrac{3\pi}{4}+k2\pi,k\in\mathbb{Z}\)
d) \(x=300^0+k540^0,k\in\mathbb{Z}\)

Em nghĩ là thầy viết tương đương là sai. Phương trình đầu không thể nhận sinx = 1 làm nghiệm được, còn phương trình cuối thì có ... nên không tương đương ạ
Lời giải:
ĐKXĐ:.........
PT \(\Leftrightarrow (1-\sin x).\frac{\sin ^2x}{\cos ^2x}=1+\cos x\)
\(\Rightarrow (1-\sin x)\sin ^2x=\cos ^2x(1+\cos x)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (\sin^2x-\cos ^2x)-(\sin ^3x+\cos ^3x)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (\sin x+\cos x)[(\sin x-\cos x)-(\sin ^2x-\sin x\cos x+\cos ^2x)]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (\sin x+\cos x)(\sin x-\cos x-1+\sin x\cos x)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (\sin x+\cos x)(\sin x-1)(\cos x+1)=0\)
Đến đây thì đơn giản rồi.

Câu 2:
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(n+2\right)!}{2!\cdot n!}-4\cdot\dfrac{\left(n+1\right)!}{n!\cdot1!}=2\left(n+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(n+1\right)\left(n+2\right)}{2}-4\cdot\dfrac{n+1}{1}=2\left(n+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(n+1\right)\left(n+2\right)-8\left(n+1\right)=4\left(n+1\right)\)
=>(n+1)(n+2-8-4)=0
=>n=-1(loại) hoặc n=10
=>\(A=\left(\dfrac{1}{x^4}+x^7\right)^{10}\)
SHTQ là: \(C^k_{10}\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{x^4}\right)^{10-k}\cdot x^{7k}=C^k_{10}\cdot1\cdot x^{11k-40}\)
Số hạng chứa x^26 tương ứng với 11k-40=26
=>k=6
=>Số hạng cần tìm là: \(210x^{26}\)

a, Ta có : \(\sin\left(3x+60\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow3x+60=30+2k180\)
\(\Rightarrow3x=2k180-30\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=120k-10\)
Vậy ...
b, Ta có : \(\cos\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=-\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow2x-\dfrac{\pi}{3}=\dfrac{3}{4}\pi+k2\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{13}{24}\pi+k\pi\)
Vậy ...
c, Ta có : \(tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)=\sqrt{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}=\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\)
Vậy ...
d, Ta có : \(\cot\left(2x+\pi\right)=-1\)
\(\Rightarrow2x+\pi=\dfrac{3}{4}\pi+k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{8}\pi+\dfrac{k}{2}\pi\)
Vậy ...
a) \(sin\left(3x+60^0\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\left(3x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=sin\dfrac{\pi}{6}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi\\3x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}=\dfrac{5\pi}{6}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)(\(k\in Z\))\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-\pi}{18}+\dfrac{k2\pi}{3}\\x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+\dfrac{k2\pi}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)(\(k\in Z\))
Vậy...
b) Pt\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=cos\dfrac{3\pi}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-\dfrac{\pi}{3}=\dfrac{3\pi}{4}+k2\pi\\2x-\dfrac{\pi}{3}=-\dfrac{3\pi}{4}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)(\(k\in Z\))\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{13\pi}{24}+k\pi\\x=-\dfrac{5\pi}{24}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)(\(k\in Z\))
Vậy...
c) Pt \(\Leftrightarrow tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)=tan\dfrac{\pi}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}=\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k\pi,k\in Z\)\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi,k\in Z\)
Vậy...
d) Pt \(\Leftrightarrow tan\left(2x+\pi\right)=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+\pi=-\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi,k\in Z\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{5\pi}{8}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2},k\in Z\)
Vậy...
a) tan(2x + 1)tan(3x - 1) = 1 ⇔sin(3x&space;-&space;1)%7D%7Bcos(2x&space;+&space;1)cos(3x&space;-&space;1)%7D) = 1.
= 1.
Với điều kiện cos(2x + 1)cos(3x - 1) ≠ 0 phương trình tương đương với
cos(2x + 1)cos(3x - 1) - sin(2x + 1)sin(3x - 1) = 0
⇔ cos(2x + 1 + 3x - 1) = 0 ⇔ 5x =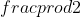 + k π ⇔ x =
+ k π ⇔ x = 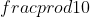 +
+ 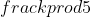 , k ∈ Z.
, k ∈ Z.
Cần chọn các k nguyên để x =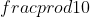 +
+ 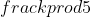 không thỏa mãn điều kiện của phương trình (để loại bỏ). Điều này chỉ xảy ra trong các trường hợp sau:
không thỏa mãn điều kiện của phương trình (để loại bỏ). Điều này chỉ xảy ra trong các trường hợp sau:
(i) x =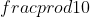 +
+ 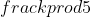 làm cho cos(2x + 1) = 0, tức là
làm cho cos(2x + 1) = 0, tức là
cos[2(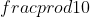 +
+ 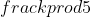 ) + 1] = 0 ⇔
) + 1] = 0 ⇔ prod&space;%7D%7B5%7D) + 1 =
+ 1 = 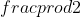 + lπ, (l ∈ Z)
+ lπ, (l ∈ Z)
⇔ π(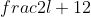 -
- 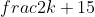 ) = 1 ⇔ π =
) = 1 ⇔ π = %7D) , suy ra π ∈ Q, vô lí.
, suy ra π ∈ Q, vô lí.
Vì vậy không có k nguyên nào để x =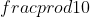 +
+ 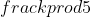 làm cho cos(2x + 1) = 0.
làm cho cos(2x + 1) = 0.
(ii) x =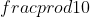 +
+ 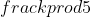 làm cho cos(3x - 1) = 0. Tương tự (i),ta cũng thấy không có k nguyên nào để x =
làm cho cos(3x - 1) = 0. Tương tự (i),ta cũng thấy không có k nguyên nào để x = 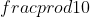 +
+ 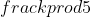 làm cho cos(3x - 1) = 0.
làm cho cos(3x - 1) = 0.
Vậy ∀ k ∈ Z, x =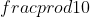 +
+ 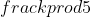 đều là nghiệm của phương trình đã cho.
đều là nghiệm của phương trình đã cho.
b)Đặt t = tan x, phương trình trở thành
t +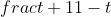 = 1 ⇔ -t2 + 3t = 0 (điều kiện t ≠ 1) ⇔ t = 0 hoặc t = 3 (thỏa mãn)
= 1 ⇔ -t2 + 3t = 0 (điều kiện t ≠ 1) ⇔ t = 0 hoặc t = 3 (thỏa mãn)
Vậy tan x = 0 ⇔ x = kπ
tan x = 3 ⇔ x = arctan 3 + kπ (k ∈ Z)