
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Câu 4:
Giả sử điều cần chứng minh là đúng
\(\Rightarrow x=y\), thay vào điều kiện ở đề bài, ta được:
\(\sqrt{x+2014}+\sqrt{2015-x}-\sqrt{2014-x}=\sqrt{x+2014}+\sqrt{2015-x}-\sqrt{2014-x}\) (luôn đúng)
Vậy điều cần chứng minh là đúng
2) \(\sqrt{x^2-5x+4}+2\sqrt{x+5}=2\sqrt{x-4}+\sqrt{x^2+4x-5}\)
⇔ \(\sqrt{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-1\right)}-2\sqrt{x-4}+2\sqrt{x+5}-\sqrt{\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)}=0\)
⇔ \(\sqrt{x-4}.\left(\sqrt{x-1}-2\right)-\sqrt{x+5}\left(\sqrt{x-1}-2\right)=0\)
⇔ \(\left(\sqrt{x-4}-\sqrt{x+5}\right)\left(\sqrt{x-1}-2\right)=0\)
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x-4}-\sqrt{x+5}=0\\\sqrt{x-1}-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x-4}=\sqrt{x+5}\\\sqrt{x-1}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\in\varnothing\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ x = 5
Vậy S = {5}

Các bước làm:
Thử nghiệm: x = 2 là nghiệm
------> Thử xem các cách làm tất nhiên là không thể bình phương -----> Như vậy thường thì cô sẽ nghĩ ra hai cách là liên hợp và đặt ẩn phụ
+) Cách liên hợp: Căn đầu tiên thay 2 vào kết quả 1 ; căn thứ 2 thay 2 vào đc kết quả là 3
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Giải: ĐK: \(1\le x\le3\) ( không cần thiết phải giải luôn điều kiện ra như thế nhé!
\(\sqrt{-x^2+4x-3}+\sqrt{-2x^2+8x+1}=x^3-4x^2+4x+4\)
<=> \(\sqrt{-x^2+4x-3}-1+\sqrt{-2x^2+8x+1}-3=x^3-4x^2+4x+4-4\)
<=> \(\frac{-\left(x-2\right)^2}{\sqrt{-x^2+4x-3}+1}+\frac{-2\left(x-2\right)^2}{\sqrt{-2x^2+8x+1}+3}=x\left(x-2\right)^2\) ( hình như là đẹp)
<=> \(\left(x-2\right)^2\left[x+\frac{1}{\sqrt{-x^2+4x-3}+1}+\frac{2}{\sqrt{-2x^2+8x+1}+3}\right]=0\)( cái trong ngoặc vuông rõ ràng là > 0 với mọi \(1\le x\le3\))
<=> x - 2 = 0
<=> x = 2 thỏa mãn đk

ĐKXĐ : ....
PT \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{-x^2+4x-3}-1+\sqrt{-2x^2+8x+1}-3=x\left(x^2-4x+4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{-x^2+4x-4}{\sqrt{-x^2+4x-3}+1}+\frac{-2x^2+8x-8}{\sqrt{-2x^2+8x+1}+3}=x\left(x-2\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{\sqrt{-x^2+4x-3}+1}+\frac{2\left(x-2\right)^2}{\sqrt{-2x^2+8x+1}+3}+x\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{-x^2+4x-3}+1}+\frac{2}{\sqrt{-2x^2+8x+1}+3}+x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\left(x-2\right)^2=0\\\frac{1}{\sqrt{-x^2+4x-3}+1}+\frac{2}{\sqrt{-2x^2+8x+1}+3}+x=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\\frac{1}{\sqrt{-x^2+4x-3}+1}+\frac{2}{\sqrt{-2x^2+8x+1}+3}+x>0\left(loai\right)\end{cases}}\)


Điều kiện 1 =<x=<3
\(\sqrt{-x^2+4x-3}+\sqrt{-2x^2+8x+1}=x^3-4x^2+4x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{-x^2+4x-3}-1+\sqrt{-2x^2+8x+1}-3=x\left(x^2-4x+4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{-x^2+4x-4}{\sqrt{-x^2+4x-3}+1}+\frac{-2x^2+8x-8}{\sqrt{-2x^2+8x+x}+3}=x\left(x-2\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)^2+\frac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{\sqrt{-x^2+4x-3}+1}+\frac{2\left(x-2\right)^2}{\sqrt{-2x^2+8x+x}+3}=x\left(x-2\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2\left(x+\frac{1}{\sqrt{-x^2+4x-3}+1}+\frac{2\left(x-2\right)^2}{\sqrt{-2x^2+8x+1}+3}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=0\left(x+\frac{1}{\sqrt{-x^2+4x-3}+1}+\frac{2}{\sqrt{-2x^2+8x+1}+3}>0\right)\)
<=> x=2(tmđk)

\(ĐKXĐ:\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\\5-4x^2\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\) (*)
Ta có pt cho tương đương :
\(8-6\sqrt{2x-1}-2x\sqrt{5-4x^2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(5-4x^2-2x\sqrt{5-4x^2}+x^2\right)+3.\left(2x-1-2\sqrt{2x-1}+1\right)+3\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{5-4x^2}-x\right)^2+3\left(\sqrt{2x-1}-1\right)^2+3\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi và chỉ ra \(x=1\) ( Thỏa mãn (*) )
Vậy pt có nghiệm duy nhất \(x=1\)

a)ĐK:\(\begin{cases}25x^2-9 \ge 0\\5x+3 \ge 0\\\end{cases}\)
`<=>` \(\begin{cases}(5x-3)(5x+3) \ge 0\\5x+3 \ge 0\\\end{cases}\)
`<=>` \(\begin{cases}\left[ \begin{array}{l}x\ge \dfrac35\\x \le -\dfrac35\end{array} \right.\\\end{cases}\)
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=-\dfrac35\\x \ge \dfrac35\end{array} \right.\)
`pt<=>\sqrt{5x+3}(\sqrt{5x-3}-2)=0`
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}5x+3=0\\\sqrt{5x-3}=2\end{array} \right.\)
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=-\dfrac35\\5x-3=4\end{array} \right.\)
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=-\dfrac35\\x=7/5\end{array} \right.\)
`b)sqrt{x-3}/sqrt{2x+1}=2`
ĐK:\(\begin{cases}x-3 \ge 0\\2x+1>0\\\end{cases}\)
`<=>x>=3`
`pt<=>sqrt{x-3}=2sqrt{2x+1}`
`<=>x-3=8x+4`
`<=>7x=7`
`<=>x=1(l)`
`c)sqrt{x^2-2x+1}+sqrt{x^2-4x+4}=3`
`<=>sqrt{(x-1)^2}+sqrt{(x-2)^2}=3`
`<=>|x-1|+|x-2|=3`
`**x>=2`
`pt<=>x-1+x-2=3`
`<=>2x=6`
`<=>x=3(tm)`
`**x<=1`
`pt<=>1-x+2-x=3`
`<=>3-x=3`
`<=>x=0(tm)`
`**1<=x<=2`
`pt<=>x-1+2-x=3`
`<=>=-1=3` vô lý
Vậy `S={0,3}`
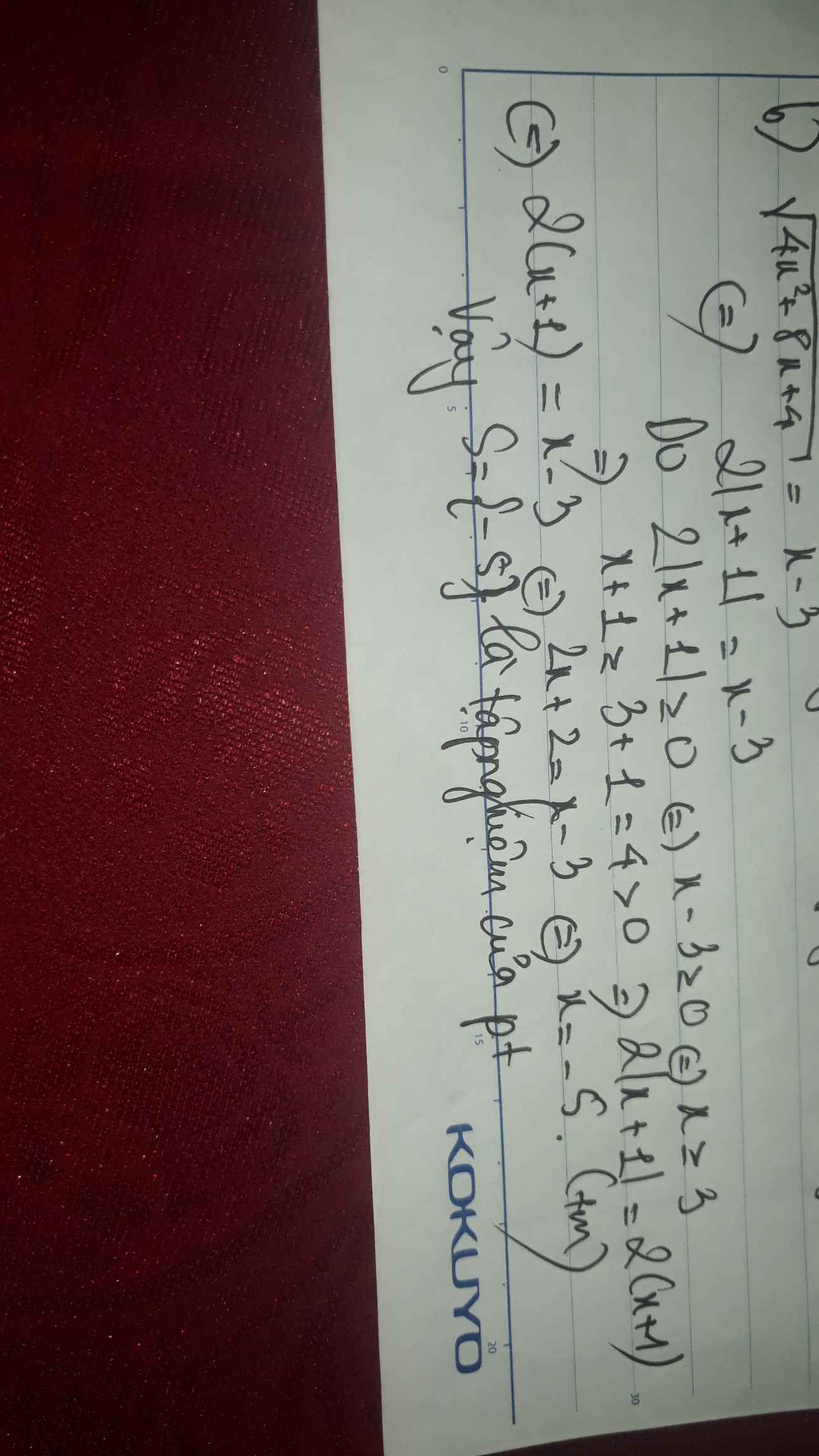

ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge0\)
\(x^2+2x+4=3\sqrt{x^3+4x}\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+4=3.\sqrt{x}.\sqrt{x^2+4}\)
Ta có: x=0 không là nghiệm của phương trình => \(x\ne0\)\(\Rightarrow\)Chia cả 2 vế cho x ta được:
\(x+2+\frac{4}{x}=3.\frac{\sqrt{x^2+4}}{\sqrt{x}}=3.\sqrt{\frac{x^2+4}{x}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+2+\frac{4}{x}\right)^2=\left(3.\sqrt{\frac{x^2+4}{x}}\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+4+\frac{16}{x^2}+4x+\frac{16}{x}+8=9.\frac{x^2+4}{x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+\frac{16}{x^2}+4x+\frac{16}{x}+12=\frac{9x^2+36}{x}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+\frac{16}{x^2}+4x+\frac{16}{x}+12\right).x=9x^2+36\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+\frac{16}{x}+4x^2+16+12x=9x^2+36\Leftrightarrow x^3-5x^2-20+12x+\frac{16}{x}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^4-5x^3-20x+12x^2+16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^4-2x^3\right)-\left(3x^3-6x^2\right)+\left(6x^2-12x\right)-\left(8x-16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right).\left(x^3-3x^2+6x-8\right)=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right).\left(\left(x^3-2x^2\right)-\left(x^2-2x\right)+\left(4x-8\right)\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right).\left(x-2\right).\left(x^2-x+4\right)=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2.\left(\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{15}{4}\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-2=0\Leftrightarrow x=2\)(thỏa mãn x>0)
Vậy x=2