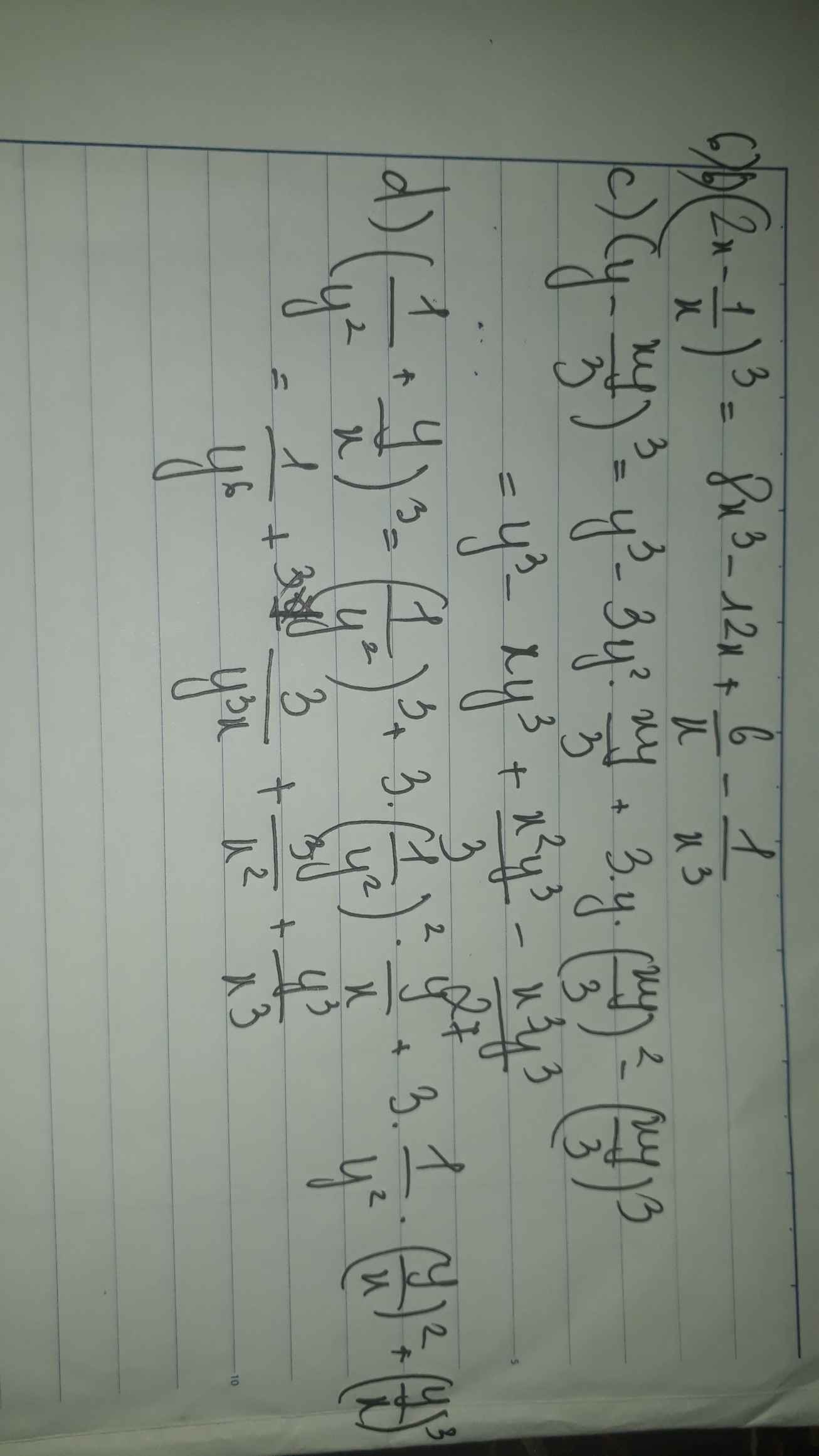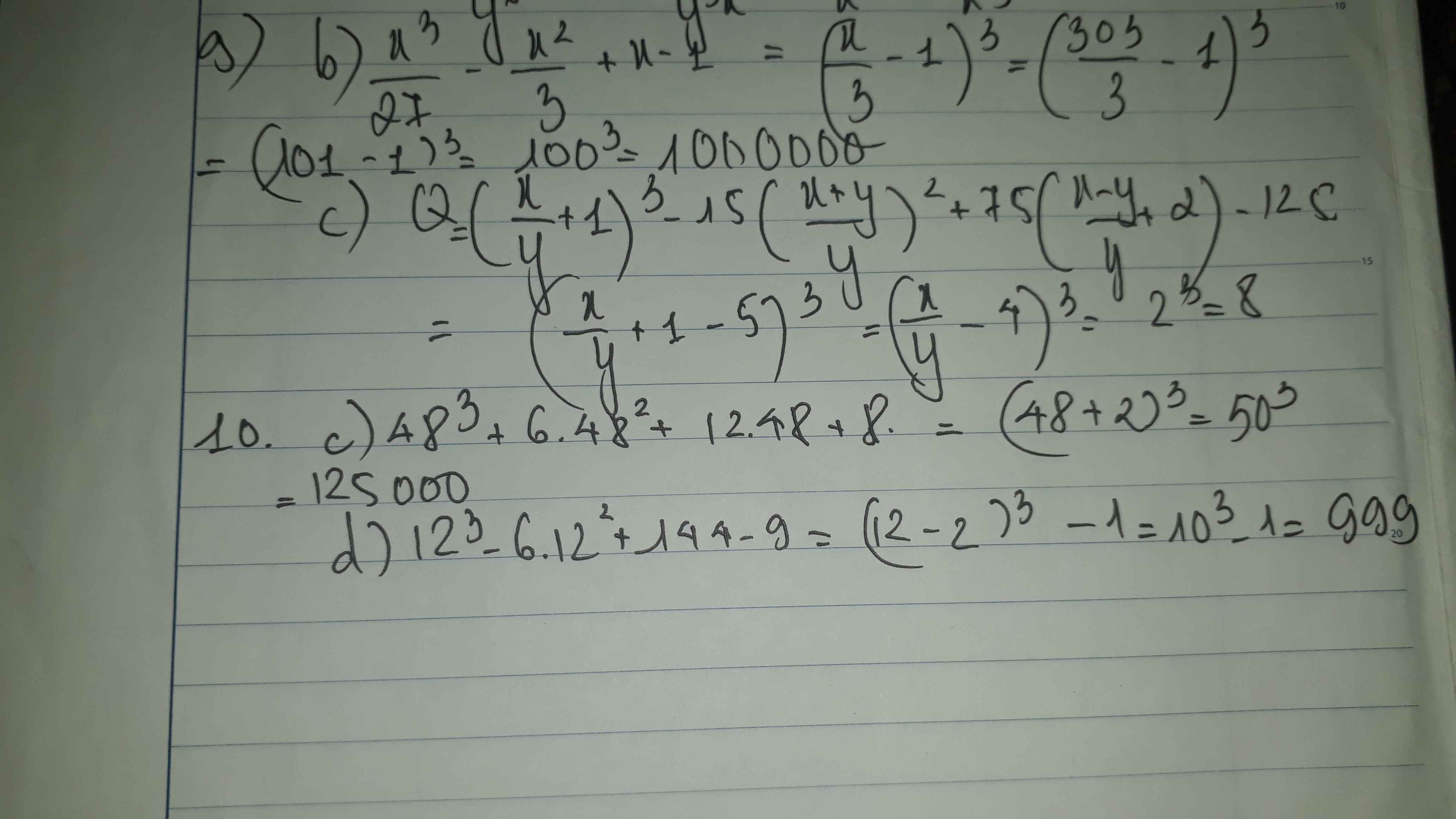Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) \(\dfrac{2x}{3}\)+\(\dfrac{2x-1}{6}\)=4 - \(\dfrac{x}{3}\)
<=>\(\dfrac{2x}{3}\)+\(\dfrac{2x-1}{6}\) - 4+\(\dfrac{x}{3}\)=0
<=>\(\dfrac{2x.2+2x-1-4.6+x.2}{6}\)=0
=>4x-2x-24+2x=0
<=>4x-24=0
<=>4x=24
<=>x=6
Vậy x=6
b)\(\dfrac{x-1}{2}\)+\(\dfrac{x-1}{4}\)=1 - \(\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)}{3}\)
<=>\(\dfrac{x-1}{2}\)+\(\dfrac{x-1}{4}\)-1+\(\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)}{3}\)=0
<=>\(\dfrac{6.\left(x-1\right)+3\left(x-1\right)-1.12+4.2\left(x-1\right)}{12}\)=0
=>6x-6+3x-3-12+4x-4+2x-2=0
<=>15x-27=0
<=>15x=27
<=>x=\(\dfrac{9}{5}\)
Vậy x=\(\dfrac{9}{5}\)

Lời giải.
c.
$x^3-3x^2+3x-1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-1)^3=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=1$
Vậy pt có tập nghiệm $S=\left\{1\right\}$
d. ĐKXĐ: $x\neq \frac{-1}{3}; -3$
PT $\Leftrightarrow \frac{(3x-1)(x+3)+(x-3)(3x+1)}{(3x+1)(x+3)}=2$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{6x^2-6}{3x^2+10x+3}=2$
$\Leftrightarrow 6x^2-6=2(3x^2+10x+3)$
$\Leftrightarrow 20x+12=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-3}{5}$ (tm)
Vậy tập nghiệm của pt là $S=\left\{\frac{-3}{5}\right\}$
Bài 2:
a.
\(\left\{\begin{matrix} 2x-3y=11\\ 5x-4y=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} 10x-15y=55\\ 10x-8y=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow (10x-8y)-(10x-15y)=6-55\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 7y=-49\Leftrightarrow y=-7\)
\(x=\frac{3y+11}{2}=\frac{3.(-7)+11}{2}=-5\)
Vậy hpt có nghiệm $(x,y)=(-5,-7)$
b. Không đủ cơ sở để tìm $x,y$
c.
\(\left\{\begin{matrix} 5x+3y=\lambda\\ -x+\lambda y=-8\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} 5x+3y=\lambda\\ -5x+5\lambda y=-40\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow (3+5\lambda)y=\lambda-40\)
Nếu $\lambda = \frac{-3}{5}$ thì $0.y=\frac{-203}{5}$ (vô lý) nên hpt vô nghiệm
Nếu $\lambda \neq \frac{-3}{5}$ thì:
$y=\frac{\lambda - 40}{3+5\lambda}$
$x=8+\lambda y=\frac{\lambda ^2+24}{5\lambda +3}$

1.
\(\left(x+y\right)^2=\left(\dfrac{1}{2}.2x+\dfrac{1}{3}.3y\right)^2\le\left(\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{9}\right)\left(4x^2+9y^2\right)=\dfrac{169}{36}\)
\(\Rightarrow-\dfrac{13}{6}\le x+y\le\dfrac{13}{6}\)
Dấu "=" lần lượt xảy ra tại \(\left(-\dfrac{3}{2};-\dfrac{2}{3}\right)\) và \(\left(\dfrac{3}{2};\dfrac{2}{3}\right)\)
2.
\(\left(y-2x\right)^2=\left(\dfrac{1}{4}.4y+\left(-\dfrac{1}{3}\right).6x\right)^2\le\left(\dfrac{1}{16}+\dfrac{1}{9}\right)\left(16y^2+36x^2\right)=\dfrac{25}{16}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|y-2x\right|\le\dfrac{5}{4}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(\mp\dfrac{2}{5};\pm\dfrac{9}{20}\right)\)
3.
\(B^2=\left(6.\sqrt{x-1}+8\sqrt{3-x}\right)^2\le\left(6^2+8^2\right)\left(x-1+3-x\right)=200\)
\(\Rightarrow B\le2\sqrt{10}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(\dfrac{\sqrt{x-1}}{6}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3-x}}{8}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{43}{25}\)
\(B=6\sqrt{x-1}+6\sqrt{3-x}+2\sqrt{3-x}\ge6\sqrt{x-1}+6\sqrt{3-x}\)
\(B\ge6\left(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{3-x}\right)\ge6\sqrt{x-1+3-x}=6\sqrt{2}\)
\(B_{min}=6\sqrt{2}\) khi \(\sqrt{3-x}=0\Rightarrow x=3\)
4.
\(49=\left(3a+4b\right)^2=\left(\sqrt{3}.\sqrt{3}a+2.2b\right)^2\le\left(3+4\right)\left(3a^2+4b^2\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow3a^2+4b^2\ge\dfrac{49}{7}=7\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(a=b=1\)

- Gọi quãng đường AB là x (km)
vì thời gian là bằng quãng đường chia vận tốc, ta có:
- Thời gian của ô tô là \(\dfrac{x}{50}\) (km)
- Thời gian của xe máy là \(\dfrac{x}{40}\) (km)
vì ta dùng đơn vị là km/h nên ta phải đổi 30 phút qua giờ, ta có:
- Đổi: 30 phút = 0,5 giờ
vì thời gian đi của ô tô ít hơn xe máy là 0,5 giờ nên ta có phương trình:
\(\dfrac{x}{40}\) \(-\) \(\dfrac{x}{50}\) = 0,5
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\dfrac{x\times50}{40\times50}\)\(-\)\(\dfrac{x\times40}{50\times40}\) = \(\dfrac{0,5\times40\times50}{40\times50}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\dfrac{50x}{40\times50}\)\(-\dfrac{40x}{50\times40}=\dfrac{1000}{50\times40}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) 50x - 40x = 1000
\(\Leftrightarrow\)10x = 1000
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x = 1000 : 10
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x = 100
vậy quãng đường AB là 100 (km)
----chúc cậu học tốt----
Đổi \(30phút=\dfrac{1}{2}h\)
Gọi quãng đường AB là \(x\left(km;x>0\right)\)
Thì thời gian ô tô đi từ A đến B là \(\dfrac{x}{50}\left(h\right)\)
Thời gian xe máy đi từ A đến B là \(\dfrac{x}{40}\left(h\right)\)
Vì thời gian đi từ A đến B của ô tô ít hơn của xe máy là \(\dfrac{1}{2}h\) nên ta có phương trình :
\(\dfrac{x}{40}-\dfrac{x}{50}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x-4x=100\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=100\left(nhận\right)\)
Vậy quãng đường AB dài \(100km\)

b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-7\right)\left(3x+7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=-\dfrac{7}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a: Xét tứ giác AEDF có
AE//DF
AF//DE
Do đó: AEDF là hình bình hành
mà \(\widehat{DAE}=90^0\)
nên AEDF là hình chữ nhật

Bài 2:
a: Xét ΔEHK và ΔGFI có
\(\widehat{EHK}=\widehat{GFI}\)
EH=GF
\(\widehat{E}=\stackrel\frown{G}\)
Do đó: ΔEHK=ΔGFI
Suy ra: EK=GI và KH=IF
Ta có: EK+KF=EF
GI+IH=GH
mà EF=GH
và EK=GI
nên KF=IH
Xét tứ giác FKHI có
FK=HI
HK=FI
Do đó: FKHI là hình bình hành




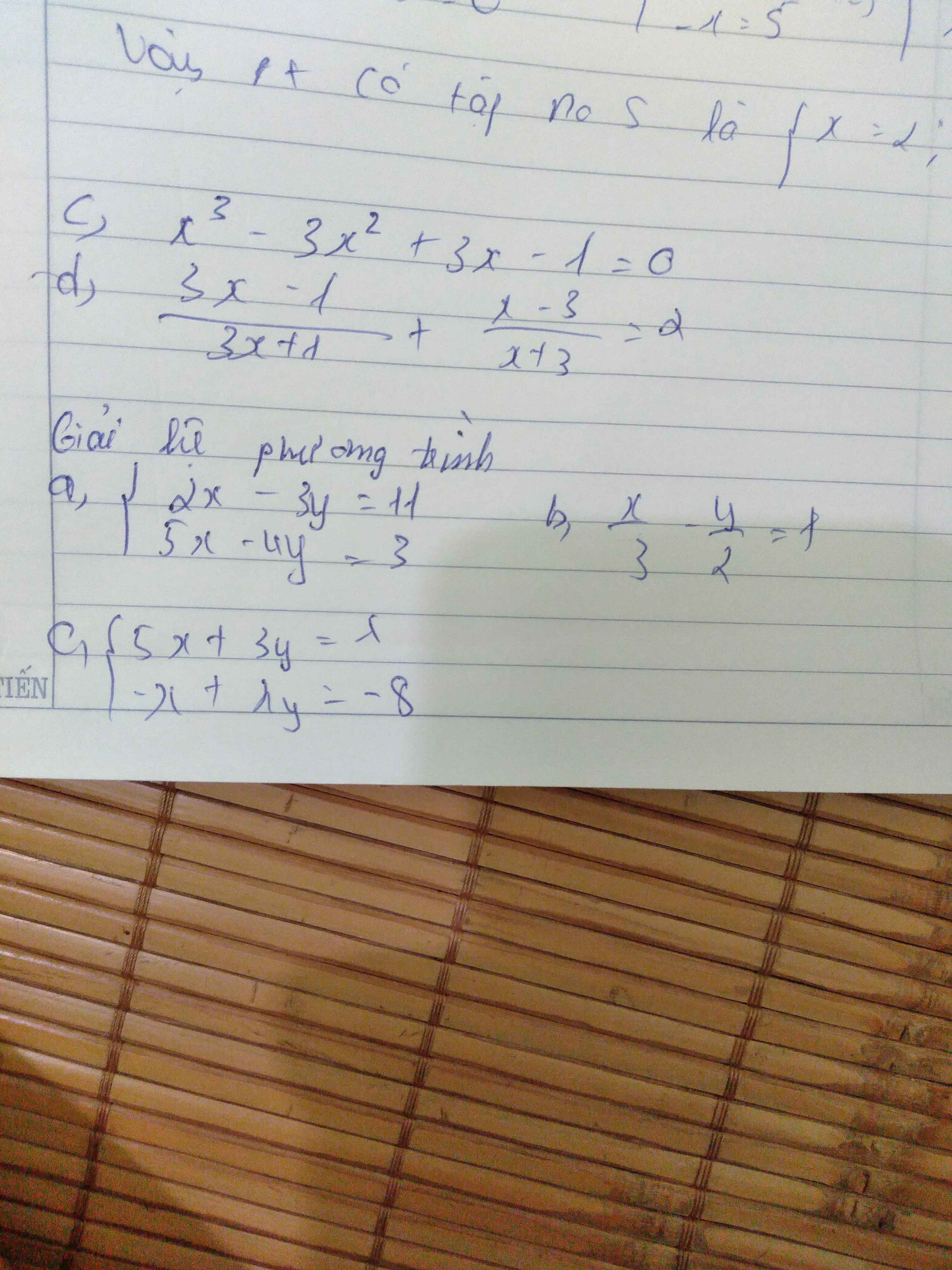


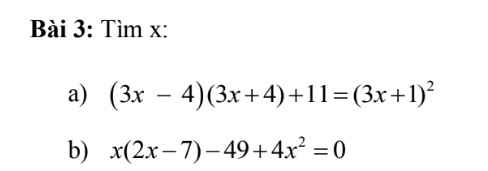


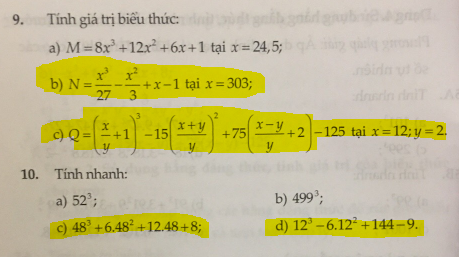 Mọi người ơi giúp em với ạ. Mai em phải nộp rồi. Mấy phần em đánh dấu đó mọi người.
Mọi người ơi giúp em với ạ. Mai em phải nộp rồi. Mấy phần em đánh dấu đó mọi người.