
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Ta có: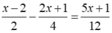
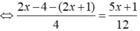
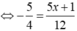
⇔ 5x + 1 = - 15 ⇔ x = - 16/5
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S = { - 16/5 }

4) Ta có: \(\dfrac{2x-5}{5}-\dfrac{x+3}{3}=\dfrac{2-3x}{2}-x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{6\left(2x-5\right)}{30}-\dfrac{10\left(x+3\right)}{30}=\dfrac{15\left(2-3x\right)}{30}-\dfrac{30\left(x+2\right)}{30}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-30-10x-30=30-45x-30x-60\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-22x-60=-75x-30\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-22x+75x=-30+60\)
\(\Leftrightarrow53x=30\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{30}{53}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{30}{53}\right\}\)
5) Ta có: \(\dfrac{5x-3}{6}-\dfrac{7x-1}{4}=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\left(5x-3\right)}{12}-\dfrac{3\left(7x-1\right)}{12}=\dfrac{60}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow10x-6-21x+3=60\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-11x-3=60\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-11x=63\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{63}{11}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{63}{11}\right\}\)
`9,x^3+x^2-2=0`
`x^3-x^2+2x^2-2=0`
`<=>x^2(x-1)+2(x-1)(x+1)=0`
`<=>(x-1)(x^2+2x+2)=0`
`<=>x=1`
`14,x^2-2x+1=0`
`<=>(x-1)^2=0`
`<=>x-1=0`
`<=>x=1`
`15,x^3+3x^2+3x+1=0`
`<=>(x+1)^3=0`
`<=>x+1=0`
`<=>x=-1`

Bài 6:
1) Ta có: \(2x\left(x-5\right)-\left(x+3\right)^2=3x-x\left(5-x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-10x-\left(x^2+6x+9\right)=3x-5x+x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-10x-x^2-6x-9-3x+5x-x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-14x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-14x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{9}{14}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{9}{14}\right\}\)
`1)2x(x-5)-(x+3)^2=3x-x(5-x)`
`<=>2x^2-10x-x^2-6x-9=3x-5x+x^2`
`<=>x^2-16x-9=x^2-2x`
`<=>14x=-9`
`<=>x=-9/14`

x(2x – 7) – 4x + 14 = 0
⇔ x.(2x - 7) – (4x – 14) = 0
⇔ x(2x – 7) – 2(2x – 7) = 0
⇔(x – 2)(2x – 7) = 0
⇔ x – 2 = 0 hoặc 2x – 7 = 0
+ x – 2 = 0 ⇔ x = 2.
+ 2x – 7 = 0 ⇔ 2x = 7 ⇔ x = 7/2
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là 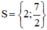

x - 1 2 + x - 1 4 = 1 - 2 x - 1 2 ⇔ x - 1 2 + x - 1 4 = 1 - 2 x - 2 3
⇔ 6(x – 1) + 3(x – 1) = 12 – 4(2x – 2)
⇔ 6x – 6 + 3x – 3 = 12 – 8x + 8 ⇔ 6x + 3x + 8x = 12 + 8 + 6 + 3
⇔ 17x = 29 ⇔ x = 29/17
Phương trình có nghiệm x = 29/17

x + 1 3 + 3 2 x + 1 4 = 2 x + 3 x + 1 6 + 7 + 12 x 12 ⇔ x + 1 3 + 6 x + 3 4 = 5 x + 3 6 + 7 + 12 x 12
⇔ 4(x + 1) + 3(6x + 3) = 2(5x + 3) + 7 + 12x
⇔ 4x + 4 + 18x + 9 = 10x + 6 + 7 + 12x
⇔ 4x + 18x – 10x – 12x = 6 + 7 – 4 – 9
⇔ 0x = 0
Phương trình có vô số nghiệm.
2x – 14 = 0
⇔ 2x = 14
⇔ x = 7
Vậy phương trình có 1 nghiệm x = 7