Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

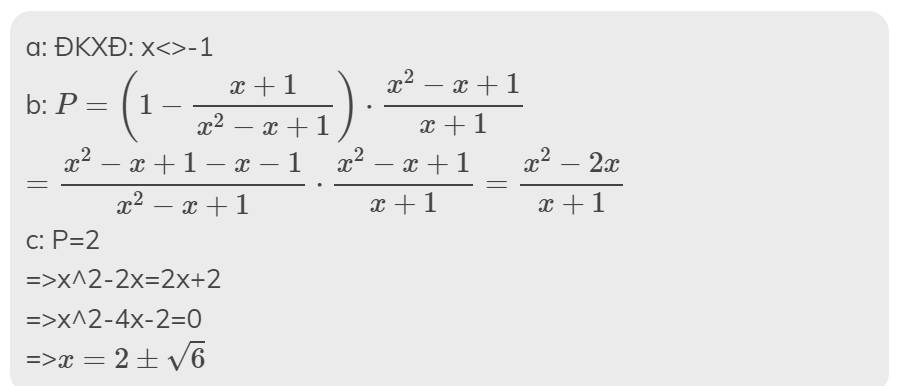
a: ĐKXĐ: x<>-1
b: \(P=\left(1-\dfrac{x+1}{x^2-x+1}\right)\cdot\dfrac{x^2-x+1}{x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-x+1-x-1}{x^2-x+1}\cdot\dfrac{x^2-x+1}{x+1}=\dfrac{x^2-2x}{x+1}\)
c: P=2
=>x^2-2x=2x+2
=>x^2-4x-2=0
=>\(x=2\pm\sqrt{6}\)

Điều kiện xác định của \(P\)là:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x^2+2x+1\ne0\\x^2-1\ne0\\x\ne0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne\pm1\\x\ne0\end{cases}}\)
\(P=\left(\frac{2+x}{x^2+2x+1}-\frac{x-2}{x^2-1}\right).\frac{1-x^2}{x}\)
\(=\left[\frac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)^2\left(x-1\right)}-\frac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)^2\left(x-1\right)}\right].\frac{1-x^2}{x}\)
\(=\frac{2x}{\left(x+1\right)^2\left(x-1\right)}.\frac{1-x^2}{x}=\frac{-2}{x+1}\)
Để \(P\)nguyên mà \(x\)nguyên suy ra \(x+1\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{-2,-1,1,2\right\}\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-3,-2,0,1\right\}\)
Đối chiếu điều kiện ta được \(x\in\left\{-3,-2\right\}\)thỏa mãn.

\(M=\frac{4x+8}{x^2-1}:\frac{x+2}{x+1}-\frac{x-2}{1-x}\) \(ĐKXĐ:x\ne\pm1\)
\(M=\frac{4\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}.\frac{x+1}{x+2}+\frac{x-2}{x-1}\)
\(M=\frac{4}{x-1}+\frac{x-2}{x-1}\)
\(M=\frac{4+x-2}{x-1}\)
\(M=\frac{x+2}{x-1}\)
vậy \(M=\frac{x+2}{x-1}\)

a) Điều kiện: \(x\ne0;x\ne1\)
b) \(A=\left(\frac{x}{x-1}-\frac{1}{x^2-x}\right):\frac{x^2+2x+1}{x}\)
\(A=\left(\frac{x}{x-1}-\frac{1}{x.\left(x-1\right)}\right):\frac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{x}\)
\(A=\left(\frac{x^2}{\left(x-1\right).x}-\frac{1}{x.\left(x-1\right)}\right):\frac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{x}\)
\(A=\frac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right).x}.\frac{x}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
\(A=\frac{x+1}{x}.\frac{x}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=\frac{1}{x+1}\)
c) Thay: \(x=2\)vào \(\frac{1}{x+1}\)ta có: \(A=\frac{1}{2+1}=\frac{1}{3}\)
a) ĐKXĐ : \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne1\end{cases}}\)
b)
\(A=\left(\frac{x}{x-1}-\frac{1}{x^2-x}\right):\frac{x^2+2x+1}{x}\)
\(A=\left(\frac{x}{x-1}-\frac{1}{x\left(x-1\right)}\right)\cdot\frac{x}{x^2+2x+1}\)
\(A=\left(\frac{x\cdot x}{x\left(x-1\right)}-\frac{1}{x\left(x-1\right)}\right)\cdot\frac{x}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
\(A=\frac{x^2-1}{x\left(x-1\right)}\cdot\frac{x}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=\frac{\left(x^2-1\right)\cdot x}{x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)^2}=\frac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\cdot x}{x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)^2}=\frac{1}{x+1}\)
c) \(A=\frac{1}{x+1}=\frac{1}{2+1}=\frac{1}{3}\)
Vậy \(A=\frac{1}{3}\)
\(P=\left(\frac{2+x}{x^2+2x+1}-\frac{x-2}{x^2-1}\right).\frac{1-x^2}{x}\)
a) ĐKXĐ:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x^2+2x+1\ne0\\x^2-1\ne0\\x\ne0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}\left(x+1\right)^2\ne0\\\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\ne0\\x\ne0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x+1\ne0\\x\ne1;x\ne-1\\x\ne0\end{cases}}}\)
<=> x khác -1
x khác 1; x khác -1
x khác 0
<=> x khác -1;1;0
Vậy ĐKXĐ là x khác -1;1;0
b) \(P=\left(\frac{2+x}{x^2+2x+1}-\frac{x-2}{x^2-1}\right).\frac{1-x^2}{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow P=\left(\frac{2+x}{\left(x+1\right)^2_{x-1}}-\frac{x-2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)_{x+1}}\right).\frac{1-x}{x}\)
MTC: (x+1)^2(x-1)
\(\Rightarrow P=\left(\frac{\left(2+x\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)^2\left(x-1\right)}-\frac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)^2\left(x-1\right)}\right).\frac{1-x}{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow P=\left(\frac{2x-2+x^2-x}{\left(x+1\right)^2\left(x-1\right)}-\frac{x^2+x-2x-2}{\left(x+1\right)^2\left(x-1\right)}\right)\frac{1-x}{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow P=\left(\frac{x-2+x^2-x^2+x+2}{\left(x+1\right)^2\left(x-1\right)}\right).\frac{1-x}{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow P=\frac{2x}{\left(x+1\right)^2\left(x-1\right)}.\frac{1-x}{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow P=\frac{2x}{-\left(1-x\right)\left(x+1\right)^2}.\frac{1-x}{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow P=-\frac{x}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\) (tmđkxđ)
c)
\(P=-\frac{x}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=-\frac{x+1-1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=-\frac{x+1}{x+1}-\frac{1}{x+1}=-1-\frac{1}{x+1}\) ( ĐKXĐ là x khác -1;1;0) \(\left(P\in Z\right)\)
\(P\in Z\Leftrightarrow\frac{-1}{x+1}\)
Nên x+1 thuộc Ư(-1)={1;-1)
x+1=1=>x=1-1=0 ( o t/m đk)
x+1=-1=>x=-1-1=-2( (t/m đk)
<=> x thuộc -2 thì gt của BT P là số nguyên