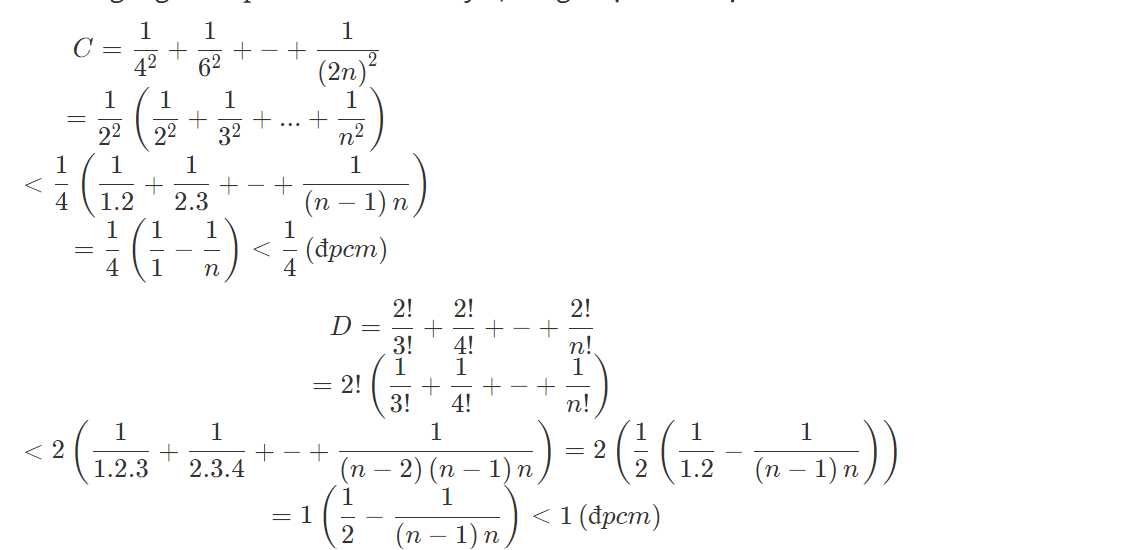bài 1:tìm min A=\(\dfrac{5x^2-12x+8}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
bài 2: chứng minh với mọi n\(\in\)N* và n\(\ge\)3:
\(\dfrac{1}{9}+\dfrac{1}{25}+...+\dfrac{1}{\left(2n+1\right)^2}< \dfrac{1}{4}\)
bài 3: tìm min, max của A=2x+3y biết \(2x^2+3y^2\le5\)
bài 4: tìm min của B=\(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{5-x}\)
và A=\(\sqrt{x^2+x+1}+\sqrt{x^2-x+1}\)
ai giải được là thiên tài!