Cho dãy số nguyên dương A=(a1,…,an) với 3<n<_100 viết đoạn chương trình in ra tổng số lẻ trong dãy số vừa nhập
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


uses crt;
var a:array[1..100]of integer;
i,n,dem,dem1,dem2,t:integer;
s:real;
begin
clrscr;
write('Nhap n='); readln(n);
for i:=1 to n do
begin
repeat
write('A[',i,']='); readln(a[i]);
until a[i]>0;
end;
for i:=1 to n do
write(a[i]:4);
writeln;
dem:=0;
for i:=1 to n do
if a[i]>10 then inc(dem);
writeln('So phan tu lon hon 10 la: ',dem);
dem1:=0;
dem2:=0;
for i:=1 to n do
begin
if a[i] mod 2=0 then inc(dem1)
else inc(dem2);
end;
writeln('So luong so chan la: ',dem1);
writeln('So luong so le la: ',dem2);
t:=0;
s:=1;
for i:=1 to n do
begin
if (i mod 2=0) and (a[i] mod 2<>1) then t:=t+a[i];
if (i mod 2=1) and (a[i] mod 2=0) then s:=s*a[i];
end;
writeln('Tong cac so o vi tri chan co gia tri le la: ',t);
writeln('Tich cac so o vi tri le co gia tri chan la: ',s:4:2);
writeln('Cac so le la: ');
for i:=1 to n do
if a[i] mod 2<>0 then write(a[i]:4);
writeln;
writeln('Cac so chan va lon hon 10 la: ');
for i:=1 to n do
if (a[i] mod 2=0) and (a[i]>10) then write(a[i]:4);
readln;
end.

#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long a[1000],n,i;
int main()
{
freopen("dayd.inp","r",stdin);
freopen("dayd.out","w",stdout);
cin>>n;
for (i=1; i<=n; i++) cin>>a[i];
for (i=1; i<=n; i++)
if (a[i]>0) cout<<a[i]<<" ";
return 0;
}

a: #incldue <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long i,n,x,t;
int main()
{
cin>>n;
t=0;
for (i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
cin>>x;
if (x>0) t=t+x;
}
cout<<t;
return 0;
}

Bài 1:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long a[100],n,i,j,tam;
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for (i=1; i<=n; i++)
cin>>a[i];
for (i=1; i<=n-1; i++)
for (j=i+1; j<=n; j++)
if (a[i]<a[j]) swap(a[i],a[j]);
for (i=1; i<=n;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
return 0;
}

#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long i,n,x,k;
int main()
{
cin>>n>>k;
for (i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
cin>>x;
if (x==k) cout<<i<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
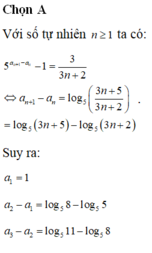

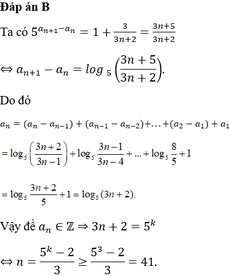
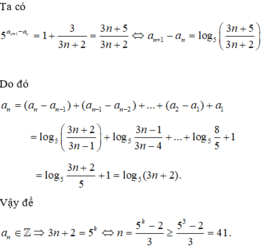


uses crt;
var a:array[1..100]of integer;
i,n,t:integer;
begin
clrscr;
readln(n);
t:=0;
for i:=1 to n do
begin
readln(a[i]);
if a[i] mod 2<>0 then t:=t+a[i];
end;
writeln(t);
readln;
end.