Giúp mình bài này với ạ , mình cảm ơn nhiều 
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



c)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u_1+u_3=3\\u_1^2+u_3^2=5\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u_1+u_3=3\\\left(u_1+u_3\right)^2-2u_1u_3=5\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u_1+u_3=3\\u_1u_3=2\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u_1=2\\u_3=1\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u_1=1\\u_3=2\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
Làm nốt (sử dụng công thức: \(u_n=u_1+\left(n-1\right)d\) để tìm được công sai
\(S_n=nu_1+\dfrac{n\left(n-1\right)}{2}d\) để tính tổng 15 số hạng đầu)
d)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u_1+u_2+u_3=14\\u_1u_2u_3=64\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u_2-d+u_2+u_2+d=14\\\left(u_2-d\right)u_2\left(u_2+d\right)=64\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u_2=\dfrac{14}{3}\\\left(u_2^2-d^2\right)u_2=64\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{14}{3}=u_2=u_1+d\\d=\dfrac{2\sqrt{889}}{21}\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{14}{3}=u_1+d\\d=\dfrac{-2\sqrt{889}}{21}\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
(Làm nốt,số xấu quá)
e)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u_1+u_2+u_3=7\\u_1^2+u_2^2+u_3^2=21\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u_1+u_2+u_3=7\\u_1u_2u_3=\dfrac{21-\left(u_1+u_2+u_3\right)^2}{2}=-14\end{matrix}\right.\)
Làm như ý d)

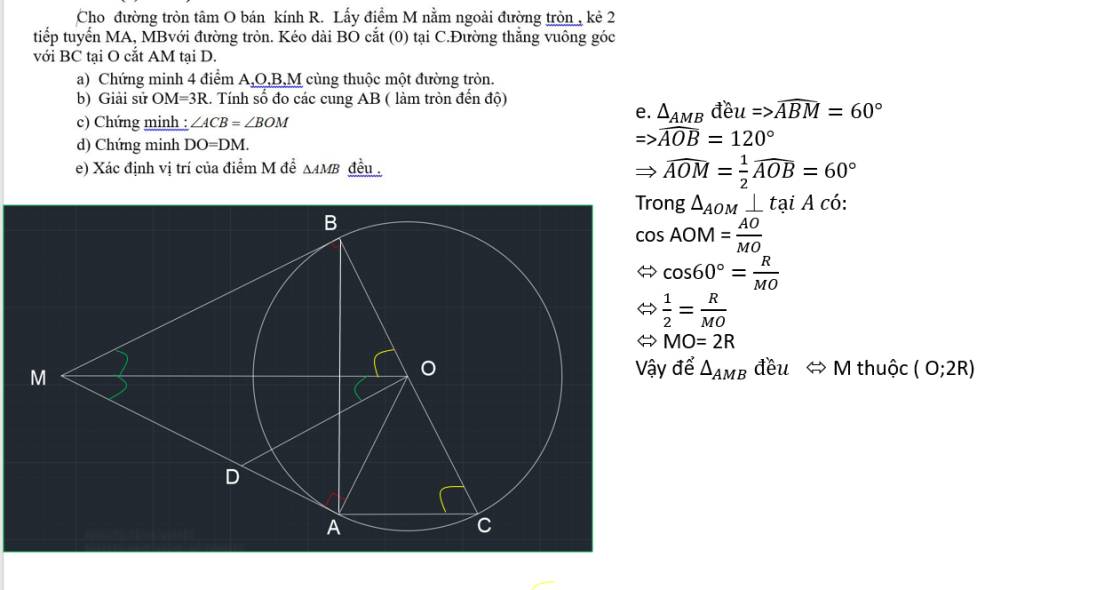
a: Xét tứ giác AOBM có
góc OAM+góc OBM=180 độ
=>AOBM nội tiếp
b: \(cosAOM=\dfrac{OA}{OM}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
nên \(\widehat{AOM}\simeq71^0\)
=>\(\widehat{AOB}\simeq142^0\)
=>sđ cung nhỏ AB là 142 độ; sđ cung lơn AB=360-142=218 độ
c:
Xét (O) có
ΔBAC nội tiếp
BC là đường kính
=>ΔBAC vuông tại A
=>BA vuông góc AC
Xét(O) có
MA,MB là tiêp tuyến
nên MA=MB
mà OA=OB
nên OM là trung trực của AB
=>OM//AC
góc ACB=góc OAC
góc OAC=góc AOM
=>góc ACB=góc AOM=góc BOM
d: góc DOM+góc BOM=90 độ
góc DMO+góc AOM=90 độ
mà góc BOM=góc AOM
nên góc DOM=góc DMO
=>DO=DM

Kẻ đường cao AH
Áp dụng PTG: \(BC=\sqrt{AB^2+AC^2}=10\left(cm\right)\)
Áp dụng HTL: \(BH=\dfrac{AB^2}{BC}=\dfrac{18}{5}\left(cm\right);AH=\dfrac{AB\cdot AC}{BC}=\dfrac{24}{5}\left(cm\right)\)
Vì AD là p/g nên \(\dfrac{BD}{DC}=\dfrac{AB}{AC}=\dfrac{3}{4}\Rightarrow BD=\dfrac{3}{4}DC\)
Mà \(BD+DC=BC=10\Rightarrow\dfrac{7}{4}DC=10\Rightarrow DC=\dfrac{40}{7}\left(cm\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow BD=\dfrac{30}{7}\left(cm\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow HD=BD-BH=\dfrac{30}{7}-\dfrac{18}{5}=\dfrac{24}{35}\)
Áp dụng PTG: \(AD=\sqrt{AH^2+HD^2}=\sqrt{\left(\dfrac{24}{35}\right)^2+\left(\dfrac{24}{5}\right)^2}=\dfrac{24\sqrt{2}}{7}\approx4,85\left(cm\right)\)

`sin3x sinx+sin(x-π/3) cos (x-π/6)=0`
`<=> 1/2 (cos2x - cos4x) + 1/2(-sin π/6 + sin (2x-π/2)=0`
`<=> cos2x-cos4x-1/2+ sin(2x-π/2)=0`
`<=>cos2x-cos4x-1/2+ sin2x .cos π/2 - cos2x. sinπ/2=0`
`<=> cos2x - cos4x - cos2x = 1/2`
`<=> cos4x = cos(2π)/3`
`<=>` \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x=\dfrac{2\text{π}}{3}+k2\text{π}\\4x=\dfrac{-2\text{π}}{3}+k2\text{π}\end{matrix}\right.\)
`<=>` \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\text{π}}{6}+k\dfrac{\text{π}}{2}\\x=-\dfrac{\text{π}}{6}+k\dfrac{\text{π}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Nửa chu vi hình chữ nhật:14 cm
Gọi chiều dài hình chữ nhật là x (cm) với \(7< x< 14\)
Chiều rộng hình chữ nhật là: \(14-x\) (cm)
Diện tích ban đầu của hình chữ nhật: \(x\left(14-x\right)\)
Chiều dài hình chữ nhật sau khi tăng 1cm: \(x+1\)
Chiều rộng sau khi tăng 2cm: \(14-x+2=16-x\)
Diện tích lúc sau: \(\left(x+1\right)\left(16-x\right)\)
Do diện tích tăng lên 25 \(cm^2\) nên ta có pt:
\(\left(x+1\right)\left(16-x\right)-x\left(14-x\right)=25\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+16=25\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=9\left(cm\right)\)
Vậy hình chữ nhật ban đầu dài 9cm và rộng 5cm








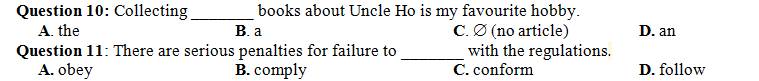 Mọi người giúp mình bài này với, mình cảm ơn nhiều ạ.
Mọi người giúp mình bài này với, mình cảm ơn nhiều ạ.